
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined.
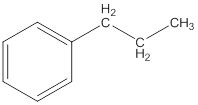
Concept Introduction:
When the mixture of hydrocarbons from natural resources such as coal or petroleum are separated, certain compounds are emerged with pleasant odors and are thus known as
Hydrocarbons with sigma bonds and delocalization of pi electrons between carbon atoms, thus forms a circle is said to be aromatic hydrocarbons.
Rules of naming aromatic compounds are:
- Aromatic compounds are named as a benzene derivative.
- For single substituent, the benzene ring is symmetrical. Thus, all the positions are equivalent.
- For more than one substituent, the benzene ring is not symmetrical. Thus, numbering will be done from one substituent which is attached to ring to other substituent through shorter path. Numbering should be done in a way that the first substituent gets the lowest number.
- In naming, the names of substituents are listed in alphabetical order.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined.
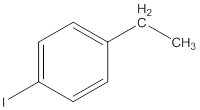
Concept Introduction:
When the mixture of hydrocarbons from natural resources such as coal or petroleum are separated, certain compounds are emerged with pleasant odors and are thus known as aromatic hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons with sigma bonds and delocalization of pi electrons between carbon atoms, thus forms a circle is said to be aromatic hydrocarbons.
Rules of naming aromatic compounds are:
- Aromatic compounds are named as a benzene derivative.
- For single substituent, the benzene ring is symmetrical. Thus, all the positions are equivalent.
- For more than one substituent, the benzene ring is not symmetrical. Thus, numbering will be done from one substituent which is attached to ring to other substituent through shorter path. Numbering should be done in a way that the first substituent gets the lowest number.
- In naming, the names of substituents are listed in alphabetical order.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined.
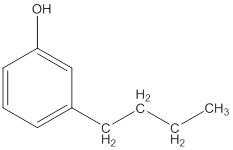
Concept Introduction:
When the mixture of hydrocarbons from natural resources such as coal or petroleum are separated, certain compounds are emerged with pleasant odors and are thus known as aromatic hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons with sigma bonds and delocalization of pi electrons between carbon atoms, thus forms a circle is said to be aromatic hydrocarbons.
Rules of naming aromatic compounds are:
- Aromatic compounds are named as a benzene derivative.
- For single substituent, the benzene ring is symmetrical. Thus, all the positions are equivalent.
- For more than one substituent, the benzene ring is not symmetrical. Thus, numbering will be done from one substituent which is attached to ring to other substituent through shorter path. Numbering should be done in a way that the first substituent gets the lowest number.
- In naming, the names of substituents are listed in alphabetical order.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined.
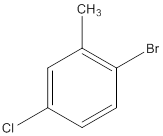
Concept Introduction:
When the mixture of hydrocarbons from natural resources such as coal or petroleum are separated, certain compounds are emerged with pleasant odors and are thus known as aromatic hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons with sigma bonds and delocalization of pi electrons between carbon atoms, thus forms a circle is said to be aromatic hydrocarbons.
Rules of naming aromatic compounds are:
- Aromatic compounds are named as a benzene derivative.
- For single substituent, the benzene ring is symmetrical. Thus, all the positions are equivalent.
- For more than one substituent, the benzene ring is not symmetrical. Thus, numbering will be done from one substituent which is attached to ring to other substituent through shorter path. Numbering should be done in a way that the first substituent gets the lowest number.
- In naming, the names of substituents are listed in alphabetical order.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Connect One Semester Access Card for General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- The following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula?arrow_forwardWhich region(s) of the following phospholipid is/are hydrophobic? RO I hydro-water phobic-dislikes = Hydrophobic dislikes water ○ I only Il only I and III only II and IV only O II, III, and IV only III || IVarrow_forwardPredict the product of the following reactions: O 0= excess Х Кон ОН H+ H+ Iarrow_forward
- How many chiral centers/stereocenters are there in the following molecule? 1 2 3 4arrow_forwardWhich of these correspond to the molecule: 2,5-dimethylheptanearrow_forwardGiven the following data, determine the order of the reaction with respect to H2. H2(g) + 21Cl(g) → I2(g) + 2HCl(g) Experiment [H2] (torr) [ICI] (torr) Rate (M/s) 1 250 325 0.266 2 250 81 0.0665 3 50 325 0.266arrow_forward
