
A ball of mass M = 5.00 kg and radius r = 5.00 cm is attached to one end of a thin, cylindrical rod of length L = 15.0 cm and mass m = 0.600 kg. The ball and rod, initially at rest in a vertical position and free to rotate around the axis shown in Figure P13.70, are nudged into motion. a. What is the rotational kinetic energy of the system when the ball and rod reach a horizontal position? b. What is the angular speed of the ball and rod when they reach a horizontal position? c. What is the linear speed of the center of mass of the ball when the ball and rod reach a horizontal position? d. What is the ratio of the speed found in part (c) to the speed of a ball that falls freely through the same distance?
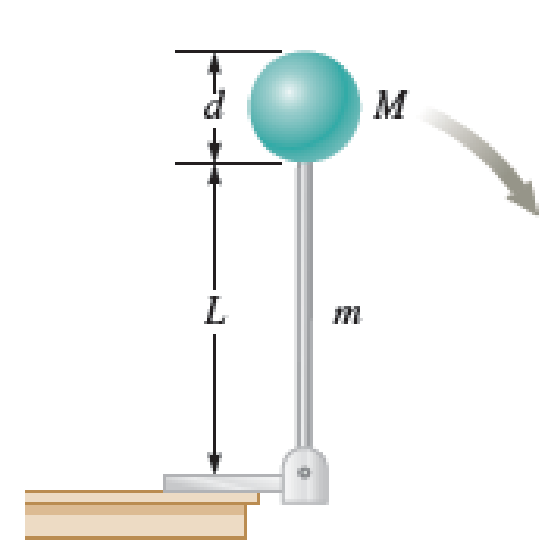
FIGURE P13.70
(a)
The rotational kinetic energy of the system when the ball and rod reach a horizontal position.
Answer to Problem 70PQ
The rotational kinetic energy of the system when the ball and rod reach a horizontal position is
Explanation of Solution
For the isolated rod-ball-Earth system with no friction, the mechanical energy is conserved.
Here,
The initially the system has only potential energy and has no kinetic energy. At the final position, the entire potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. Thus, equation (I) can be modified as,
Write the expression for the initial potential energy of the given system.
Here,
Use equation (III) in (II) and solve for
For the uniform rod, the center of mass is at the mid-point. Since the length of the rod is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the rotational kinetic energy of the system when the ball and rod reach a horizontal position is
(b)
The angular speed of the system when it reach the horizontal position.
Answer to Problem 70PQ
The angular speed of the system when it reach the horizontal position is
Explanation of Solution
The system can be assumed as, the sphere as a point particle which occupies at a distance
Write the expression for the rotational inertia of the given rod-ball system.
Here,
Write the expression for the rotational kinetic energy of the system at the horizontal position..
Here,
Solve equation (VI) for
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the angular speed of the system when it reach the horizontal position is
(c)
The linear speed of the center of mass of the ball when the system reach the horizontal position.
Answer to Problem 70PQ
The linear speed of the center of mass of the ball when the system reach the horizontal position is
Explanation of Solution
It is obtained that the angular speed of the system when it reach the horizontal position is
Write the expression for the linear speed in terms of the angular speed.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the linear speed of the center of mass of the ball when the system reach the horizontal position is
(d)
The ratio of the speed of the ball when the system is at the horizontal position and the speed of the ball that falls freely through the same distance.
Answer to Problem 70PQ
The ratio of the speed of the ball when the system is at the horizontal position and the speed of the ball that falls freely through the same distance is
Explanation of Solution
It is obtained that the linear speed of the center of mass of the ball when the system reach the horizontal position is
Write the expression for the speed of the freely balling ball.
Here,
Since the ball falls from rest, and reaches the ground, the initial speed is zero, and the final height is zero. Thus, equation (IX) can be modified and solved for
Conclusion:
Substitute
This indicates that the speed of the ball when the system is at the horizontal position and the speed of the ball that falls freely through the same distance are the same so that their ratio is obtained as,
Therefore, the ratio of the speed of the ball when the system is at the horizontal position and the speed of the ball that falls freely through the same distance is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK WEBASSIGN FOR KATZ'S PHYSICS FOR SC
- Below you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Answer questions a-d. a) What was the total race time for each team, in seconds? b) Which team won the race? What was the difference in the teams’ times? c) What was the average speed for each team for the whole race? (provide answer to 3 decimal places). d) Calculate the average speed for each swimmer and report the results in a table like the one above. Remember to show the calculation steps. (provide answer to 3 decimal places). PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK AND STEPS.arrow_forwardNeed complete solution Pleasearrow_forwardBelow you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Fill out the chart below. Calculate average speed per split (m/s). Show all work.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forward4.4 A man is dragging a trunk up the loading ramp of a mover's truck. The ramp has a slope angle of 20.0°, and the man pulls upward with a force F whose direction makes an angle of 30.0° 75.0° with the ramp (Fig. E4.4). (a) How large a force F is necessary for the component Fx parallel to the ramp to be 90.0 N? (b) How large will the component Fy perpendicular to the ramp be then? Figure E4.4 30.0 20.0°arrow_forward
- 1. * A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle e, with an initial velocity magnitude v., from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile lands on the tabletop a horizontal distance R (the "range") away from where it left the launcher. Set this up as a formal problem, and solve for vo (i.e., determine an expression for Vo in terms of only R, 0., and g). Your final equation will be called Equation 1.arrow_forward2. A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle 0,, with an initial velocity magnitude vo, from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile hits an apple atop a child's noggin (see Figure 1). The apple is a height y above the tabletop, and a horizontal distance x from the launcher. Set this up as a formal problem, and solve for x. That is, determine an expression for x in terms of only v₁, o,y and g. Actually, this is quite a long expression. So, if you want, you can determine an expression for x in terms of v., 0., and time t, and determine another expression for timet (in terms of v., 0., y and g) that you will solve and then substitute the value of t into the expression for x. Your final equation(s) will be called Equation 3 (and Equation 4).arrow_forward4.56 ... CALC An object of mass m is at rest in equilibrium at the origin. At t = 0 a new force F(t) is applied that has components Fx(t) = k₁ + k₂y Fy(t) = k3t where k₁, k2, and k3 are constants. Calculate the position (1) and veloc- ity (t) vectors as functions of time.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





