
Concept explainers
The motor applies a constant downward force
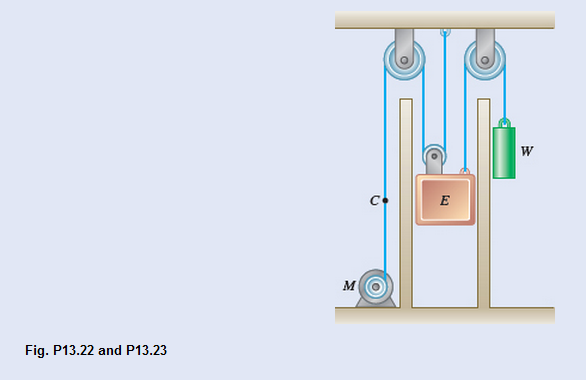
(a)
The velocity of the elevator.
Answer to Problem 13.22P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
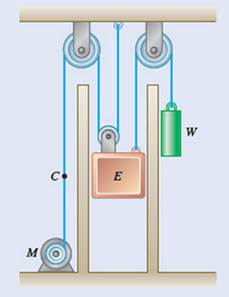
The constant downward force is equal to
Weight of elevator E is equal to
Counterweight is equal to
Elevator travels
In a dependent motion of particles such as the pulley system shown above,
The total length of the rope is a constant
For example,
The kinetic energy of a particle is defined as,
Principle of work and energy is defined as,
Above equation states “If a particle moves from A1 to A2 under an action of force F, the work of the force F is equal to the change in kinetic energy.”
Calculation:
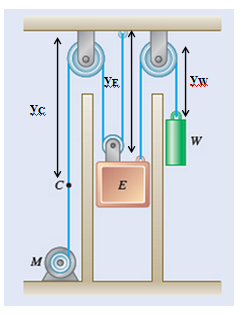
Length of both cables is constant, therefore
For cable 1,
Differentiate,
For cable 2,
Differentiate,

For elevator E,
Apply principle of work and energy,

For counter weight,
Apply principle of work and energy,
But we know that,
Therefore,
Add both equations,
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The velocity of elevator E is equal to
(b)
The velocity of the counter weight.
Answer to Problem 13.22P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
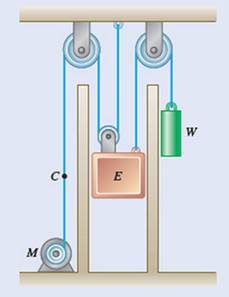
The constant downward force is equal to
Weight of elevator E is equal to
Counterweight is equal to
Elevator travels
In a dependent motion of particles such as the pulley system shown above,
The total length of the rope is a constant
For example,
The kinetic energy of a particle is defined as,
Principle of work and energy is defined as,
Above equation states “If a particle moves from A1 to A2 under an action of force F, the work of the force F is equal to the change in kinetic energy.”
Calculation:
According to sub part a,
We have found,
And,
Therefore, the velocity of counter weight is equal to,
Conclusion:
The velocity of counter weight is equal to
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,DYNAMICS(LOOSE)-W/ACCESS
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardCE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forward
- CE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct asnwerarrow_forwardthis is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = -4, Ay = -12,Az = 32.5, Bx= 34, Bz = 5, By = 0 but how?arrow_forwardThis is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = Az = 0, Ay = 2000, TDE = 4750, Cx = 2000, Cy = 2000, Cz = -800 but how?arrow_forward
- this is an old practice exam, the answer is Fmin = 290.5lb but howarrow_forwardThis is an exam review question. The answer is Pmin = 622.9 lb but whyarrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardThis is an old practice exam. Fce = 110lb and FBCD = 62 lb but whyarrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
