
Curing concrete is known to be vulnerable to shock vibrations, which may cause cracking or hidden damage to the material. As part of a study of vibration phenomena, the paper “Shock Vibration Test of Concrete” (ACI Materials J., 2002: 361–370) reported the accompanying data on peak particle velocity (mm/sec) and ratio of ultrasonic pulse velocity after impact to that before impact in concrete prisms.
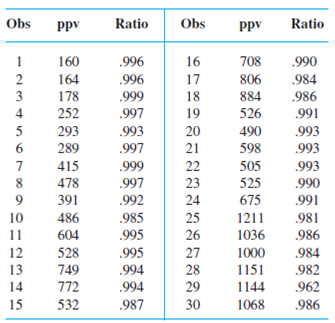
Transverse cracks appeared in the last 12 prisms, whereas there was no observed cracking in the first 18 prisms.
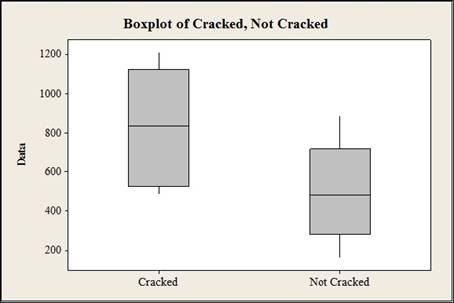
a. Construct a comparative boxplot of ppv for the cracked and uncracked prisms and comment. Then estimate the difference between true average ppv for cracked and uncracked prisms in a way that conveys information about precision and reliability.
b. The investigators fit the simple linear regression model to the entire data set consisting of 30 observations, with ppv as the independent variable and ratio as the dependent variable. Use a statistical software package to fit several different regression models, and draw appropriate inferences.
a.
Construct a comparative boxplot for the given data.
Answer to Problem 65SE
The comparative boxplot is given below:
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The data shows the ultra sonic pulse velocity ratio before and after impact in concrete prisms for peak velocity. The first 18 observations shows the values before cracking and last 12 observations shows the values after cracking.
Calculation:
Comparative boxplot:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to construct the boxplot is given below:
- Choose Graph > Boxplot.
- Under Multiple Y's, choose Simple. Click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the data of cracked and not cracked.
- Click OK.
Interpretation:
Thus, the box plot is constructed for the cracked ratio and not cracked ratio and the box plot suggests that the ultra sonic pulse velocity ratio for cracked ppv is greater than the ratio of not cracked ppv.
b.
Fit several different regression models and draw conclusions.
Answer to Problem 65SE
The simple linear regression model is given below:
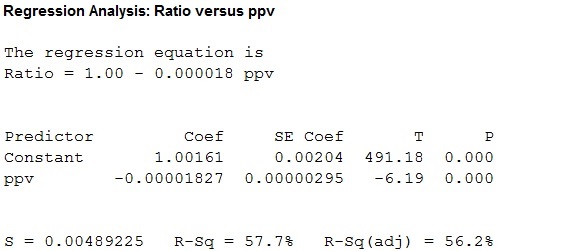
Figure 2
The multiple linear regression model is given below:
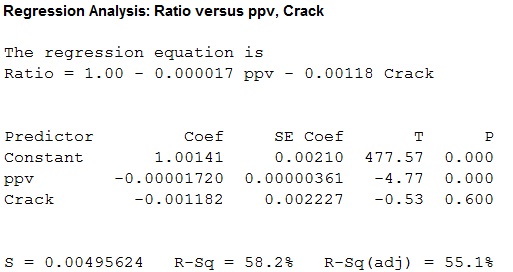
Figure 2
The multiple linear regression model with interaction is given below:
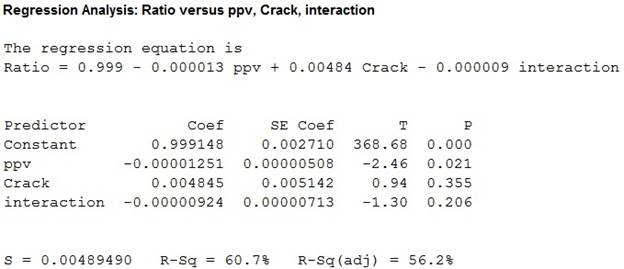
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Simple linear regression:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to fit a simple linear regression model is given below:
- Click Stat>Regression>Regression.
- Under Response (Y) select the column containing ratio.
- Under Predictor (X) select the column containing ppv.
- Click OK.
Interpretation:
Thus, a simple regression is fitted for the given data, the value of coefficient of determination is 57.7 which tells that the peak particle velocity can explain 57.7% of the variation in ratio of ultrasonic pulse velocity.
Multiple regression model with indicator variable (crack):
The new indicator variable is created by coding the observations with crack as 1 and observations without a crack as 0. Then the multiple regression model is built.
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to fit a simple linear regression model is given below:
- Click Stat>Regression>Regression.
- Under Response (Y) select the column containing ratio.
- Under Predictor (X) select the column containing ppv, crack.
- Click OK.
Interpretation:
Thus, a multiple regression model is fitted for the given data , the value of coefficient of determination is 58.2 which tells that the peak particle velocity and crack can explain 58.2% of the variation in ratio of ultrasonic pulse velocity.
Multiple regression model with interaction between ppv and indicator variable (crack):
The indication variable is created by multiplying the ppv with indicator variable.
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to fit a simple linear regression model is given below:
- Click Stat>Regression>Regression.
- Under Response (Y) select the column containing ratio.
- Under Predictor (X) select the column containing ppv, crack and interaction.
- Click OK.
Interpretation:
Thus, a multiple regression model with interaction between crack and ppv is fitted for the given data , the value of coefficient of determination is 60.7 which tells that the peak particle velocity, crack and interaction can explain 60.7% of the variation in ratio of ultrasonic pulse velocity.
The P- value for the individual t statistic corresponding to ppv and interaction are 0.355 and 0.206 which greater than the 5% level of significance.
Conclusion:
The simple linear, multiple linear model and multiple linear model with interaction gives almost the same
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Bundle: Probability and Statistics for Engineering and the Sciences, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Devore's Probability ... and the Sciences, 9th Edition, Single-Term
- You find out that the dietary scale you use each day is off by a factor of 2 ounces (over — at least that’s what you say!). The margin of error for your scale was plus or minus 0.5 ounces before you found this out. What’s the margin of error now?arrow_forwardSuppose that Sue and Bill each make a confidence interval out of the same data set, but Sue wants a confidence level of 80 percent compared to Bill’s 90 percent. How do their margins of error compare?arrow_forwardSuppose that you conduct a study twice, and the second time you use four times as many people as you did the first time. How does the change affect your margin of error? (Assume the other components remain constant.)arrow_forward
- Out of a sample of 200 babysitters, 70 percent are girls, and 30 percent are guys. What’s the margin of error for the percentage of female babysitters? Assume 95 percent confidence.What’s the margin of error for the percentage of male babysitters? Assume 95 percent confidence.arrow_forwardYou sample 100 fish in Pond A at the fish hatchery and find that they average 5.5 inches with a standard deviation of 1 inch. Your sample of 100 fish from Pond B has the same mean, but the standard deviation is 2 inches. How do the margins of error compare? (Assume the confidence levels are the same.)arrow_forwardA survey of 1,000 dental patients produces 450 people who floss their teeth adequately. What’s the margin of error for this result? Assume 90 percent confidence.arrow_forward
- The annual aggregate claim amount of an insurer follows a compound Poisson distribution with parameter 1,000. Individual claim amounts follow a Gamma distribution with shape parameter a = 750 and rate parameter λ = 0.25. 1. Generate 20,000 simulated aggregate claim values for the insurer, using a random number generator seed of 955.Display the first five simulated claim values in your answer script using the R function head(). 2. Plot the empirical density function of the simulated aggregate claim values from Question 1, setting the x-axis range from 2,600,000 to 3,300,000 and the y-axis range from 0 to 0.0000045. 3. Suggest a suitable distribution, including its parameters, that approximates the simulated aggregate claim values from Question 1. 4. Generate 20,000 values from your suggested distribution in Question 3 using a random number generator seed of 955. Use the R function head() to display the first five generated values in your answer script. 5. Plot the empirical density…arrow_forwardFind binomial probability if: x = 8, n = 10, p = 0.7 x= 3, n=5, p = 0.3 x = 4, n=7, p = 0.6 Quality Control: A factory produces light bulbs with a 2% defect rate. If a random sample of 20 bulbs is tested, what is the probability that exactly 2 bulbs are defective? (hint: p=2% or 0.02; x =2, n=20; use the same logic for the following problems) Marketing Campaign: A marketing company sends out 1,000 promotional emails. The probability of any email being opened is 0.15. What is the probability that exactly 150 emails will be opened? (hint: total emails or n=1000, x =150) Customer Satisfaction: A survey shows that 70% of customers are satisfied with a new product. Out of 10 randomly selected customers, what is the probability that at least 8 are satisfied? (hint: One of the keyword in this question is “at least 8”, it is not “exactly 8”, the correct formula for this should be = 1- (binom.dist(7, 10, 0.7, TRUE)). The part in the princess will give you the probability of seven and less than…arrow_forwardplease answer these questionsarrow_forward
- Selon une économiste d’une société financière, les dépenses moyennes pour « meubles et appareils de maison » ont été moins importantes pour les ménages de la région de Montréal, que celles de la région de Québec. Un échantillon aléatoire de 14 ménages pour la région de Montréal et de 16 ménages pour la région Québec est tiré et donne les données suivantes, en ce qui a trait aux dépenses pour ce secteur d’activité économique. On suppose que les données de chaque population sont distribuées selon une loi normale. Nous sommes intéressé à connaitre si les variances des populations sont égales.a) Faites le test d’hypothèse sur deux variances approprié au seuil de signification de 1 %. Inclure les informations suivantes : i. Hypothèse / Identification des populationsii. Valeur(s) critique(s) de Fiii. Règle de décisioniv. Valeur du rapport Fv. Décision et conclusion b) A partir des résultats obtenus en a), est-ce que l’hypothèse d’égalité des variances pour cette…arrow_forwardAccording to an economist from a financial company, the average expenditures on "furniture and household appliances" have been lower for households in the Montreal area than those in the Quebec region. A random sample of 14 households from the Montreal region and 16 households from the Quebec region was taken, providing the following data regarding expenditures in this economic sector. It is assumed that the data from each population are distributed normally. We are interested in knowing if the variances of the populations are equal. a) Perform the appropriate hypothesis test on two variances at a significance level of 1%. Include the following information: i. Hypothesis / Identification of populations ii. Critical F-value(s) iii. Decision rule iv. F-ratio value v. Decision and conclusion b) Based on the results obtained in a), is the hypothesis of equal variances for this socio-economic characteristic measured in these two populations upheld? c) Based on the results obtained in a),…arrow_forwardA major company in the Montreal area, offering a range of engineering services from project preparation to construction execution, and industrial project management, wants to ensure that the individuals who are responsible for project cost estimation and bid preparation demonstrate a certain uniformity in their estimates. The head of civil engineering and municipal services decided to structure an experimental plan to detect if there could be significant differences in project evaluation. Seven projects were selected, each of which had to be evaluated by each of the two estimators, with the order of the projects submitted being random. The obtained estimates are presented in the table below. a) Complete the table above by calculating: i. The differences (A-B) ii. The sum of the differences iii. The mean of the differences iv. The standard deviation of the differences b) What is the value of the t-statistic? c) What is the critical t-value for this test at a significance level of 1%?…arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





