
Concept explainers
The Doppler equation presented in the text is valid when the motion between the observer and the source occurs on a straight line so that the source and observer are moving either directly toward or directly away from each other. If this restriction is relaxed, one must use the more general Doppler equation
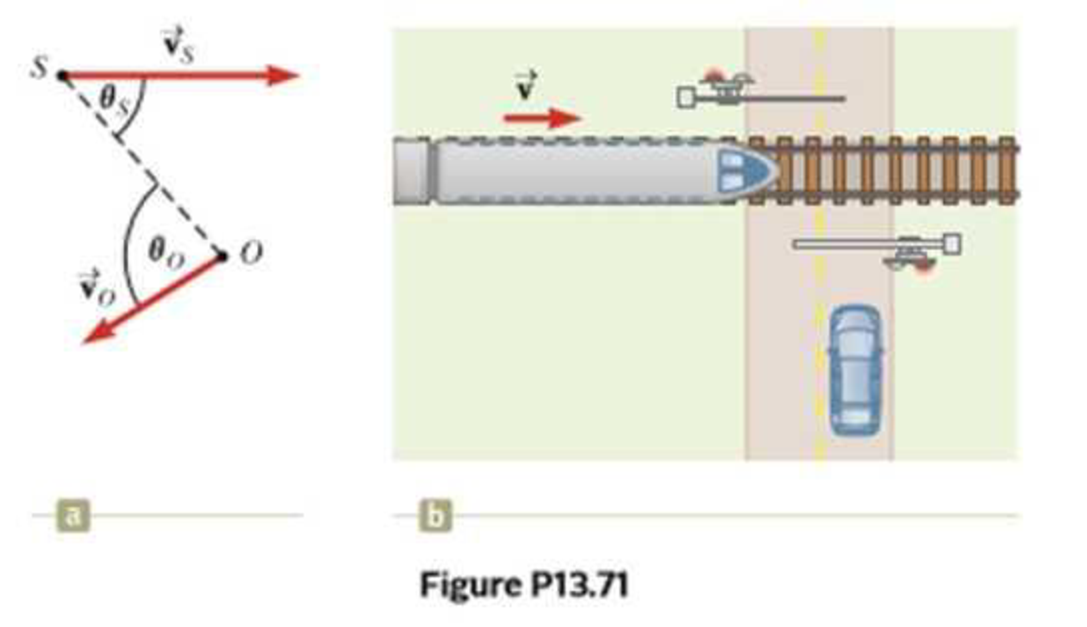
where θo and θs are defined in figure P13.7la. Use the preceding equation to solve the following problem. A train moves at a constant speed of v = 25.0 m/s toward the intersection shown in Figure P13.71b. A car is stopped near the crossing, 30.0 m from the tracks. The train’s horn emits a frequency of 500 Hz when the train is 40.0 m from the intersection. (a) What is the frequency heard by the passengers in the car? (b) If the train emits this sound continuously and the car is stationary at this position long before the train arrives until long after it leaves, what range of frequencies do passengers in the car hear? (c) Suppose the car is foolishly trying to beat the train to the intersection and is traveling at 40.0 m/s toward the tracks. When the car is 30.0 m from the tracks and the train is 40.0 m from the intersection, what is the frequency heard by the passengers in the car now?
(a)
The frequency heard by the passengers in the car.
Answer to Problem 71P
The frequency heard by the passengers in the car is
Explanation of Solution
The Doppler equation is given by,
Here,
In this case the value of
Conclusion:
Since the train is
Substitute
Therefore, The frequency heard by the passengers in the car is
(b)
The range of frequencies that heard by the passenger.
Answer to Problem 71P
The range of frequencies that heard by the passenger is from
Explanation of Solution
The value of
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, The range of frequencies that heard by the passenger is from
(c)
The frequency heard by the passengers in the car when the car is
Answer to Problem 71P
The frequency heard by the passengers in the car when the car is
Explanation of Solution
Since the rain is
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, The frequency heard by the passengers in the car when the car is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
- pls help on thesearrow_forward20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- 19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- 6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





