
Concept explainers
The
two signals, one due to the
absorption. (b) Do the
(a)
Interpretation: The chemical shifts of the given absorptions are to be calculated.
Concept introduction: In NMR spectrum, peaks are known as resonances, lines or absorptions. On the horizontal axis, the position of absorption is generally referred to as chemical shift. The chemical shift of any absorption is calculated by the formula,
Answer to Problem 14.1P
The chemical shifts of the given absorptions are
Explanation of Solution
The observed chemical shift due to the
The observed chemical shift due to the
The operating frequency is
The conversion of
Therefore, the conversion of
Chemical shift
Chemical shift due to
The chemical shift of absorption is calculated by the formula,
Where,
Substitute the values of observed chemical shift and operating frequency in the above formula to calculate the chemical shift due to
Therefore, the chemical shift is
The conversion of
Therefore, the conversion of
Hence, the chemical shift is
Chemical shift due to
Substitute the values of observed chemical shift and operating frequency in the above formula to calculate the chemical shift due to
Therefore, the chemical shift is
The conversion of
Therefore, the conversion of
Hence, the chemical shift is
The chemical shifts of the given absorptions are
(b)
Interpretation: Whether the
Concept introduction: In NMR spectrum, peaks are known as resonances, lines or absorptions. On the horizontal axis, the position of absorption is generally referred to as chemical shift. The increasing order of chemical shift is plotted from right to left in NMR spectrum.
Answer to Problem 14.1P
The peak of
Explanation of Solution
The terms, upfield and downfield expresses the relative location of signals. The meaning of upfield is to the right and of downfield is to the left. The
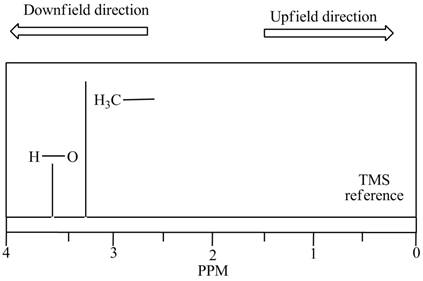
Figure 1
Hence, the peak of
The peak of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
HUMAN ANATOMY
Physical Science
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
- H H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forward
- choose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forward
- OH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardb. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forwardFor the reaction A (g) → 3 B (g), Kp = 0.379 at 298 K. What is the value of ∆G for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures of A and B are 5.70 atm and 0.250 atm?arrow_forward

 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning

