
Concept explainers
15-7 Answer true or false.
- The cis and trans stereoisomers of 2-butene are achiral.
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement- The cis and trans stereoisomers of 2-butene are achiral, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry.
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 1P
The cis and trans stereoisomers of 2-butene are achiral. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
A stereocenter is defined as an atom having groups of suitable nature so that interchange of any two groups will give a stereoisomer. However all stereocenters are not tetrahedral. The unsaturaled carbon atoms of cis-trans But-2-ene are examples of the trigonal planar stereocenter. Since an interchange of groups at these stereocenters gives a strereoisomer.
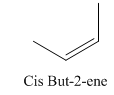 or
or 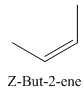
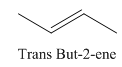 or
or 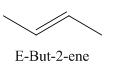
Both cis-and trans but-2-ene have non-superimposable mirror images but posses an alternating axis of symmetry, therefore cis-and trans But-2-ene are achiral.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement- The carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, or ester cannot be a stereocenter, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
The carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, or ester cannot be a stereocenter. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
A stereocenter is defined as an atom having groups of suitable nature so that interchange of any two groups will give a stereoisomer. However all stereocenters are not tetrahedral. But in case of aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acids and ester, the carbonyl carbon is sp2 hybridized due to which it forms a planar structure. Planar structures a have plane of symmetry due to which they do not possess a stereocenter. Also in carbonyl group, carbonyl carbon is linked with oxygen by two bonds that is double bond. Therefore, all the four groups are not different.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement- Stereoisomers have the same connectivity of their atoms, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
Stereoisomers have the same connectivity of their atoms. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Stereoisomerism deals with the study of the spatial arrangements of the atoms in space. It does not mean to alter the connectivity of the atoms by mean of forming or breaking the bonds.
Since no bond breaking and forming takes place, thus the stereoisomers have the same connectivity of their atoms.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement- Constitutional isomers have the same connectivity of their atoms, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
Constitutional isomers do not have the same connectivity of their atoms. Thus, statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Constitutional isomers are those isomers which have the different connectivity with atoms but have same molecular formula.
Example-
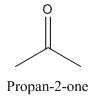 and
and 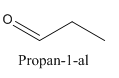
Both have same molecular formula, but they both differ in connectivity of atoms.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement-An unmarked cube is achiral, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
An unmarked cube is achiral. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Achiral are those compounds, that have elements of symmetry or a molecule is superimposable on its mirror image.
An unmarked cube is an achiral because it can be superimposable on its mirror image.
(f)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement-A human foot is chiral, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
A human foot is chiral. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
If an object can be cut exactly into two equal halves so that half of its become mirror image of other half, it has plane of symmetry.
A human foot has a non-superimposable mirror image, thus human foot is chiral.
(g)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement-Every object in nature has a mirror image, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
Every object in nature has a mirror image. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
If an object is superimposable on its mirror image, it cannot rotate plane polarized light and hence optically inactive.
If an object can be cut exactly into two equal halves so that half of its become mirror image of other half, it has plane of symmetry.
Every object in nature has a mirror image. It may or may not superimpose, and therefore the object may or may not be chiral.
(h)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement-The most common cause of chirality in organic molecules is the presence of a tetrahedral carbon atom with four different groups bonded to it, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
The most common cause of chirality in organic molecules is the presence of a tetrahedral carbon atom with four different groups bonded to it. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
A carbon atom bonded in tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule is termed as chiral centre. It is not necessary all the time that the chiral centre is tetrahedral in shape; trigonal centres are also present in case of alkenes or unsaturated compounds.
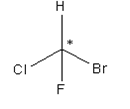
Asterisk represents the chiral centre, due to which the molecule becomes chiral.
(i)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement-If a molecule is not superposable on its mirror image, the molecule is chiral, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
Answer to Problem 1P
If a molecule is not superposable on its mirror image, the molecule is chiral. Thus, statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
A carbon atom bonded in tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule is termed as chiral centre. It is not necessary all the time that the chiral centre is tetrahedral in shape; trigonal centres are also present in case of alkenes or unsaturated compounds.
If an object is superimposable on its mirror image, it cannot rotate plane polarized light and hence optically inactive.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
- Part I. a) Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl - 1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward3. The explosive decomposition of 2 mole of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) is shown below: Assume the C(s) is soot-basically atomic carbon (although it isn't actually atomic carbon in real life). 2 CH3 H NO2 NO2 3N2 (g)+7CO (g) + 5H₂O (g) + 7C (s) H a. Use bond dissociation energies to calculate how much AU is for this reaction in kJ/mol.arrow_forwardPart I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone and (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward
- Show the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardDraw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forward
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardPart I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forward
- what are the Iupac names for each structurearrow_forwardWhat are the IUPAC Names of all the compounds in the picture?arrow_forward1) a) Give the dominant Intermolecular Force (IMF) in a sample of each of the following compounds. Please show your work. (8) SF2, CH,OH, C₂H₂ b) Based on your answers given above, list the compounds in order of their Boiling Point from low to high. (8)arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co



