
Concept explainers
The following balance sheets and income statement were taken from the records of Rosie-Lee Company:
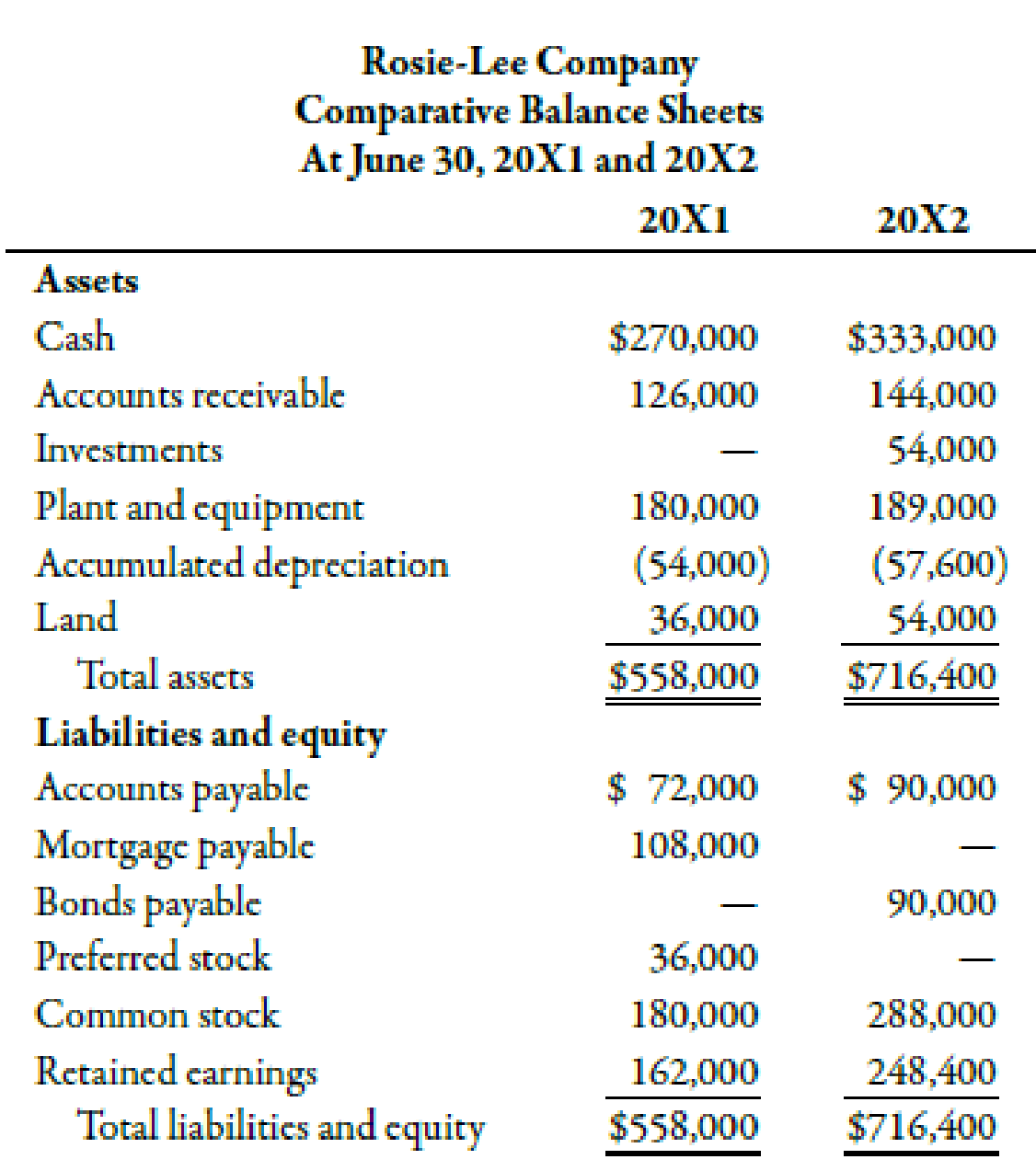

Additional transactions were as follows:
- a. Sold equipment costing $21,600, with
accumulated depreciation of $16,200, for $3,600. - b. Issued bonds for $90,000 on December 31.
- c. Paid cash dividends of $36,000.
- d. Retired mortgage of $108,000 on December 31.
Required:
- 1. Prepare a schedule of operating
cash flows using (a) the indirect method and (b) the direct method. - 2. Prepare a statement of cash flows using the indirect method.
1.
(a).
Construct a schedule showing the operating cash flows with the use of indirect method.
Explanation of Solution
Cash Flows from Operating Activities:
This category of a cash flow statement shows the operational and profit generating activities in a firm. The operating cash flows increase or decrease the current assets and current liabilities of a firm.
The schedule showing operating cash flows using indirect method is in the table below:
| R-L Company | |
| Schedule for Cash Flow from Operating Activities | |
| For the year ended June 30, 20X2 | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | |
| Net income | 122,400 |
| Add/ Less: | |
| Increase in accounts receivable1 | (18,000) |
| Increase in accounts payable2 | 18,000 |
| Depreciation expense3 | 19,800 |
| Loss on sale of equipment | 1,800 |
| Net cash from operating activities | 144,000 |
Table (1)
Therefore, net cash flow from operating activities is $144,000.
Working Note:
1.
Calculation of difference in accounts receivable:
2.
Calculation of difference in accounts payable:
3.
The total depreciation expense is $19,800
1.
(b).
Construct a schedule showing the operating cash flows with the use of direct method.
Explanation of Solution
The schedule showing operating cash flows using direct method is in the table below:
| Schedule for Operating Cash Flows | |||
| R-L Company | |||
| For the year ended June 30, 20X2 | |||
| Direct Method | |||
| Particulars | Income statement ($) | Adjustments ($) | Cash flows ($) |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | |||
| Revenues | 920,000 | (18,000)1 | 902,000 |
| Cost of goods sold | (620,000) | 18,0002 | (602,000) |
| Operating expenses | (177,600) | 19,8003 | |
| 1,800 | (156,000) | ||
| Net cash from operating activities | 144,000 | ||
Table (2)
Therefore, net cash flow from operating activities is $144,000.
Working Note:
1.
Calculation of difference in accounts receivable:
2.
Calculation of difference in accounts payable:
3.
The total depreciation expense is $19,800
2.
Construct the statement of cash flows with the use of indirect method.
Explanation of Solution
Cash Flow Statement:
Cash flow statement is a financial statement prepared to provide information about the sources and uses of cash in a firm. In this statement, the activities increasing cash are referred as cash inflows and the activities that decrease cash are referred as cash outflows.
The statement of cash flows for R-L Company for 20X2 using indirect method is shown below:
| R-L Company | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| For the year ended June 30, 20X2 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||
| Net income | 122,400 | |
| Add/ Less: | ||
| Increase in accounts receivable1 | (18,000) | |
| Increase in accounts payable2 | 18,000 | |
| Depreciation expense3 | 19,800 | |
| Loss on sale of equipment | 1,800 | |
| Net cash from operating activities | 144,000 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | ||
| Sale of equipment | 3,600 | |
| Purchase of investments | (54,000) | |
| Purchase of equipment4 | (30,600) | |
| Purchase of land5 | (18,000) | |
| Net cash from investing activities | (99,000) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||
| Retirement of mortgage | (108,000) | |
| Issuance of bonds | 90,000 | |
| Retirement of preferred stock | (36,000) | |
| Payment of dividends | (36,000) | |
| Issuance of common stock6 | 108,000 | |
| Net cash from financing activities | 18,000 | |
| Net increase in cash | 63,000 | |
Table (3)
Therefore, there is a net increase in cash of $63,000.
Working Note:
1.
Calculation of difference in accounts receivable:
2.
Calculation of difference in accounts payable:
3.
The total depreciation expense is $19,800
4.
Calculation of purchase value of equipment:
5.
Calculation of purchase value of land:
6.
Calculation of issuance value of common stock:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
- help this answer accountingarrow_forwardLMT Corporation manufactures and sells a product called Product ZX. Each unit of Product ZX requires 2.5 hours of direct labor at the rate of $20.00 per direct labor hour. The company plans to sell 38,000 units of Product ZX in July. The finished goods inventories on July 1 and July 31 are budgeted to be 720 and 220 units, respectively. Budgeted direct labor costs for July would be __.arrow_forwardDuring 2018, Dalton Enterprises earned revenues of $95,000, had expenses of $72,000, purchased assets costing $10,500, and paid dividends of $7,200. What was Dalton Enterprises' net income for the year?arrow_forward
- Davidson Corporation owns a non-depreciable capital asset held for investment. The asset was purchased for $300,000 ten years earlier and is now subject to a $50,000 liability. During the current year, Davidson transfers the asset to Martin in exchange for $80,000 cash and a new boat with a $40,000 FMV to be used by Davidson for personal use. Martin assumes the $50,000 liability. Determine the amount of Davidson's LTCG or LTCL.arrow_forwardCalculate predetermined overhead ratearrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
