
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100663659
Author: ULABY
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.4, Problem 5E
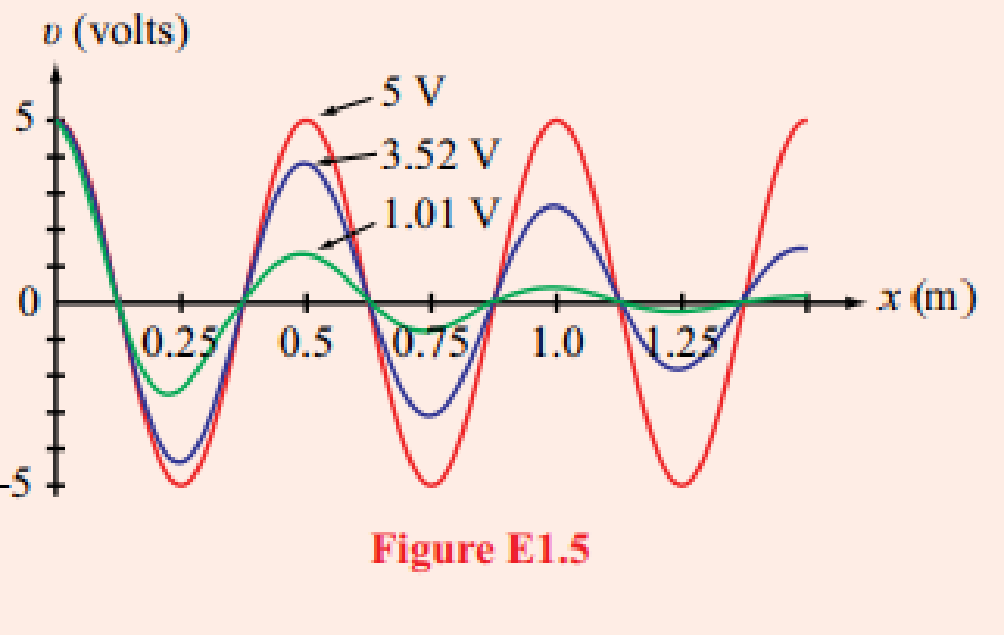
The red wave shown in Fig. E1.5 is given by
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
"For the network in the figure, determine RE and RB if A₁
Zb = BRE."
=
-10 and re
=
3.8. Assume that
2.a. Simplify and determine Zk+ for:
2.x. 60 [Hz]
⚫ 2.y. 180 [Hz]
a.x.
60[Hz]
a.y. 180 [Hz]
Joo
(127
2[H]
w
240
[√]
P3. Given the following network, determine:
⚫ 3.a. Equivalent Y
⚫ 3.b. Equivalent A
2
R[2]
10
8
b
20
30
5
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 1CQCh. 1.3 - What is Coulombs law? State its properties.Ch. 1.3 - What are the two important properties of electric...Ch. 1.3 - What do the electrical permittivity and magnetic...Ch. 1.3 - What are the three branches and associated...Ch. 1.4 - How can you tell if a wave is traveling in the...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 7CQCh. 1.4 - Why does a negative value of 0 signify a phase...Ch. 1.4 - Consider the red wave shown in Fig. E1.1. What is...Ch. 1.4 - The wave shown in red in Fig. E1.2 is given by...
Ch. 1.4 - The electric field of a traveling electromagnetic...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 4ECh. 1.4 - The red wave shown in Fig. E1.5 is given by...Ch. 1.4 - An electromagnetic wave is propagating in the z...Ch. 1.5 - What are the three fundamental properties of EM...Ch. 1.5 - What is the range of frequencies covered by the...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 11CQCh. 1.6 - Express the following complex functions in polar...Ch. 1.6 - Show that 2j=(1+j). (See EM.)Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 12CQCh. 1.7 - How is the phasor technique used when the forcing...Ch. 1.7 - A series RL circuit is connected to a voltage...Ch. 1.7 - A phasor voltage is given by V=j5V. Find (t).Ch. 1 - A 2 kHz sound wave traveling in the x direction in...Ch. 1 - For the pressure wave described in Example 1-1,...Ch. 1 - A harmonic wave traveling along a string is...Ch. 1 - A wave traveling along a string is given by...Ch. 1 - Two waves, y1(t) and y2(t), have identical...Ch. 1 - The height of an ocean wave is described by the...Ch. 1 - A wave traveling along a string in the +x...Ch. 1 - Two waves on a string are given by the following...Ch. 1 - Give expressions for y(x, t) for a sinusoidal wave...Ch. 1 - An oscillator that generates a sinusoidal wave on...Ch. 1 - Prob. 11PCh. 1 - Given two waves characterized by...Ch. 1 - The voltage of an electromagnetic wave traveling...Ch. 1 - A certain electromagnetic wave traveling in...Ch. 1 - Prob. 15PCh. 1 - Prob. 16PCh. 1 - Complex numbers z1 and z2 are given z1=3j2z2=4+j3...Ch. 1 - Complex numbers z1 and z2 are given by...Ch. 1 - If z=2+j4, determine the following quantities in...Ch. 1 - Find complex numbers t=z1+z2 and s=z1z2, both in...Ch. 1 - Complex numbers z1 and z2 are given by...Ch. 1 - If z=3j5, find the value of ln(z).Ch. 1 - If z = 3 j4. find the value of ez.Ch. 1 - Prob. 24PCh. 1 - A voltage source given by s(t)=25cos(2103t30)(V)...Ch. 1 - Find the phasors of the following time functions:...Ch. 1 - Find the instantaneous time sinusoidal functions...Ch. 1 - A series RLC circuit is connected to a generator...Ch. 1 - The voltage source of the circuit shown in Fig....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- [Electrical Circuits] P1. Using the mesh current method, calculate the magnitude and direction of: 1.a. I and I (mesh currents) 1.b. I10 (test current in R10 = 1082) 1.c. (Calculate the magnitude and signs of V10) 6[A] 12 [√] بي 10 38 20 4A] Iw -800arrow_forwardNeed handwritten solution do not use chatgptarrow_forward[07/01, 16:59] C P: Question: Calculate the following for 100Hz and 500Hz (express all answers in phasor form). Show all work. A) Xc and ZTB) VR1 and VC1 C) IT Handwritten Solution Pleasearrow_forward
- 1. Sketch the root loci of a system with the following characteristic equation: s²+2s+2+K(s+2)=0 2. Sketch the root loci for the following loop transfer function: KG(s)H(s)=- K(s+1) s(s+2)(s²+2s+4)arrow_forward3. For the unity feedback system with forward path transfer function, G(s), below: G(s)= K(s² +8) (s+4)(s+5) Sketch the root locus and show the breakaway/break-in point(s) and jo-axis crossing. Determine the angle of arrival and K value at the breakaway/break- in point(s). Give your comment the system is stable or unstable.arrow_forwardFind the step response of each of the transfer functions shown in Eqs. (4.62) through (4.64) and compare them. [Shown in the image]Book: Norman S. Nise - Control Systems Engineering, 6th EditionTopic: Chapter-4: Time Response, Example 4.8Solve the math with proper explanation. Please don't give AI response. Asking for a expert verified answer.arrow_forward
- 2. With respect to the circuit shown in Figure 2 below V2 -R1 R2 R4 w R3 R5 Figure 2: DC Circuit 2 a. Using Ohm's and Kirchhoff's laws calculate the current flowing through R3 and so determine wattage rating of R3. b. Verify your results with simulations. Note: you must use the values for the components in Table 2. Table 2 V2 (Volts) R1 (KQ) R2 (KQ) R3 (KQ) R4 (KQ) R5 (KQ) 9 3.3 5 10 6 1 3.3arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer i will report your answerarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- circuit value of i1 and i2arrow_forwardIn the circuit shown in the figure, the switch opens at time t = 0. For t≥ 0 use I(t) and V₁(t) or Find Vc(t) and lc(t). D to icht) w 43 ViLC+) + vc(+) 5. F + 1252 18 A 3) 2H2VLCH 8 V 4л warrow_forwardQ1/obtain the transfer function for the block diagram shown in the figure below: G4 Garrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
What Is a Plane Wave? — Lesson 2; Author: EMViso;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ES2WFevGM0g;License: Standard Youtube License