
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The number of carbon atoms with
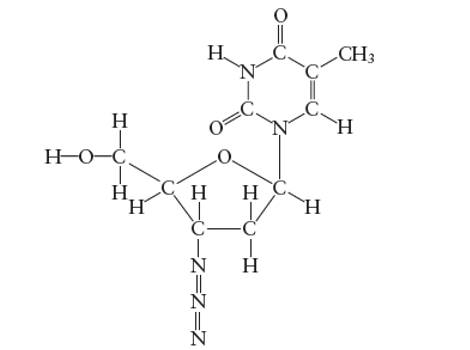
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(a)
Answer to Problem 29E
There are 6 carbon atoms in
Explanation of Solution
A
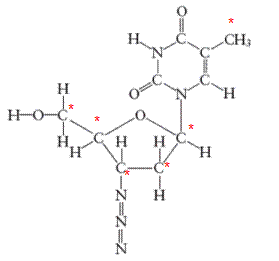
All the asterisk C atoms are
(b)
Interpretation: The number of carbon atoms with
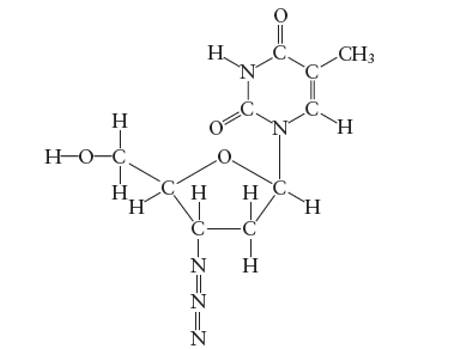
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(b)
Answer to Problem 29E
There are 4 carbon atoms in
Explanation of Solution
A
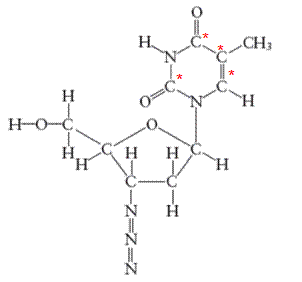
All the asterisk C atoms are
(c)
Interpretation: The number of carbon atoms with
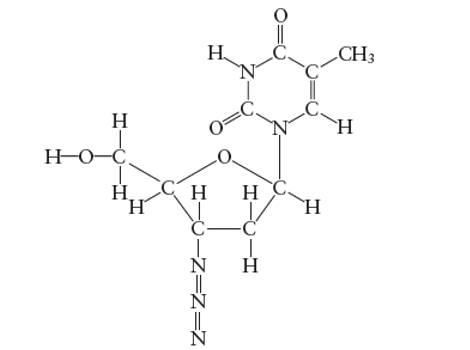
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(c)
Answer to Problem 29E
The N atoms which forms two double covalent bond is sp-hybridized only.
Explanation of Solution
A
There is no
(d)
Interpretation: The number of σ-bonds in AZT molecule needs to be determined.
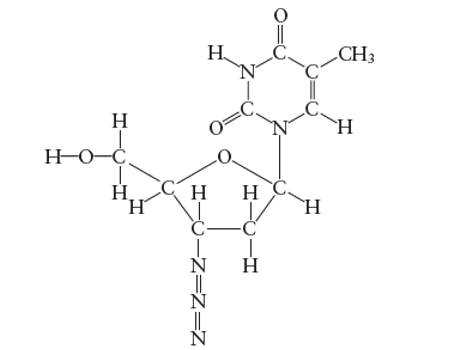
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(d)
Answer to Problem 29E
The total number of σ bonds are 33 in AZT molecule
Explanation of Solution
There are two types of covalent bonds; σ bond and π-bonds. A σ-bond is formed by head-to head overlapping of hybridized orbitals. It is a strong bond and can exist between two bonded atoms. On the contrary, a π-bond is a weak covalent bond as it forms by side-way-overlapping of un-hybridized orbitals.
Since it is a weak bond therefore it is always exist with σ-bond in a double and triple covalent bond. A double covalent bond is formed by 1σ and 1 π bond whereas a triple covalent bond is formed by 1σ and two π bonds. In the given molecule, all single bonds are σ-bonds and all double bonds have 1 σ bonds. Therefore total number of σ bonds are 33 in AZT molecule.
(e)
Interpretation: The number of π-bonds in AZT molecule needs to be determined.
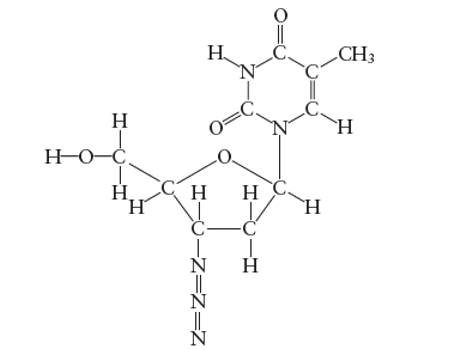
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(e)
Answer to Problem 29E
The total number of π bonds are 5 in AZT molecule
Explanation of Solution
There are two types of covalent bonds; σ bond and π-bonds. A σ-bond is formed by head-to head overlapping of hybridized orbitals. It is a strong bond and can exist between two bonded atoms. On the contrary, a π-bond is a weak covalent bond as it forms by side-way-overlapping of un-hybridized orbitals.
Since it is a weak bond therefore it is always exist with σ-bond in a double and triple covalent bond. A double covalent bond is formed by 1σ and 1 π bond whereas a triple covalent bond is formed by 1σ and two π bonds. In the given molecule, total number of π bonds are 5 in AZT molecule.
(f)
Interpretation: The bond angle in the N-N-N (azide group) of AZT molecule needs to be determined.
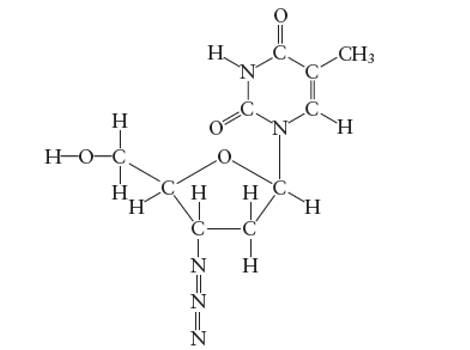
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(f)
Answer to Problem 29E
With sp-hybridization, the bond angle must be 180°.
Explanation of Solution
Hybridization of central N atom in azide group is:
With sp-hybridization, the bond angle must be 180°.
(g)
Interpretation: The bond angle in the H-O-C in the side group attached to the five membered ring of AZT molecule needs to be determined.
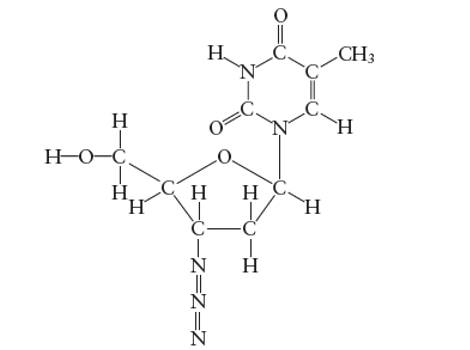
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(g)
Answer to Problem 29E
With
Explanation of Solution
Hybridization of central C atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring:
With
(h)
Interpretation: The hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring of AZT molecule needs to be determined.
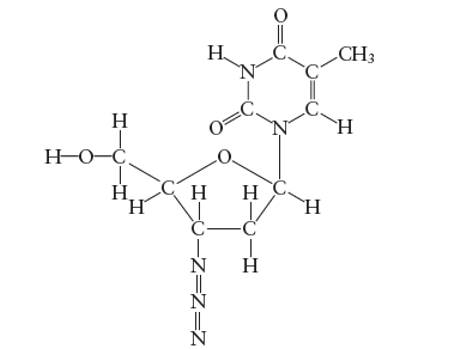
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(h)
Answer to Problem 29E
The hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring is
Explanation of Solution
Hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring:
The hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardDraw the mechanism (including all curved arrows for electron movement) showing how the maleicanhydride is attacked by the anthracene and formation of the final Diels Alder product.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardI have a bottle of butanal that has been improperly used by lab workers. They allowed a traceamount NaOH (aq) to contaminate the bottle. What is now in my bottle of “butanal? What is the molecular name and functional group name? Draw the structure.arrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardFirst image: Why can't the molecule C be formed in those conditions Second image: Synthesis for lactone C its not an examarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion Second image: I have to show the mecanism of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primaryarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





