
MECHANICS OF MATERIAL IN SI UNITS
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781292178202
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.3, Problem 13.18P
The 10-fl wooden column has the dimensions shown. Determine the critical load if the bottom is fixed and the top is pinned.
Ew = 1.6 (103) ksi, σY = 5 ksi.
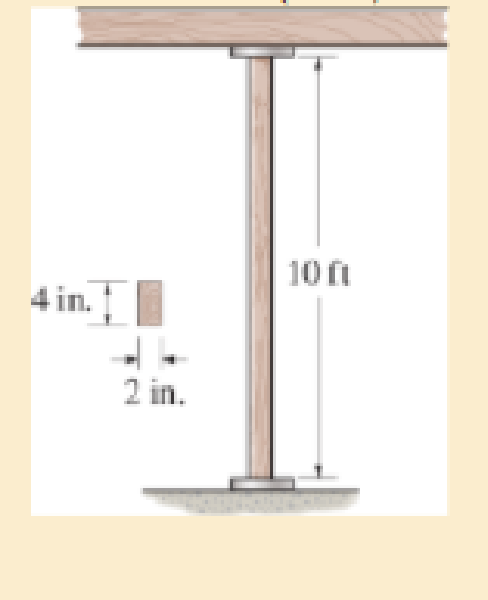
Probs. 13−17/18
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Determine the moments of the force about the x and the
a axes.
O
4 m
F = {-40i +20j + 10k} N
3 m
6 m
a
6. A part of the structure for a factory automation system is
a beam that spans 30.0 in as shown in Figure P5-6. Loads
are applied at two points, each 8.0 in from a support. The
left load F₁ = 1800 lb remains constantly applied, while
the right load F₂ = 1800 lb is applied and removed fre-
quently as the machine cycles. Evaluate the beam at both
B and C.
A
8 in
F₁ = 1800 lb
14 in
F2 = 1800 lb
8 in
D
RA
B
C
4X2X1/4
Steel
tube
Beam cross section
RD
30. Repeat Problem 28, except using a shaft that is rotating
and transmitting a torque of 150 N⚫m from the left bear-
ing to the middle of the shaft. Also, there is a profile key-
seat at the middle under the load.
Chapter 13 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIAL IN SI UNITS
Ch. 13.3 - A 50-in long steel rod has a diameter of 1 in....Ch. 13.3 - A 12-ft wooden rectangular column has the...Ch. 13.3 - The A992 steel column can be considered pinned at...Ch. 13.3 - A steel pipe is fixed supported at its ends. If it...Ch. 13.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be...Ch. 13.3 - The A992 steel rod BC has a diameter of 50 mm and...Ch. 13.3 - Determine the critical buckling load for the...Ch. 13.3 - The column consists of a rigid member that is...Ch. 13.3 - The aircraft link is made from an A992 steel rod....Ch. 13.3 - Rigid bars AB and BC are pin connected at B. If...
Ch. 13.3 - A 2014-T6 aluminium alloy column has a length of 6...Ch. 13.3 - Solve Prob. 13-5 if the column is pinned at its...Ch. 13.3 - The W12 50 is made of A992 steel and is used as a...Ch. 13.3 - The W12 50 is made of A992 steel and is used as a...Ch. 13.3 - A steel column has a length of 9 m and is fixed at...Ch. 13.3 - A steel column has a length of 9 m and is pinned...Ch. 13.3 - The A992 steel angle has a cross-sectional area of...Ch. 13.3 - The 50-mm-diameter C86100 bronze rod is fixed...Ch. 13.3 - Determine the maximum load P the frame can support...Ch. 13.3 - The W8 67 wide-flange A-36 steel column can be...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.15PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.16PCh. 13.3 - The 10-ft wooden rectangular column has the...Ch. 13.3 - The 10-fl wooden column has the dimensions shown....Ch. 13.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 13.3 - The A-36 steel pipe has an outer diameter of 2 in....Ch. 13.3 - The A-36 steel pipe has an outer diameter of 2 in....Ch. 13.3 - The deck is supported by the two 40-mm-square...Ch. 13.3 - The deck is supported by the two 40-mm-square...Ch. 13.3 - The beam is supported by the three pin-connected...Ch. 13.3 - The W14 30 A992 steel column is assumed pinned at...Ch. 13.3 - The A992 steel bar AB has a square cross section....Ch. 13.3 - The linkage is made using two A992 steel rods,...Ch. 13.3 - The linkage is made using two A992 steel rods,...Ch. 13.3 - The linkage is made using two A-36 steel rods,...Ch. 13.3 - The linkage is made using two A-36 steel rods,...Ch. 13.3 - The steel bar AB has a rectangular cross section....Ch. 13.3 - Determine if the frame can support a load of P =...Ch. 13.3 - Determine the maximum allowable load P that can be...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.34PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.35PCh. 13.3 - The members of the truss are assumed to be pin...Ch. 13.3 - Solve Prob. 1336 for member AB, which has a radius...Ch. 13.3 - The truss is made from A992 steel bars, each of...Ch. 13.3 - The truss is made from A992 steel bars, each of...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.40PCh. 13.3 - The ideal column has a weight w (force/length) and...Ch. 13.3 - The ideal column is subjected to the force F at...Ch. 13.3 - The column with constant El has the end...Ch. 13.3 - Consider an ideal column as in Fig.13-10 c, having...Ch. 13.3 - Consider an ideal column as in Fig. 13-10d, having...Ch. 13.5 - The wood column is fixed at its base and free at...Ch. 13.5 - The W10 12 structural A-36 steel column is used...Ch. 13.5 - The W10 12 structural A-36 steel column is used...Ch. 13.5 - The aluminium column is fixed at the bottom and...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 13.50PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 13.51PCh. 13.5 - The aluminum rod is fixed at its base and free and...Ch. 13.5 - Assume that the wood column is pin connected at...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 13.54PCh. 13.5 - The wood column is pinned at its base and top. If...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 13.56PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 13.57PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 13.58PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 13.59PCh. 13.5 - The wood column is pinned at its base and top. If...Ch. 13.5 - The brass rod is fixed at one end and free at the...Ch. 13.5 - The brass rod is fixed at one end and free at the...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 13.63PCh. 13.5 - A W14 30 structural A-36 steel column is pin...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 13.65PCh. 13.5 - The 6061-T6 aluminum alloy solid shaft is fixed at...Ch. 13.5 - The 6061-T6 aluminum alloy solid shaft is fixed at...Ch. 13.5 - The W14 53 structural A992 steel column is fixed...Ch. 13.5 - The W14 53 column is fixed at its base and free...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 13.70PCh. 13.5 - The stress-strain diagram for a material can be...Ch. 13.5 - The stress-strain diagram for a material can be...Ch. 13.5 - The stress-strain diagram for the material of a...Ch. 13.5 - Construct the buckling curve, P/A versus L/ r, for...Ch. 13.5 - The stress-strain diagram of the material can be...Ch. 13.5 - The stress-strain diagram of the material can be...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 13.77PCh. 13.6 - Determine the largest length of a W10 12...Ch. 13.6 - Using the AISC equations, select from AppendixB...Ch. 13.6 - Take Y = 50 ksi.Ch. 13.6 - Determine the longest length of a W8 31...Ch. 13.6 - Using the AISC equations, select from AppendixB...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 13.83PCh. 13.6 - Using the AISC equations, select from AppendixB...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 13.85PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.86PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.87PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.88PCh. 13.6 - Using the AISC equations, check if a column having...Ch. 13.6 - The beam and column arrangement is used in a...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 13.91PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.92PCh. 13.6 - The 1-in.-diameter rod is used to support an axial...Ch. 13.6 - The 1-in.-diameter rod is used to support an axial...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 13.95PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.96PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.97PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.98PCh. 13.6 - The tube is 0.25 in. thick, is made of 2014-T6...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 13.100PCh. 13.6 - A rectangular wooden column has the cross section...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 13.102PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.103PCh. 13.6 - The bar is made of aluminum alloy 2014-T6....Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 13.105PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.106PCh. 13.7 - The W8 15 wide-flange A-36 steel column is...Ch. 13.7 - Solve Prob.13-107 if the column is fixed at its...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 13.109PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 13.110PCh. 13.7 - The W8 15 wide-flange A992 steel column is fixed...Ch. 13.7 - The W8 15 wide-flange A992 steel column is fixed...Ch. 13.7 - The W12 22 wide-flange A-36 steel column is fixed...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 13.114PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 13.115PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 13.116PCh. 13.7 - A 20-ft-long column is made of aluminum alloy...Ch. 13.7 - A 20-ft-long column is made of aluminum alloy...Ch. 13.7 - The 2014-T6 aluminum hollow column is fixed at its...Ch. 13.7 - The 2014-T6 aluminum hollow column is fixed at its...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 13.121PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 13.122PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 13.123PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 13.124PCh. 13.7 - The 10-in.-diameter utility pole supports the...Ch. 13.7 - Using the NFPA equations of Sec 13.6. and Eq....Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 13.127PCh. 13 - The wood column has a thickness of 4 in. and a...Ch. 13 - The wood column has a thickness of 4 in. and a...Ch. 13 - A steel column has a length of 5 m and is free at...Ch. 13 - The square structural A992 steel tubing has outer...Ch. 13 - If the A-36 steel solid circular rod BD has a...Ch. 13 - If P = 15 kip, determine the required minimum...Ch. 13 - The steel pipe is fixed supported at its ends. If...Ch. 13 - The W200 46 wide-flange A992-steel column can be...Ch. 13 - The wide-flange A992 steel column has the cross...Ch. 13 - The wide-flange A992 steel column has the cross...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Consider the adage Never ask a question for which you do not want the answer. a. Is following that adage ethica...
Experiencing MIS
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 28. The shaft shown in Figure P5-28 is supported by bear- ings at each end, which have bores of 20.0 mm. Design the shaft to carry the given load if it is steady and the shaft is stationary. Make the dimension a as large as pos- sible while keeping the stress safe. Determine the required d = 20mm D = ? R = ?| 5.4 kN d=20mm Length not to scale -a = ?- +а= a = ? + -125 mm- -250 mm- FIGURE P5-28 (Problems 28, 29, and 30)arrow_forward12. Compute the estimated actual endurance limit for SAE 4130 WQT 1300 steel bar with a rectangular cross sec- tion of 20.0 mm by 60 mm. It is to be machined and subjected to repeated and reversed bending stress. A reli- ability of 99% is desired.arrow_forward28. The shaft shown in Figure P5-28 is supported by bear- ings at each end, which have bores of 20.0 mm. Design the shaft to carry the given load if it is steady and the shaft is stationary. Make the dimension a as large as pos- sible while keeping the stress safe. Determine the required d = 20mm D = ? R = ?| 5.4 kN d=20mm Length not to scale -a = ?- +а= a = ? + -125 mm- -250 mm- FIGURE P5-28 (Problems 28, 29, and 30)arrow_forward
- 2. A strut in a space frame has a rectangular cross section of 10.0 mm by 30.0 mm. It sees a load that varies from a tensile force of 20.0 kN to a compressive force of 8.0 kN.arrow_forwardfind stress at Qarrow_forwardI had a theoretical question about attitude determination. In the attached images, I gave two axis and angles. The coefficient of the axes are the same and the angles are the same. The only difference is the vector basis. Lets say there is a rotation going from n hat to b hat. Then, you introduce a intermediate rotation s hat. So, I want to know if the DCM produced from both axis and angles will be the same or not. Does the vector basis affect the numerical value of the DCM? The DCM formula only cares about the coefficient of the axis and the angle. So, they should be the same right?arrow_forward
- 3-15. A small fixed tube is shaped in the form of a vertical helix of radius a and helix angle y, that is, the tube always makes an angle y with the horizontal. A particle of mass m slides down the tube under the action of gravity. If there is a coefficient of friction μ between the tube and the particle, what is the steady-state speed of the particle? Let y γ 30° and assume that µ < 1/√3.arrow_forwardThe plate is moving at 0.6 mm/s when the force applied to the plate is 4mN. If the surface area of the plate in contact with the liquid is 0.5 m^2, deterimine the approximate viscosity of the liquid, assuming that the velocity distribution is linear.arrow_forward3-9. Given that the force acting on a particle has the following components: Fx = −x + y, Fy = x − y + y², F₂ = 0. Solve for the potential energy V. -arrow_forward
- 2.5 (B). A steel rod of cross-sectional area 600 mm² and a coaxial copper tube of cross-sectional area 1000 mm² are firmly attached at their ends to form a compound bar. Determine the stress in the steel and in the copper when the temperature of the bar is raised by 80°C and an axial tensile force of 60 kN is applied. For steel, E = 200 GN/m² with x = 11 x 10-6 per °C. E = 100 GN/m² with α = 16.5 × 10-6 For copper, per °C. [E.I.E.] [94.6, 3.3 MN/m².]arrow_forward3–16. A particle of mass m is embedded at a distance R from the center of a massless circular disk of radius R which can roll without slipping on the inside surface of a fixed circular cylinder of radius 3R. The disk is released with zero velocity from the position shown and rolls because of gravity, all motion taking place in the same vertical plane. Find: (a) the maximum velocity of the particle during the resulting motion; (b) the reaction force acting on the disk at the point of contact when it is at its lowest position. KAR 60° 3R M Fig. P3-16arrow_forwardI have figured out the support reactions, Ay = 240 kN, Ax = 0 kN, Ma = 639.2 kN*m and the constant term for V(x) is 240. I am not figuring out the function of x part right. Show how to derive V(x) and M(x) for this distributed load.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Column buckling; Author: Amber Book;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AvvaCi_Nn94;License: Standard Youtube License