
Concept explainers
15-7 Answer true or false.
- The cis and trans stereoisomers of 2-butene are achiral.
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement- The cis and trans stereoisomers of 2-butene are achiral, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry.
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 1P
The cis and trans stereoisomers of 2-butene are achiral. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
A stereocenter is defined as an atom having groups of suitable nature so that interchange of any two groups will give a stereoisomer. However all stereocenters are not tetrahedral. The unsaturaled carbon atoms of cis-trans But-2-ene are examples of the trigonal planar stereocenter. Since an interchange of groups at these stereocenters gives a strereoisomer.
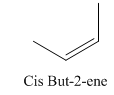 or
or 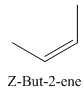
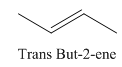 or
or 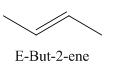
Both cis-and trans but-2-ene have non-superimposable mirror images but posses an alternating axis of symmetry, therefore cis-and trans But-2-ene are achiral.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement- The carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, or ester cannot be a stereocenter, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
The carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, or ester cannot be a stereocenter. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
A stereocenter is defined as an atom having groups of suitable nature so that interchange of any two groups will give a stereoisomer. However all stereocenters are not tetrahedral. But in case of aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acids and ester, the carbonyl carbon is sp2 hybridized due to which it forms a planar structure. Planar structures a have plane of symmetry due to which they do not possess a stereocenter. Also in carbonyl group, carbonyl carbon is linked with oxygen by two bonds that is double bond. Therefore, all the four groups are not different.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement- Stereoisomers have the same connectivity of their atoms, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
Stereoisomers have the same connectivity of their atoms. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Stereoisomerism deals with the study of the spatial arrangements of the atoms in space. It does not mean to alter the connectivity of the atoms by mean of forming or breaking the bonds.
Since no bond breaking and forming takes place, thus the stereoisomers have the same connectivity of their atoms.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement- Constitutional isomers have the same connectivity of their atoms, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
Constitutional isomers do not have the same connectivity of their atoms. Thus, statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Constitutional isomers are those isomers which have the different connectivity with atoms but have same molecular formula.
Example-
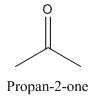 and
and 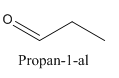
Both have same molecular formula, but they both differ in connectivity of atoms.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement-An unmarked cube is achiral, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
An unmarked cube is achiral. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Achiral are those compounds, that have elements of symmetry or a molecule is superimposable on its mirror image.
An unmarked cube is an achiral because it can be superimposable on its mirror image.
(f)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement-A human foot is chiral, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
A human foot is chiral. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
If an object can be cut exactly into two equal halves so that half of its become mirror image of other half, it has plane of symmetry.
A human foot has a non-superimposable mirror image, thus human foot is chiral.
(g)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement-Every object in nature has a mirror image, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
Every object in nature has a mirror image. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
If an object is superimposable on its mirror image, it cannot rotate plane polarized light and hence optically inactive.
If an object can be cut exactly into two equal halves so that half of its become mirror image of other half, it has plane of symmetry.
Every object in nature has a mirror image. It may or may not superimpose, and therefore the object may or may not be chiral.
(h)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement-The most common cause of chirality in organic molecules is the presence of a tetrahedral carbon atom with four different groups bonded to it, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
The most common cause of chirality in organic molecules is the presence of a tetrahedral carbon atom with four different groups bonded to it. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
A carbon atom bonded in tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule is termed as chiral centre. It is not necessary all the time that the chiral centre is tetrahedral in shape; trigonal centres are also present in case of alkenes or unsaturated compounds.
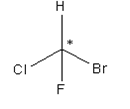
Asterisk represents the chiral centre, due to which the molecule becomes chiral.
(i)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement-If a molecule is not superposable on its mirror image, the molecule is chiral, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
If a molecule is not superposable on its mirror image, the molecule is chiral. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
A carbon atom bonded in tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule is termed as chiral centre. It is not necessary all the time that the chiral centre is tetrahedral in shape; trigonal centres are also present in case of alkenes or unsaturated compounds.
If an object is superimposable on its mirror image, it cannot rotate plane polarized light and hence optically inactive.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
- In an electrolytic cell, indicate the formula that relates E0 to the temperature T.arrow_forward-- 14:33 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 11. Compound A can transform into compound B through an organic reaction. From the structures below, mark the correct one: HO A تھے۔ די HO B ○ A) Compounds A and B are isomers. B) Both have the same number of chiral carbons. C) Compound A underwent an addition reaction of Cl2 and H2O to form compound B. D) Compound A underwent a substitution reaction forming the intermediate chlorohydrin to obtain compound B. E) Compound A underwent an addition reaction of Cl2 forming the chloronium ion and then added methanol to obtain compound B. 60arrow_forward-- 14:40 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 13. The compound 1-bromo-hex-2-ene reacts with methanol to form two products. About this reaction, mark the correct statement: OCH3 CH3OH Br OCH3 + + HBr A B A) The two products formed will have the same percentage of formation. B) Product B will be formed by SN1 substitution reaction with the formation of an allylic carbocation. C) Product A will be formed by SN1 substitution reaction with the formation of a more stable carbocation than product B. D) Product A will be formed by an SN2 substitution reaction occurring in two stages, the first with slow kinetics and the second with fast kinetics. E) The two compounds were obtained by addition reaction, with compound B having the highest percentage of formation. 57arrow_forward
- -- ☑ 14:30 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 10. Amoxicillin (figure X) is one of the most widely used antibiotics in the penicillin family. The discovery and synthesis of these antibiotics in the 20th century made the treatment of infections that were previously fatal routine. About amoxicillin, mark the correct one: HO NH2 H S -N. HO Figura X. Amoxicilina A) It has the organic functions amide, ester, phenol and amine. B) It has four chiral carbons and 8 stereoisomers. C) The substitution of the aromatic ring is of the ortho-meta type. D) If amoxicillin reacts with an alcohol it can form an ester. E) The structure has two tertiary amides. 62arrow_forwardThe environmental police of a Brazilian state received a report of contamination of a river by inorganic arsenic, due to the excessive use of pesticides on a plantation on the riverbanks. Arsenic (As) is extremely toxic in its many forms and oxidation states. In nature, especially in groundwater, it is found in the form of arsenate (AsO ₄ ³ ⁻ ), which can be electrochemically reduced to As ⁰ and collected at the cathode of a coulometric cell. In this case, Potentiostatic Coulometry (at 25°C) was performed in an alkaline medium (pH = 7.5 throughout the analysis) to quantify the species. What potential (E) should have been selected/applied to perform the analysis, considering that this is an exhaustive electrolysis technique (until 99.99% of all AsO ₄ ³ ⁻ has been reduced to As ⁰ at the electrode, or n( final) = 0.01% n( initial )) and that the concentration of AsO ₄ ³ ⁻ found in the initial sample was 0.15 mmol/L ? Data: AsO ₄ 3 ⁻ (aq) + 2 H ₂ O ( l ) + 2 e ⁻ → A s O ₂ ⁻ ( a…arrow_forward-- 14:17 15. Water-soluble proteins are denatured when there is a change in the pH of the environment in which they are found. This occurs due to the protonation and deprotonation of functional groups present in their structure. Choose the option that indicates the chemical bonds modified by pH in the protein represented in the following figure. E CH2 C-OH CH2 H₂C H₁C CH CH3 CH3 CH CH₂-S-S-CH₂- 910 H B -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH₂-NH3* −0—C—CH₂- ○ A) A, C e D. • В) Вес ○ C) DeE ○ D) B, De E ○ E) A, B e C 68arrow_forward
- Suppose sodium sulfate has been gradually added to 100 mL of a solution containing calcium ions and strontium ions, both at 0.15 mol/L. Indicate the alternative that presents the percentage of strontium ions that will have precipitated when the calcium sulfate begins to precipitate. Data: Kps of calcium sulfate: 2.4x10 ⁻ ⁵; Kps of strontium sulfate: 3.2x10 ⁻ ⁷ A) 20,2 % B) 36,6 % C) 62,9 % D) 87,5 % E) 98.7%arrow_forward14:43 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 14. The following diagrams represent hypothetical membrane structures with their components numbered from 1 to 6. Based on the figures and your knowledge of biological membranes, select the correct alternative. | 3 5 || 人 2 500000 6 A) Structures 1, 3, 5, 2 and 4 are present in a constantly fluid arrangement that allows the selectivity of the movement ○ of molecules. Structure 4, present integrally or peripherally, is responsible for this selection, while the quantity of 6 regulates the fluidity. B) The membranes isolate the cell from the environment, but allow the passage of water-soluble molecules thanks to the presence of 2 and 3. The membrane in scheme is more fluid than that in 55arrow_forward12. Mark the correct statement about reactions a and b : a. Br + -OH Br b. + Br H₂O + Br -OH + H₂O A) The reactions are elimination reactions, with reaction "a" being of type E2 and reaction "b" being of type E1. B) Reaction "a" is an E2 type elimination occurring in one step and reaction "b" is an SN1 type substitution. C) Both reactions can result in the formation of carbocation, but in reaction "b" the most stable carbocation will be formed. D) Both reactions occur at the same rate ○ and have the same number of reaction steps. E) Reaction "b" is an E2 type elimination occurring in two steps and reaction "a" is an SN2 type substitution.arrow_forward
- Chloroform, long used as an anesthetic and now considered carcinogenic, has a heat of vaporization of 31.4 kJ/mol. During vaporization, its entropy increases by 94.2 J/mol.K. Therefore, select the alternative that indicates the temperature, in degrees Celsius, at which chloroform begins to boil under a pressure of 1 atm. A) 28 B) 40 C) 52 D) 60 E) 72arrow_forwardIf we assume a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of n as a function of current density: 1. at low fields is linear 2. at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law Obtain the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value when calculated for 1 and 2 cases (maximum relative difference of 5% compared to the behavior for higher fields). To which overpotential range does this correspond? Data: i = 1.5 mA cm², T = 300°C, B = 0.64, R = 8.314 J K1 mol-1 and F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forwardAnswer by equation pleasearrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co



