
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781305577213
Author: Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 14.7QAP
A 3.03-g petroleum specimen was decomposed by wet ashing and subsequently diluted to 500 mL in a volumetric flask. Cobalt was determined by treating 25.00-mL aliquots of this diluted solution as follows:
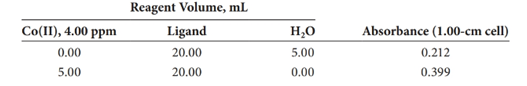
Assume that the Co(II)-ligand chelate obeys Beer’s law, and calculate the percentage of cobalt in the original sample.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Illustrate reaction mechanisms of
alkenes with water in the presence of
H2SO4, detailing each step of the
process. Please show steps of
processing. Please do both, I will
thumb up for sure
#1
#3
Draw the following molecule: (Z)-1-chloro-1-butene
Identify the molecule as having a(n) E, Z, cis, or trans configuration.
CH3
H₁₂C
○ E
○ z
○ cis
trans
Chapter 14 Solutions
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.1QAPCh. 14 - A 0.4740-g pesticide sample was decomposed by wet...Ch. 14 - Sketch a photometric titration curve for the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.4QAPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.5QAPCh. 14 - The accompanying data (1.00-cm cells) were...Ch. 14 - A 3.03-g petroleum specimen was decomposed by wet...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.8QAPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.9QAPCh. 14 - The acid-base indicator HIn undergoes the...
Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.11QAPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.12QAPCh. 14 - Copper(II) forms a 1:1 complex with the organic...Ch. 14 - Aluminum forms a 1:1 complex with...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.15QAPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.16QAPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.17QAPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.18QAPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.19QAPCh. 14 - Given the Information that...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.21QAPCh. 14 - Mixing the chelating reagent B with Ni(II) forms...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.23QAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Identify the molecule as having a(n) E, Z, cis, or trans configuration. H₂C- CH3 О Е ○ cis ○ transarrow_forwardThe decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide according to the equation: 50°C 2 N2O5(g) 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) follows first-order kinetics with a rate constant of 0.0065 s-1. If the initial concentration of N2O5 is 0.275 M, determine: the final concentration of N2O5 after 180 seconds. ...arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- CS2(g) →CS(g) + S(g) The rate law is Rate = k[CS2] where k = 1.6 × 10−6 s−¹. S What is the concentration of CS2 after 5 hours if the initial concentration is 0.25 M?arrow_forwardCS2(g) → CS(g) + S(g) The rate law is Rate = k [CS2] where k = 1.6 × 10-6 s−1. S Calculate the half-life.arrow_forwardThe following is a first order reaction where the rate constant, k, is 6.29 x 10-3 min-*** What is the half-life? C2H4 C2H2 + H2arrow_forward
- Control Chart Drawing Assignment The table below provides the number of alignment errors observed during the final inspection of a certain model of airplane. Calculate the central, upper, and lower control limits for the c-chart and draw the chart precisely on the graph sheet provided (based on 3-sigma limits). Your chart should include a line for each of the control limits (UCL, CL, and LCL) and the points for each observation. Number the x-axis 1 through 25 and evenly space the numbering for the y-axis. Connect the points by drawing a line as well. Label each line drawn. Airplane Number Number of alignment errors 201 7 202 6 203 6 204 7 205 4 206 7 207 8 208 12 209 9 210 9 211 8 212 5 213 5 214 9 215 8 216 15 217 6 218 4 219 13 220 7 221 8 222 15 223 6 224 6 225 10arrow_forwardCollagen is used to date artifacts. It has a rate constant = 1.20 x 10-4 /years. What is the half life of collagen?arrow_forwardיווי 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 [ppm] 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 6 [ppm] 1 1.5 -2.5 3.5arrow_forward
- 2H2S(g)+3O2(g)→2SO2(g)+2H2O(g) A 1.2mol sample of H2S(g) is combined with excess O2(g), and the reaction goes to completion. Question Which of the following predicts the theoretical yield of SO2(g) from the reaction? Responses 1.2 g Answer A: 1.2 grams A 41 g Answer B: 41 grams B 77 g Answer C: 77 grams C 154 g Answer D: 154 grams Darrow_forwardPart VII. Below are the 'HNMR, 13 C-NMR, COSY 2D- NMR, and HSQC 2D-NMR (similar with HETCOR but axes are reversed) spectra of an organic compound with molecular formula C6H1003 - Assign chemical shift values to the H and c atoms of the compound. Find the structure. Show complete solutions. Predicted 1H NMR Spectrum 4.7 4.6 4.5 4.4 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 3.1 3.0 2.9 2.8 2.7 2.6 2.5 2.4 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.0 1.9 1.8 1.7 1.6 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.1 f1 (ppm) Predicted 13C NMR Spectrum 100 f1 (ppm) 30 220 210 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 90 80 70 -26 60 50 40 46 30 20 115 10 1.0 0.9 0.8 0 -10arrow_forwardQ: Arrange BCC and Fec metals, in sequence from the Fable (Dr. R's slides) and Calculate Volume and Density. Aa BCC V 52 5 SFCCarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Bohr Model of the atom and Atomic Emission Spectra: Atomic Structure tutorial | Crash Chemistry; Author: Crash Chemistry Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=apuWi_Fbtys;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY