
Concept explainers
Platinum nanoparticles of diameter ~2 nm are important catalysts in carbon monoxide oxidation to carbon dioxide. Platinum crystallizes in a face-centered cubic arrangement with an edge length of 3.924Å. (a) Estimate how many platinum atoms would fit into a 2.0-nm sphere; the volume of a sphere is (4/3). 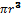
 Recall that 1Å= 1×10-10 m and 1nm = 1×10-9 m. (b) Estimate how many platinum atoms are on the surface of a 2.0-nm Pt sphere, using the surface area of a sphere (4
Recall that 1Å= 1×10-10 m and 1nm = 1×10-9 m. (b) Estimate how many platinum atoms are on the surface of a 2.0-nm Pt sphere, using the surface area of a sphere (4
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
CHEMISTRY THE CENTRAL SCIENCE >EBOOK<
- Nickel has a face-centered cubic structure and has a density of 8.90 g/cm3. Calculate its atomic radius?arrow_forwardThe ionic compound, CsI, forms a body centered cubic structure (see below) where the anions occupy the corners of the crystal (red) and the cations the body centered position (green). If the density of the compound is 4.51 g/cm^3 and the ionic radius of Cs + is 169 pm, what is the ionic radius of I − in pm? Key Concept: The atoms are touching the diagonal in the center of the cube. This makes it equal to the sum of 2 times the radius of each atom. Strategy: Determine the length of the diagonal,d, and recall that the length of the side, l, is given by l = d/3 0.5. This is a result of the use of the Pythagorean theorem relating the length of the side to d.With the length of the side you can determine the volume of the unit cell.From the number of atoms in the unit cell determine the mass of the unit cell.Use these to get the density.arrow_forward1) Palladium (electron configuration is [Kr]4d¹) crystallizes in a face-centered cubic unit cell. its density is 12.0 g/cm³. (NA = 6.02 x 10²³) (a) What is the total mass of palladium atoms contained within one unit cell? (b) Calculate the atomic radius (r) of Pd.arrow_forward
- Tantalum is a rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion-resistant. It has a density of 17.6 grams per cubic centimeter and a molecular weight of 185.23 g/mol. What is the atomic radius of Ta if it adopts the body centered cubic unit structure? Express answer in scientific notation (e.g. 3.47e-23).arrow_forwardCopper (Cu) has an fcc structure, where the mass of a Cu atom is 63 in atomic mass units.The density of Cu is 8.9×103 kgm−3.Tungsten (W) typically has a bcc structure, where the mass of a W atom is 184 in atomicmass units. The density of W is 19.3×103 kgm−3.(i) Use the above data to find the radius of a Cu atom, and of a W atom.(ii) Which atom has the larger radius, and why?You may use the fact that 1 atomic mass unit is equivalent to 1.66 × 10−27 kg.arrow_forwardQ619 Calculate the radius of a copper atom. Copper has a face centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure with a volume density of 8.95 x 106g m-3 and an atomic weight of 63.54 g mol-1 (Given the Avogadro’s, NA = 6.023 x 1023 atoms mol-1arrow_forward
- 2) Sodium is a bright and white, soft, wax-like element dissolved in seawater, crystallized in rock salt. Sodium is common in nature and crystallizes with a body-centered cubic unit cell and its density is 0.971 g/cm³. (Na: 23 g/mol) (a) What is the volume of the unit cell, in cm³? (b) What is the edge length of the unit cell, in pm? (c) What is the radius of a sodium atom, in pm?arrow_forwardThe ionic compound, CsCl, forms a body centered cubic structure (see below) where the anions occupy the corners of the crystal (red) and the cations the body centered position (green). If the density of the compound is 3.99 g/cm3 and the ionic radius of Cs+ is 169 pm, what is the ionic radius of Cl− in pm?arrow_forwardA hypothetical element, Ny, forms a face-centered cubic lattice with an atomic radius of 165 pm. Calculate the density of the element in g/cm3. Atomic Mass: Ny: 112.024 g/mol Round to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
- Decide what kind of crystalline solid each element or compound in the table forms, and what kind of force holds the solid together. Then, rank the solids in order of decreasing melting point. That is, select "1" next to the solid with the highest melting point, "2" next to the solid with the next highest melting point, and so on. (You may need to use the scrollbar to see all the choices.) element or compound ΝΗ, ZnI₂ Ne type of solid force holding the solid formed together ? ? ? ? ? ? X melting point of solid ? ? ? Garrow_forwardif you can. If there is not enough information to decide, choose can't decide in the element 1 2 3 description Element 1 is a hard dark-red solid. A 10. g cube of it is set on a hot plate. After 10 minutes, the temperature of the top of the cube has risen by less than 1 °C. Element 2 is a moderately soft silvery-gray solid. A 5 cm x 5 cm square of it, only 1 mm thick, is flexed slightly by hand. The sheet snaps in half. Element 3 is a moderately soft silvery-gray solid. A small cube of it is put into a ceramic crucible and heated strongly. It melts about not far above room temperature. metal or nonmetal? O metal O nonmetal O (can't decide) O metalk O nonmetal O (can't decide) O metal O nonmetal O (can't decide)arrow_forward8. Clausthalite is a mineral composed of lead(II) selenide. The mineral adopts a NaCl octahedral-type structure. If the density of PbSe is 8.27 g/cm³, calculate the radius of the lead(II) ion. (The radius of selenide ion is given below.)arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

