
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as
Concept introduction:
Heterocyclic compounds are defined as cyclic compounds which consist of at least one heteroatom, mostly nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen. Heterocyclic compounds can be aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. In some heterocyclic compounds, a noncarbon atom contributes to a p atomic orbital to the aromatic
Huckel’s
1) Aromatic if the number of electrons in that
Answer to Problem 14.20P
The given compound is antiaromatic.
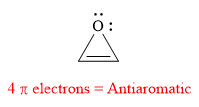
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
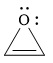
It is a heterocyclic compound with an oxygen atom. The hybridization of the oxygen atom must be

The total number of electrons in this
The given heterocyclic compound is antiaromatic if the total number of electrons in that
(b)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Heterocyclic compounds are defined as cyclic compounds which consists of at least one heteroatom mostly nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen. Heterocyclic compounds can be aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. In some heterocyclic compounds, a noncarbon atom contributes a p atomic orbital to the aromatic
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species possesses a pi system of molecular orbitals constructed from p-orbitals that are fully conjugated around a ring (
1) Aromatic if the number of electrons in that
Answer to Problem 14.20P
The given compound is aromatic.
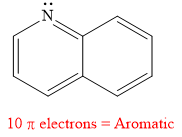
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
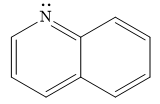
It is a heterocyclic compound with a nitrogen atom. The hybridization of the nitrogen atom must be

Thus, the total number of electrons in this
The given heterocyclic compound is aromatic if the number of electrons in that
(c)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Heterocyclic compounds are defined as cyclic compounds which consist of at least one heteroatom mostly nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen. Heterocyclic compounds can be aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. In some heterocyclic compounds, a noncarbon atom contributes a p atomic orbital to the aromatic
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species possesses a pi system of molecular orbitals constructed from p-orbitals that are fully conjugated around a ring (
1) Aromatic if the number of electrons in that
Answer to Problem 14.20P
The given compound is nonaromatic.
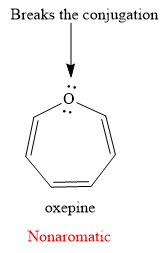
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
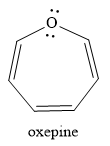
It is an oxygen containing a heterocycle consisting of a seven-membered ring with three double bonds. Due to geometrical constrains, the lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom are not in conjugation with the

If the molecule is assumed to be planar (flat), then too it would contain
The rule for aromaticity or antiaromaticity applies only if the system is planar, cyclic and has overlap of p-orbitals.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Heterocyclic compounds are defined as cyclic compounds which consists of at least one heteroatom mostly nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen. Heterocyclic compounds can be aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. In some heterocyclic compounds, a noncarbon atom contributes a p atomic orbital to the aromatic
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species possesses a pi system of molecular orbitals constructed from p-orbitals that are fully conjugated around a ring (
1) Aromatic if the number of electrons in that
Answer to Problem 14.20P
The given compound is nonaromatic.
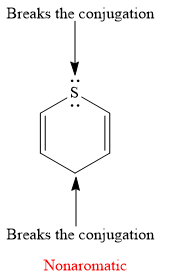
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
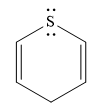
It is a sulfur containing a heterocycle consisting of a six-membered ring with two double bonds. There are two lone pair of electrons on the sulfur atom, but the sulfur atom is

As the
The rule for aromaticity or antiaromaticity applies only if the system is planar, cyclic and has overlap of p-orbitals.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Heterocyclic compounds are defined as cyclic compounds which consists of at least one heteroatom mostly nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen. Heterocyclic compounds can be aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. In some heterocyclic compounds, a noncarbon atom contributes a p atomic orbital to the aromatic
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species possesses a pi system of molecular orbitals constructed from p-orbitals that are fully conjugated around a ring (
1) Aromatic if the number of electrons in that
Answer to Problem 14.20P
The given compound is nonaromatic.
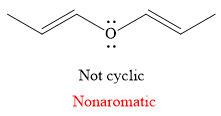
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
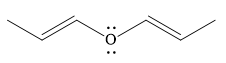
It is a straight chain compound with an oxygen atom and two double bonds. The above compound is not a cyclic compound. The rule for aromaticity or antiaromaticity applies only if the system is planar, cyclic and has overlap of p-orbitals. Thus, the

The rule for aromaticity or antiaromaticity applies only if the system is planar, cyclic and has overlap of p-orbitals.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Heterocyclic compounds are defined as cyclic compounds which consists of at least one heteroatom mostly nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen. Heterocyclic compounds can be aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. In some heterocyclic compounds, a noncarbon atom contributes a p atomic orbital to the aromatic
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species possesses a pi system of molecular orbitals constructed from p-orbitals that are fully conjugated around a ring (
1) Aromatic if the number of electrons in that
Answer to Problem 14.20P
The given compound is aromatic.
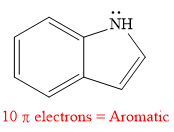
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
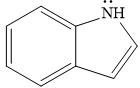
It is a heterocyclic compound with a nitrogen atom in which one six-membered and one five-membered rings are fused. The hybridization of the nitrogen atom is

Thus, the total number of electrons in this
The given heterocyclic compound is aromatic if the number of electrons in that
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
