
Concept explainers
BIO A Cricket Thermometer, by Jiminy
Insects are ectothermic, which means their body temperature is largely determined by the temperature of their surroundings. This can have a number of interesting consequences. For example, the wing coloration in some butterfly species is determined by the ambient temperature, as is the body color of several species of dragonfly. In addition, the wing beat frequency of beetles taking flight varies with temperature due to changes in the resonant frequency of their thorax.
The origin of such temperature effects can be traced back to the fact that molecules have higher speeds and greater energy as temperature is increased (see Chapters 16 and 17). Thus, for example, molecules that collide and react as part of the
One of the most interesting thermal effects is the temperature dependence of chirp rate in certain insects. This behavior has been observed in cone-headed grasshoppers, as well as several types of cricket. A particularly accurate connection between chirp rate and temperature is found in the snowy tree cricket (Oecanthus fultoni Walker), which chirps at a rate that follows the expression N = T − 39, where N is the number of chirps in 13 seconds, and T is the numerical value of the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit. This formula, which is known as Dolbear’s law, is plotted in Figure 13-46 (green line) along with data points (blue dots) for the snowy tree cricket.
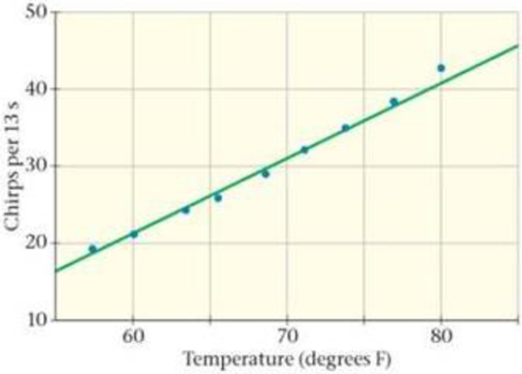
Figure 13-46 Problems 93, 94, 95, and 96
95. • What is the frequency of the cricket’s chirping (in Hz) when the temperature is 68 °F?
- A. 0.45 Hz
- B. 2.2 Hz
- C. 5.2 Hz
- D. 29 Hz
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
EP PHYSICS -MOD.MASTERING (18W)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- Please help me with this physics problemarrow_forwardIn a scene from The Avengers (the first one) Black Widow is boosted directly upwards by Captain America, where she then grabs on to a Chitauri speeder that is 15.0 feet above her and hangs on. She is in the air for 1.04 s. A) With what initial velocity was Black Widow launched? 1 m = 3.28 ft B) What was Black Widow’s velocity just before she grabbed the speeder? Assume upwards is the positive direction.arrow_forwardIn Dark Souls 3 you can kill the Ancient Wyvern by dropping on its head from above it. Let’s say you jump off the ledge with an initial velocity of 3.86 mph and spend 1.72 s in the air before hitting the wyvern’s head. Assume the gravity is the same as that of Earth and upwards is the positive direction. Also, 1 mile = 1609 m. A) How high up is the the ledge you jumped from as measured from the wyvern’s head? B) What is your velocity when you hit the wyvern?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Alreadyarrow_forwardTwo objects get pushed by the same magnitude of force. One object is 10x more massive. How does the rate of change of momentum for the more massive object compare with the less massive one? Please be able to explain why in terms of a quantitative statement found in the chapter.arrow_forwardA box is dropped on a level conveyor belt that is moving at 4.5 m/s in the +x direction in a shipping facility. The box/belt friction coefficient is 0.15. For what duration will the box slide on the belt? In which direction does the friction force act on the box? How far will the box have moved horizontally by the time it stops sliding along the belt?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





