
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Preparation of 2-bromo-2-methyl from 2-methylpropane has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Radical or free radical: The unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
Bromination:
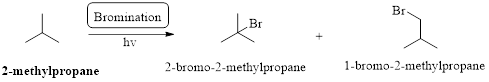
(b)
Interpretation:
Preparation of 2-methyl-1- propene from 2-methylpropane has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
Bromination:
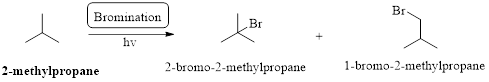
(c)
Interpretation:
Preparation of 2-Iodo-2-methylpropane form 2-methylpropane has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
Bromination:
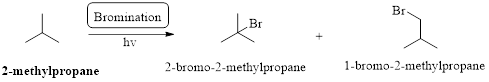
Markovnikov’s rule:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Pearson eText for Essential Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- How would you prepare each of the following compounds using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or a alonic ester synthesis? Show all intermediate structures and all reagents.[Three only] A. B. COOH OH C. D. 0 H2C CHCH2CH2CCH3arrow_forwardFats and greases have mostly aliphatic regions which are hydrophobic. Provide a schematic of howsoaps/detergents remove fats and grease from the soiled material. * see imagearrow_forwardWhat chemical has the common name "lye"? Pick one of the 3 esters and show the hydrolysis mechanism to make a carboxylic acid. The organic “R” should be used to limit the redrawing time of the entire molecule. * see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the products for each reaction. There are two and they are not related. *see imagearrow_forwardd. a phenylal Give the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all levant stereochemistry. [three only] 0 A. B. CH3 Bra CH3COOH OH 1. Br₂, PBrz 2 H₂O 12arrow_forward2arrow_forward
- Show how the following conversions might be accomplished. Show all reagents and all intermediate ructures. More than one step may be required [2 ONLY]: A. B. ° C. OH 0 OH 0arrow_forwardA 20.3 mL sample of 0.263 M triethylamine, (C2H5)3N, is titrated with 0.252 M hydrochloric acid. (1) At the titration midpoint, the pH is . (2) At the equivalence point, the pH is .arrow_forwardd. 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl chloride . What is the order of decreasing reactivity towards nucleophilic acyl substitution for the arboxylic acid derivatives? (most reactive first) A. B. 0 0 O 0 0 H3C-C-O-C-CH3 H3C-C-N(CH3)2 H3C-C-OCH 3 (CH3)2CH-C-OCH3 I || ။ IV a. I, II, III, IV b. I, III, IV, II C. II, IV, III, I d. II, I, III, IV 0 0 0 0 0 R-C-O C-R R-C-NH2 R-C OR R-C-CI a. I, III, II, IV | 11 III IV b. II, III, I, IV c. III, II, I, IV d. IV, I, III, IIarrow_forward
- B. d. a hydrate 4. Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry [4 ONLY]. A. CH₂OH PCC CH2Cl2 0 H KCN HCN 2arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis of the anti-inflammatory drug Ibuprofen from benzene. Show all reagents and all intermediate structures. Assume that ortho and para isomers can be separated. (CH3)2CHCH2 CH3 CHCOOH 1buprofen be requiredarrow_forwardAssuming that no equilibria other than dissolution are involved, calculate the molar solubility of each of the following from its solubility product: (a) KHC4H4O6arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



