
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100663659
Author: ULABY
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.4, Problem 1E
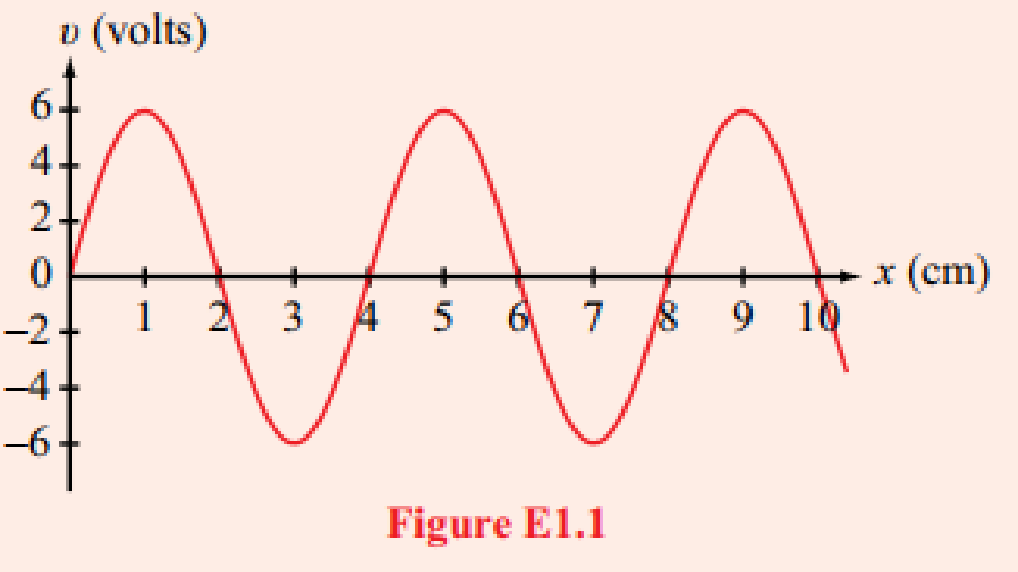
Consider the red wave shown in Fig. E1.1. What is die wave’s (a) amplitude, (b) wavelength, and (c) frequency, given that its phase velocity is 6 m/s?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 4
Consider the following system. In the figure, y(t) denotes the displacement of the mass and u(t)
denotes the force applied to the mass.
b1
u(t)
y(t)
+
b2
M
0000
0000
K1
K2
a) Find the differential equation model of the system.
b) Find the state-space model for the system. Write x, A, B, C and D clearly in your answer.
NO AI PLEASE
Not use ai please
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 1CQCh. 1.3 - What is Coulombs law? State its properties.Ch. 1.3 - What are the two important properties of electric...Ch. 1.3 - What do the electrical permittivity and magnetic...Ch. 1.3 - What are the three branches and associated...Ch. 1.4 - How can you tell if a wave is traveling in the...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 7CQCh. 1.4 - Why does a negative value of 0 signify a phase...Ch. 1.4 - Consider the red wave shown in Fig. E1.1. What is...Ch. 1.4 - The wave shown in red in Fig. E1.2 is given by...
Ch. 1.4 - The electric field of a traveling electromagnetic...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 4ECh. 1.4 - The red wave shown in Fig. E1.5 is given by...Ch. 1.4 - An electromagnetic wave is propagating in the z...Ch. 1.5 - What are the three fundamental properties of EM...Ch. 1.5 - What is the range of frequencies covered by the...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 11CQCh. 1.6 - Express the following complex functions in polar...Ch. 1.6 - Show that 2j=(1+j). (See EM.)Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 12CQCh. 1.7 - How is the phasor technique used when the forcing...Ch. 1.7 - A series RL circuit is connected to a voltage...Ch. 1.7 - A phasor voltage is given by V=j5V. Find (t).Ch. 1 - A 2 kHz sound wave traveling in the x direction in...Ch. 1 - For the pressure wave described in Example 1-1,...Ch. 1 - A harmonic wave traveling along a string is...Ch. 1 - A wave traveling along a string is given by...Ch. 1 - Two waves, y1(t) and y2(t), have identical...Ch. 1 - The height of an ocean wave is described by the...Ch. 1 - A wave traveling along a string in the +x...Ch. 1 - Two waves on a string are given by the following...Ch. 1 - Give expressions for y(x, t) for a sinusoidal wave...Ch. 1 - An oscillator that generates a sinusoidal wave on...Ch. 1 - Prob. 11PCh. 1 - Given two waves characterized by...Ch. 1 - The voltage of an electromagnetic wave traveling...Ch. 1 - A certain electromagnetic wave traveling in...Ch. 1 - Prob. 15PCh. 1 - Prob. 16PCh. 1 - Complex numbers z1 and z2 are given z1=3j2z2=4+j3...Ch. 1 - Complex numbers z1 and z2 are given by...Ch. 1 - If z=2+j4, determine the following quantities in...Ch. 1 - Find complex numbers t=z1+z2 and s=z1z2, both in...Ch. 1 - Complex numbers z1 and z2 are given by...Ch. 1 - If z=3j5, find the value of ln(z).Ch. 1 - If z = 3 j4. find the value of ez.Ch. 1 - Prob. 24PCh. 1 - A voltage source given by s(t)=25cos(2103t30)(V)...Ch. 1 - Find the phasors of the following time functions:...Ch. 1 - Find the instantaneous time sinusoidal functions...Ch. 1 - A series RLC circuit is connected to a generator...Ch. 1 - The voltage source of the circuit shown in Fig....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Show workarrow_forwardProblem 1 (a) Suppose the Laplace transform of a causal signal x₁ (t) is given by S X₁(s) = 52 +2 Using the Laplace transform properties, find the Laplace transform of the following signal x2(t). x2(t) = e2t+1 x₁(t − 1) - tx₁(2t - 1) (b) Suppose an LTI system T whose impulse response is given by h(t) e 2t 1(t) t 1(t) +28(t) What is the transfer function of the system? (c) If the input x2 (t) is applied to the system T, what will be the output Y₂(s)? Note, you just need to provide Laplace transform of the output y₂(t). Simplification is not needed in any part of this question.arrow_forwardShow workarrow_forward
- B) A 60-Hz generator is supply ing 60% of P max to an infinite bus through a reactive network. A fault occurs which increases the reactance of the network between the generator internal voltage and the infinite bus by 400%. When the fault is cleared, the maximum power that can be delivered is 80% of the original maximum value. Determine the critical clearing angle for the condition described.arrow_forwardQ3) A: A generator operating at 50 Hz delivers 1 pu power to an infinite bus through a transmission circuit in which resistance is ignored. A fault takes place reducing the maximum powe transferable to 0.5 pu whereas before the fault, this power was 2.0 pu and after the clearance of the fault, it is 1.5 pu. By the use of equal area criterion, determine the critical clearing angle.arrow_forward4. For the periodic signal shown in Fig. 4; a) Find the exponential Fourier Series for y(t). b) Use Parseval's Theorem to compute the total power contained in the 4th harmonic and all higher harmonics. 2+ y(t) + -2л -л 0 2л Зл 4л Fig. 4arrow_forward
- 2. a) Find the Fourier transform of the signal shown in Fig. 2 and express it in its most compact form; b) Find the value of the energy spectral density at f=1/4. 0 -2 -1 -3. Fig. 1 g(t) 3 1 2 t- Fig 2arrow_forward5. Consider a filter whose transfer function is: H(f) = -12xfß (a + jπ f ) ² (a) show that the filter is non-causal for α = 3, p= -1; (b) choose alternate values of α, ẞ that result in a causal filter, and demonstrate that your choice valid.arrow_forward1. Referring to the signals shown in Fig. 1: a) Find the signal energy of x(t). 6 b) Find the signal energy of y(t) . c) Find the signal energy of x(t)+y(t) . d) Are x(t) and y(t) orthogonal? Explain how you can tell. x(t) 0 2 4 y(1) 2 0 2 4 -6 Fig. 1 1-arrow_forward
- Please can you solve this question correctly in a step by step form to help understanding, please make it clear.arrow_forwardPlease can you solve this question in a step by step form correctly, please look at the refernces provided on the data path control lines, the GPLB functions, the processor instruction setarrow_forwardPlease can you solve this question in a step by step form correctly, please look at the refernces provided on the data path control lines, the GPLB functions, the processor instruction setarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
What Is a Plane Wave? — Lesson 2; Author: EMViso;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ES2WFevGM0g;License: Standard Youtube License