
EBK PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 8220103026918
Author: Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.6, Problem 6EYU
Rank the four pendulum systems in Figure 13-25 in order of increasing period. Indicate ties where appropriate.
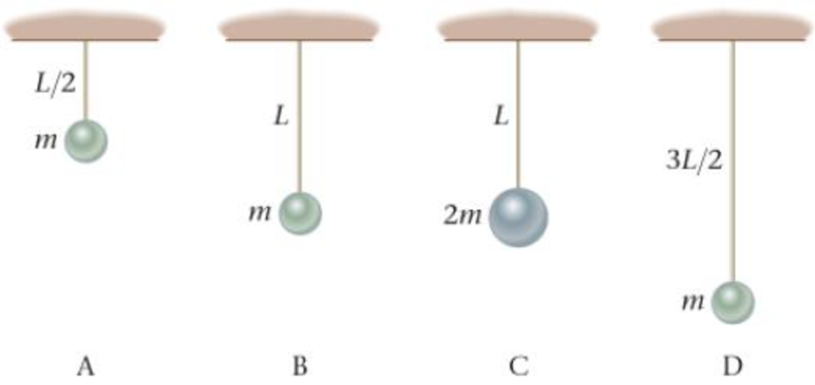
Figure 13-25 Enhance Your Understanding 6.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls
No chatgpt pls
Please help by:
Use a free body diagram
Show the equations
State your assumptions
Show your steps
Box your final answer
Thanks!
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Ch. 13.1 - If the frequency of an oscillator is halved, by...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 2EYUCh. 13.3 - An object moves with simple harmonic motion about...Ch. 13.4 - Rank the four massspring systems in Figure 13-15...Ch. 13.5 - The total mechanical energy of an ideal...Ch. 13.6 - Rank the four pendulum systems in Figure 13-25 in...Ch. 13.7 - The amplitude of a damped oscillation decreases...Ch. 13.8 - When you drive a pendulum at a frequency f1, you...Ch. 13 - A basketball player dribbles a ball with a steady...Ch. 13 - A person rides on a Ferris wheel that rotates with...
Ch. 13 - An air-track cart bounces back and forth between...Ch. 13 - If a mass m and a mass 2m oscillate on identical...Ch. 13 - An object oscillating with simple harmonic motion...Ch. 13 - The position of an object undergoing simple...Ch. 13 - The pendulum bob in Figure 13-18 leaks sand onto...Ch. 13 - A person in a rocking chair completes 12 cycles in...Ch. 13 - While fishing for catfish, a fisherman suddenly...Ch. 13 - If you dribble a basketball with a frequency of...Ch. 13 - You take your pulse and observe 74 heartbeats in a...Ch. 13 - BIO Slow-Motion Dragonfly A frame-by-frame...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate (a) Your heart beats with a...Ch. 13 - You rev your cars engine to 3300 rpm (rev/min)....Ch. 13 - A mass moves back and forth in simple harmonic...Ch. 13 - A mass moves back and forth in simple harmonic...Ch. 13 - The position of a mass oscillating on a spring is...Ch. 13 - The position of a mass oscillating on a spring is...Ch. 13 - A position-versus-time plot for an object...Ch. 13 - A mass on a spring oscillates with simple harmonic...Ch. 13 - A mass oscillates on a spring with a period of...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate Molecular Oscillations An atom...Ch. 13 - A mass oscillates on a spring with a period T and...Ch. 13 - The position of a mass on a spring is given by x =...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate A mass attached to a spring...Ch. 13 - A lawn sprinkler oscillates with simple harmonic...Ch. 13 - A ball rolls on a circular track of radius 0.62 m...Ch. 13 - An object executing simple harmonic motion has a...Ch. 13 - A child rocks back and forth on a porch swing with...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate A 30.0-g goldfinch lands on a...Ch. 13 - BIO Tuning Forks in Neurology Tuning forks are...Ch. 13 - A vibrating structural beam in a spacecraft can...Ch. 13 - A peg on a turntable moves with a constant...Ch. 13 - The pistons in an internal combustion engine...Ch. 13 - Vomit Comet NASA trains astronauts to deal with...Ch. 13 - A 0.84-kg air cart is attached to a spring and...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate A person rides on a mechanical...Ch. 13 - An object moves with simple harmonic motion of...Ch. 13 - An object executing simple harmonic motion has a...Ch. 13 - Predict/Explain If a mass m is attached to a given...Ch. 13 - Predict/Explain An old car with worn-out shock...Ch. 13 - Predict/Explain The two blocks in Figure 13-34...Ch. 13 - A 0.49-kg mass attached to a spring undergoes...Ch. 13 - A freshly caught catfish is placed on a spring...Ch. 13 - System A consists of a mass m attached to a spring...Ch. 13 - Find the periods of block 1 and block 2 in Figure...Ch. 13 - When a 0.62-kg mass is attached to a vertical...Ch. 13 - A spring with a force constant of 82 N/m is...Ch. 13 - A bunch of grapes is placed in a spring scale at a...Ch. 13 - Two people with a combined mass of 125 kg hop into...Ch. 13 - A 0.95-kg mass attached to a vertical spring of...Ch. 13 - When a 0.184-kg mass is attached to a vertical...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate The springs of a 511-kg...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate If a mass m is attached to a...Ch. 13 - A 0.285-kg mass is attached to a spring with a...Ch. 13 - A 1.6-kg mass attached to a spring oscillates with...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate A 0.40-kg mass is attached to a...Ch. 13 - Prob. 51PCECh. 13 - BIO Astronaut Mass An astronaut uses a Body Mass...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate A 0.505-kg block slides on a...Ch. 13 - A 3.55-g bullet embeds itself in a 1.47-kg block,...Ch. 13 - Metronomes, such as the penguin shown in Figure...Ch. 13 - Predict/Explain A grandfather clock keeps correct...Ch. 13 - An observant fan at a baseball game notices that...Ch. 13 - A simple pendulum of length 2.3 m makes 5.0...Ch. 13 - United Nations Pendulum A large pendulum with a...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate If the pendulum in the previous...Ch. 13 - A Hula Hoop hangs from a peg. Find the period of...Ch. 13 - A fireman tosses his 0.98-kg hat onto a peg, where...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate Consider a meterstick that...Ch. 13 - On the construction site for a new skyscraper, a...Ch. 13 - BIO (a) Find the period of a childs leg as it...Ch. 13 - Suspended from the ceiling of an elevator is a...Ch. 13 - CE An object undergoes simple harmonic motion with...Ch. 13 - CE If the amplitude of a simple harmonic...Ch. 13 - CE A mass m is suspended from the ceiling of an...Ch. 13 - CE A pendulum of length L is suspended from the...Ch. 13 - A 1.3-kg mass is attached to a spring with a force...Ch. 13 - BIO Measuring an Astronauts Mass An astronaut uses...Ch. 13 - Sunspot Observations Sunspots vary in number as a...Ch. 13 - BIO Weighing a Bacterium Scientists are using...Ch. 13 - CE An object undergoing simple harmonic motion...Ch. 13 - The maximum speed of a 4.1-kg mass attached to a...Ch. 13 - The acceleration of a block attached to a spring...Ch. 13 - Helioseismology In 1962, physicists at Cal Tech...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate A 9.50-g bullet, moving...Ch. 13 - BIO Spiderweb Oscillations A 1.44-g spider...Ch. 13 - A service dog tag (Figure 13-40) is a circular...Ch. 13 - Calculate the ratio of the kinetic energy to the...Ch. 13 - A 0.340-kg mass slides on a frictionless floor...Ch. 13 - A shock absorber is designed to quickly damp out...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate Figure 13-41 shows a...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate A 3.2-kg mass on a spring...Ch. 13 - A 0.45-kg crow lands on a slender branch and bobs...Ch. 13 - A mass m is connected to the bottom of a vertical...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate Consider the pendulum shown in...Ch. 13 - An object undergoes simple harmonic motion of...Ch. 13 - A physical pendulum consists of a light rod of...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate A vertical hollow tube is...Ch. 13 - BIO A Cricket Thermometer, by Jiminy Insects are...Ch. 13 - BIO A Cricket Thermometer, by Jiminy Insects are...Ch. 13 - BIO A Cricket Thermometer, by Jiminy Insects are...Ch. 13 - BIO A Cricket Thermometer, by Jiminy Insects are...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 13-5...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 13-12...Ch. 13 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 13-12 (a)...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
26. A hockey puck sliding along frictionless ice with speed v to the right collides with a horizontal spring an...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
What percentage of Earths land surface do glaciers presently cover? ____________
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, using complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) des...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Describe an example of bioconversion. What metabolic processes can result in fuels?
Microbiology: An Introduction
8. A human maintaining a vegan diet (containing no animal products) would be a:
a. producer
b. primary consume...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help by: Use a free body diagram Show the equations State your assumptions Show your steps Box your final answer Thanks!arrow_forwardBy please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardA collection of electric charges that share a common magnitude q (lower case) has been placed at the corners of a square, and an additional charge with magnitude Q (upper case) is located at the center of that square. The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four unique setups of charges are displayed. By moving one of the direction drawings from near the bottom to the bucket beside each of the setups, indicate the direction of the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q, located near the center, else indicate that the magnitude of the net electric force is zero, if appropriate.arrow_forward
- A number of electric charges has been placed at distinct points along a line with separations as indicated. Two charges share a common magnitude, q (lower case), and another charge has magnitude Q(upper case). The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four different configurations of charges are shown. For each, express the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q (upper case) as F⃗E=FE,xî where the positive x direction is towards the right. By repositioning the figures to the area on the right, rank the configurations from the most negative value to the most positive value of FE,x.arrow_forwardFor each part make sure to include sign to represent direction, with up being positive and down being negative. A ball is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 30.5 m/s. A) How high does it rise? y= B) How long does it take to reach its highest point? t= C) How long does it take the ball return to its starting point after it reaches its highest point? t= D) What is its velocity when it returns to the level from which it started? v=arrow_forwardFour point charges of equal magnitude Q = 55 nC are placed on the corners of a rectangle of sides D1 = 27 cm and D2 = 11cm. The charges on the left side of the rectangle are positive while the charges on the right side of the rectangle are negative. Use a coordinate system where the positive y-direction is up and the positive x-direction is to the right. A. Which of the following represents a free-body diagram for the charge on the lower left hand corner of the rectangle? B. Calculate the horizontal component of the net force, in newtons, on the charge which lies at the lower left corner of the rectangle.Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression.Fx = __________________________________________NC. Calculate the vertical component of the net force, in newtons, on the charge which lies at the lower left corner of the rectangle.Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression.Fy = __________________________________________ND. Calculate the magnitude of the…arrow_forward
- Point charges q1=50.0μC and q2=-35μC are placed d1=1.0m apart, as shown. A. A third charge, q3=25μC, is positioned somewhere along the line that passes through the first two charges, and the net force on q3 is zero. Which statement best describes the position of this third charge?1) Charge q3 is to the right of charge q2. 2) Charge q3 is between charges q1 and q2. 3) Charge q3 is to the left of charge q1. B. What is the distance, in meters, between charges q1 and q3? (Your response to the previous step may be used to simplify your solution.)Give numeric value.d2 = __________________________________________mC. Select option that correctly describes the change in the net force on charge q3 if the magnitude of its charge is increased.1) The magnitude of the net force on charge q3 would still be zero. 2) The effect depends upon the numeric value of charge q3. 3) The net force on charge q3 would be towards q2. 4) The net force on charge q3 would be towards q1. D. Select option that…arrow_forwardThe magnitude of the force between a pair of point charges is proportional to the product of the magnitudes of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of their separation distance. Four distinct charge-pair arrangements are presented. All charges are multiples of a common positive charge, q. All charge separations are multiples of a common length, L. Rank the four arrangements from smallest to greatest magnitude of the electric force.arrow_forwardA number of electric charges has been placed at distinct points along a line with separations as indicated. Two charges share a common magnitude, q (lower case), and another charge has magnitude Q (upper case). The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four different configurations of charges are shown. For each, express the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q (upper case) as F⃗E=FE,xî where the positive x direction is towards the right. By repositioning the figures to the area on the right, rank the configurations from the most negative value to the most positive value of FE,x.arrow_forward
- A collection of electric charges that share a common magnitude q (lower case) has been placed at the corners of a square, and an additional charge with magnitude Q (upper case) is located at the center of that square. The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four unique setups of charges are displayed. By moving one of the direction drawings from near the bottom to the bucket beside each of the setups, indicate the direction of the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q, located near the center, else indicate that the magnitude of the net electric force is zero, if appropriate.arrow_forwardIn Dark Souls 3 you can kill the Ancient Wyvern by dropping on its head from above it. Let’s say you jump off the ledge with an initial velocity of 3.86 mph and spend 1.72 s in the air before hitting the wyvern’s head. Assume the gravity is the same as that of Earth and upwards is the positive direction. Also, 1 mile = 1609 m. A) How high up is the the ledge you jumped from as measured from the wyvern’s head? B) What is your velocity when you hit the wyvern?arrow_forwardA conducting sphere is mounted on an insulating stand, and initially it is electrically neutral. A student wishes to induce a charge distribution similar to what is shown here. The student may connect the sphere to ground or leave it electrically isolated. The student may also place a charged insulated rod near to the sphere without touching it. Q. The diagrams below indicate different choices for whether or not to include a ground connection as well as the sign of the charge on and the placement of an insulating rod. Choose a diagram that would produce the desired charge distribution. (If there are multiple correct answers, you need to select only one of them.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XjkUcJkGd3Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY