
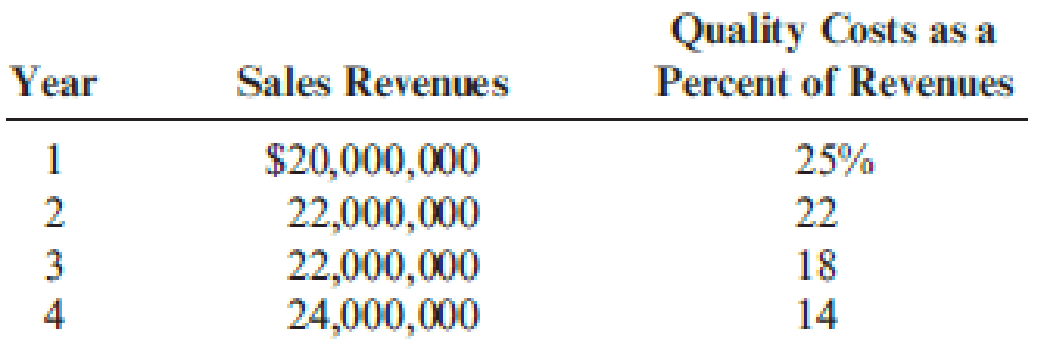
Gagnon Company reported the following sales and quality costs for the past four years. Assume that all quality costs are variable and that all changes in the quality cost ratios are due to a quality improvement program.
Required:
- 1. Compute the quality costs for all four years. By how much did net income increase from Year 1 to Year 2 because of quality improvements? From Year 2 to Year 3? From Year 3 to Year 4?
- 2. The management of Gagnon Company believes it is possible to reduce quality costs to 2.5 percent of sales. Assuming sales will continue at the Year 4 level, calculate the additional profit potential facing Gagnon. Is the expectation of improving quality and reducing costs to 2.5 percent of sales realistic? Explain.
- 3. Assume that Gagnon produces one type of product, which is sold on a bid basis. In Years 1 and 2, the average bid was $400. In Year 1, total variable costs were $250 per unit. In Year 3, competition forced the bid to drop to $380. Compute the total contribution margin in Year 3 assuming the same quality costs as in Year 1. Now, compute the total contribution margin in Year 3 using the actual quality costs for Year 3. What is the increase in profitability resulting from the quality improvements made from Year 1 to Year 3?
1.
Compute the quality costs for all four years and calculate the amount of increase in net income from year 1 to year 2, from year 2 to year 3, and from year 3 to year 4.
Explanation of Solution
Quality costs: Quality costs are costs that are incurred to avoid, identify and eliminate defects from products. Quality costs are classified into four components namely;
- “Prevention costs”.
- “Appraisal costs”.
- “Internal failure costs”.
- “External failure costs”.
Calculate the quality costs for all the four years:
| Year | Percent of revenues | × | Sales revenues | = | Quality costs |
| Year 1 | 25% | $20,000,000 | $5,000,000 | ||
| year 2 | 22% | $22,000,000 | $4,840,000 | ||
| Year 3 | 18% | $22,000,000 | $3,960,000 | ||
| Year 4 | 14% | $24,000,000 | $3,960,000 |
Table (1)
Calculate the increase in net income from year 1 to year 2:
Calculate the increase in net income from year 2 to year 3:
Calculate the increase in net income from year 3 to year 4:
2.
Calculate the additional profit potential facing Company G and state whether expecting improved quality and reduced costs to 2.5 percent of sales is realistic.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the profit potential:
Therefore, from the above calculation, it is ascertained that amount of profit potential is $2,760,000.
The 2.5 percent goal is the level identified by several quality experts that a company must strive to obtain. The experience of company G shows that it is an achievable goal
3.
Calculate the total contribution margin in year 3 assuming the same quality costs as in year 1 compute the total contribution margin in year 3 using the actual quality costs for year 3 and calculate the increase in profitability resulting from the quality improvements made from year 1 to year 3.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution Margin: The process or theory which is used to judge the benefit given by each unit of the goods produced is called as contribution margin.
Calculate the total contribution margin in year 3 assuming the same quality costs as in year 1 compute the total contribution margin in year 3 using the actual quality costs for year 3:
| Year 3-No change | Year 3-change | |
| Sales | $22,000,000 | $22,000,000 |
| Variable expenses | (1)$14,473,684 | (6)$11,764,210 |
| Contribution margin | $7,526,316 | $10,235,790 |
Table (2)
Calculate the increase in profitability:
Therefore, the amount of increase in profitability is $2,709,474.
Working notes:
(1)Calculate the variable expenses in year 3 assuming the same quality costs as in year 1:
(2)Calculate the quality cost per unit for year 1:
(3)Calculate the quality cost per unit for year 3:
(4)Calculate the decrease in per-unit variable quality cost:
(5)Calculate the decrease in per-unit total variable cost:
(6)Calculate the total variable cost for year 3:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK CORNERSTONES OF COST MANAGEMENT
- Marc and Mikkel are married and file a joint tax return. Marc and Mikkel earned salaries this year of $64,200 and $13,200, respectively. In addition to their salaries, they received interest of $354 from municipal bonds and $600 from corporate bonds. Marc contributed $2,600 to a traditional individual retirement account, and Marc paid alimony to a prior spouse in the amount of $1,600 (under a divorce decree effective June 1, 2017). Marc and Mikkel have a 10-year-old adopted son, Mason, who lived with them throughout the entire year. Thus, Marc and Mikkel are allowed to claim a $2,000 child tax credit for Mason. Marc and Mikkel paid $6,200 of expenditures that qualify as itemized deductions, and they had a total of $2,596 in federal income taxes withheld from their paychecks during the year.What is the total amount of Marc and Mikkel's deductions from AGI?arrow_forwardPlease give me true answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardCan you please give me correct solution this general accounting question?arrow_forward
- Michael McDowell Co. establishes a $108 million liability at the end of 2025 for the estimated site-cleanup costs at two of its manufacturing facilities. All related closing costs will be paid and deducted on the tax return in 2026. Also, at the end of 2025, the company has $54 million of temporary differences due to excess depreciation for tax purposes, $7.56 million of which will reverse in 2026. The enacted tax rate for all years is 20%, and the company pays taxes of $34.56 million on $172.80 million of taxable income in 2025. McDowell expects to have taxable income in 2026. Assuming that the only deferred tax account at the beginning of 2025 was a deferred tax liability of $5,400,000, draft the income tax expense portion of the income statement for 2025, beginning with the line "Income before income taxes." (Hint: You must first compute (1) the amount of temporary difference underlying the beginning $5,400,000 deferred tax liability, then (2) the amount of temporary differences…arrow_forwardHi experts please answer the financial accounting questionarrow_forwardNeed answer the financial accounting questionarrow_forward
- Harper, Incorporated, acquires 40 percent of the outstanding voting stock of Kinman Company on January 1, 2023, for $210,000 in cash. The book value of Kinman's net assets on that date was $400,000, although one of the company's buildings, with a $60,000 carrying amount, was actually worth $100,000. This building had a 10-year remaining life. Kinman owned a royalty agreement with a 20-year remaining life that was undervalued by $85,000. Kinman sold Inventory with an original cost of $60,000 to Harper during 2023 at a price of $90,000. Harper still held $15,000 (transfer price) of this amount in Inventory as of December 31, 2023. These goods are to be sold to outside parties during 2024. Kinman reported a $40,000 net loss and a $20,000 other comprehensive loss for 2023. The company still manages to declare and pay a $10,000 cash dividend during the year. During 2024, Kinman reported a $40,000 net income and declared and paid a cash dividend of $12,000. It made additional inventory sales…arrow_forwardCan you please answer this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardProvide correct answer this general accounting questionarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning



