
Concept explainers
Ozark Industries manufactures and sells three products, which are manufactured in a factory with four departments. Both labor and machine time are applied to the products as they pass through each department. The machines and labor skills required in each department are so specialized that neither machines nor labor can be switched from one department to another.
Ozark Industries’ management is planning its production schedule for the next few months. The planning is complicated, because there are labor shortages in the community and some machines will be down several months for repairs.
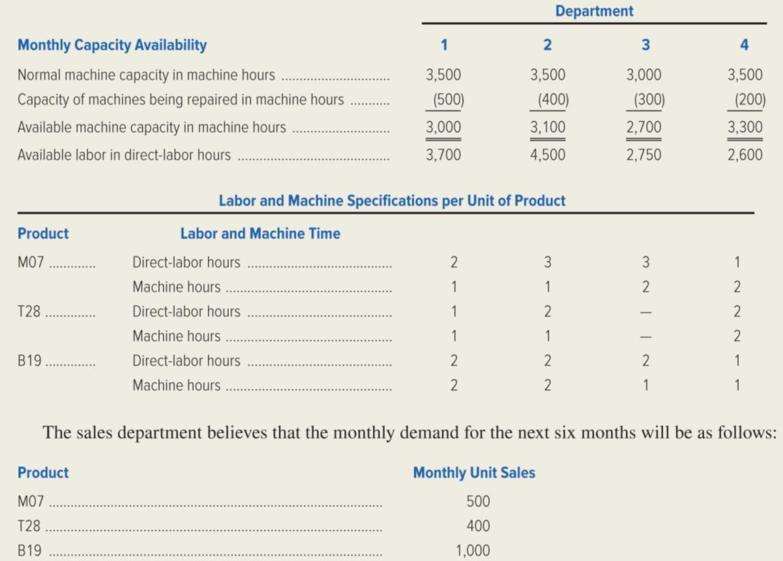
Management has assembled the following information regarding available machine and labor time by department and the machine hours and direct-labor hours required per unit of product. These data should be valid for the next six months.
Inventory levels are satisfactory and need not be increased or decreased during the next six months. Unit price and cost data that will be valid for the next six months are as follows:

Required:
- 1. Calculate the monthly requirement for machine hours and direct-labor hours for the production of products M07, T28, and B19 to determine whether the monthly sales demand for the three products can be met by the factory.
- 2. What monthly production schedule should Ozark Industries select in order to maximize its dollar profits? Explain how you selected this production schedule, and present a schedule of the contribution to profit that would be generated by your production schedule.
- 3. Identify the alternatives Ozark Industries might consider so it can supply its customers with all the product they demand.
1.
Calculate the monthly requirement for machine hours and direct labor hours for the production of products M07 and B19 to ascertain whether the monthly sales demand for the three products are met by the factory.
Explanation of Solution
Manufacturing overheads: Manufacturing overheads refers to the indirect factory- related cost that has occurred while manufacturing a product. Some of the examples of manufacturing overheads are indirect labor, indirect materials, factory building and indirect factory supplies.
The monthly requirement for machine hours is calculated as follows:
| Department | ||||
| Product | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| M07 |
500 |
500 |
1,000 |
1,000 |
| T28 |
400 |
400 | 0 |
800 |
| B19 |
2,000 |
2,000 |
1,000 |
1,000 |
| Total required | 2,900 | 2,900 | 2,000 | 2,800 |
| Total available | 3,000 | 3,100 | 2,700 | 3,300 |
| Excess (deficiency) | 100 | 200 | 700 | 500 |
Table (1)
Note: Monthly requirement for “machine hours” is computed by multiplying the monthly unit sale of each product with the “machine time” required for each department.
The monthly requirement for direct-labor requirements is calculated as follows:
| Department | ||||
| Product | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| M07 |
1,000 |
1,500 |
1,500 |
500 |
| T28 |
400 |
800 | 0 |
800 |
| B19 |
2,000 |
2,000 |
2,000 |
1,000 |
| Total required | 3,400 | 4,300 | 3,500 | 2,300 |
| Total available | 3,700 | 4,500 | 2,750 | 2,600 |
| Excess (deficiency) | 300 | 200 | (750) | 300 |
Table (2)
Due to the labor shortage in Department 3, the monthly sales demand cannot be met for all three products
Note: Monthly requirement for direct labor is computed by multiplying the monthly unit sale of each product with the direct labor required for each department.
2.
Identify the monthly production schedule that Industry O must select in order to maximize its dollar profits, explain the manner in which the production schedule is selected, and present a schedule of the contribution to profit that is generated by the production schedule.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution Margin: The process or theory which is used to judge the benefit given by each unit of the goods produced is called as contribution margin.
“The aim is to increase contribution margin. Fixed costs are irrelevant. Direct-labor hours (DLH) are the scarce resource in Department 3. Industry must initially produce the product that maximizes contribution margin per unit of the scarce resource (DLH). In this situation, two products, M07 and B19, need direct-labor hours in Department 3”.
Calculate the contribution margin:
| M07 | T28 | B19 | |
| Sales price (a) | $196 | $123 | $167 |
| Variable costs | |||
| Direct material | $7 | $13 | $17 |
| Direct labor | $66 | $38 | $51 |
| Variable overhead | $27 | $20 | $25 |
| Variable selling | $3 | $2 | $4 |
| Total variable costs (b) | $103 | $ 73 | $ 97 |
| Contribution margin | $ 93 | $ 50 | $ 70 |
Note: Direct labor is computed by adding the direct labor of Department 1, Department 2, Department 3, and Department 4.
Table (3)
| Product |
Contribution Margin (a) |
Department 3 DLH (b) |
Contribution Margin per DLH |
| M07 | $93 | $3 | $31 |
| B19 | $70 | $2 | $35 |
Table (4)
Prepare the resulting production schedule:
| Product | Units | Resulting production schedule Comments |
| M07 | 250 | Produce as much as the constraint permits |
| T28 | 400 | Produce up to monthly sales demand; unaffected by Department 3. |
| B19 | 1,000 | Produce as much as possible to increase contribution margin per DHL. |
Table (5)
Prepare the schedule of contribution margin by product:
| Schedule of contribution margin by product | |||
| Product |
Contribution Margin per Unit (a) |
Units Produced (b) |
Contribution to Profit |
| M07 | $93 | 250 | $23,250 |
| T28 | $50 | 400 | $20,000 |
| B19 | $70 | 1,000 | $70,000 |
| Total contribution margin | $113,250 | ||
Table (6)
3.
Identify the alternatives considered by Industry O for supplying all the products demanded by the customers.
Explanation of Solution
Industry O must consider the following aspects for supplying the additional quantities of MO7.
- Functioning on an overtime basis”.
- “Subcontracting the additional units”.
- “Obtaining labor from outside the community”.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: Creating Value in a Dynamic Business Environment
- correct answer best answer general accountingarrow_forwardWhat was the standard rate for mayarrow_forwardBurner, Incorporated has sales of 1,250,000, costs of 620,000, depreciation expenses of 85,000, and interest expenses of 34,000, with a tax rate of 30 percent. a. Calculate the net income for the firm. b. If the company paid out $90,000 in cash dividends, calculate the increase to retained earnings.arrow_forward
- If sales are $420,000, variable costs are 72% of sales, and operating income is $40,000, what is the operating leverage?arrow_forwardSteelMax produces metal containers that require 2.5 meters of material at $1.20 per meter and 0.3 direct labor hours at $18.00 per hour. Overhead is assigned at the rate of $12 per direct labor hour. What is the total standard cost for one unit of product that would appear on a standard cost card?arrow_forwardNeed help this question solutionarrow_forward
- The standard materials cost of TimberCraft's product is $60 per unit, based on 15 pounds of raw materials at a standard cost of $4 per pound. During March 20X9, 2,000 units of product were produced, using 30,800 pounds of raw material at a cost of $4.50 per pound. a) The standard cost for materials for March is __. b) The total materials variance for the month is __. c) The materials quantity variance is __. d) The materials price variance is __.arrow_forwardHow much lower would net income be if it used variable costing?arrow_forwardcan you please solve thisarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





