
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168277
Author: William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher: OpenStax - Rice University
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 56P
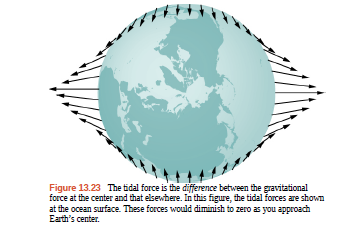
Consider Figure 13.23 in Tidal Forces. This diagram represents the tidal forces for spring tides. Sketch a similar diagram for neap tides. (Hint: For simplicity, imagine that the Sun and the Moon contribute equally. Your diagram would be the vector sum of two force fields (as in Figure 13.23), reduced by a factor of two, and superimposed at right angles.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
For each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank you
A planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).
What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V)
ammeter
I =
Chapter 13 Solutions
University Physics Volume 1
Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding What happens to force and...Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding How does your weight at...Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding Why not use the simpler...Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding If we send a probe out of...Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding Assume you are in a...Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding By what factor must the...Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding There is another...Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding Galaxies are not single...Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding The nearly circular orbit...Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding Earth exerts a tidal...
Ch. 13 - Check Your Understanding Consider the density...Ch. 13 - Action at a distance, such as is the case for...Ch. 13 - In the law of universal gravitation, Newton...Ch. 13 - Must engineers take Earth’s rotation into account...Ch. 13 - It was stated that a satellite with negative total...Ch. 13 - It was shown that the energy required to lift a...Ch. 13 - One student argues that a satellite in orbit is in...Ch. 13 - Many satellites are placed in geosynchronous...Ch. 13 - Are Kepler’s laws purely descriptive, or do they...Ch. 13 - In the diagram below for a satellite in an...Ch. 13 - As an object falls into a black hole, tidal forces...Ch. 13 - The principle of equivalence states that all...Ch. 13 - As a person approaches the Schwarzschild radius fo...Ch. 13 - Evaluate the magnitude of gravitational force...Ch. 13 - Estimate the gravitational force between two sumo...Ch. 13 - Astrology makes much of the position of the...Ch. 13 - A mountain 10.0 km from a person exerts a...Ch. 13 - The International Space Station has a mass of...Ch. 13 - Asteroid Toutatis passed near Earth in 2006 at...Ch. 13 - (a) What was the acceleration of Earth caused by...Ch. 13 - (a) Calculate Earth’s mass given the acceleratioln...Ch. 13 - (a) What is the acceleration due to gravity on the...Ch. 13 - (a) Calculate the acceleration due to gravity on...Ch. 13 - The mass of a particle is 15 kg. (a) What is its...Ch. 13 - On a planet whose radius is 1.2107m , the...Ch. 13 - The mean diameter of the planet Saturn is 1.2108m...Ch. 13 - The mean diameter of the planet Mercury is...Ch. 13 - The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of...Ch. 13 - A body on the surface of a planet with the same...Ch. 13 - Find the escape speed of a projectile from the...Ch. 13 - Find the escape speed of a projectile from the...Ch. 13 - What is the escape speed of a satellite located at...Ch. 13 - (a) Evaluate the gravitational potential energy...Ch. 13 - An average-sized asteroid located 5.0107km from...Ch. 13 - (a) What will be the kinetic energy of the...Ch. 13 - (a) What is the change in energy of a 1000-kg...Ch. 13 - If a planet with 1.5 times the mass of Earth was...Ch. 13 - Two planets in circular orbits around a star have...Ch. 13 - Using the average distance of Earth from the Sun,...Ch. 13 - What is the orbital radius of an Earth satellite...Ch. 13 - Calculate the mass of the Sun based on data for...Ch. 13 - Find the mass of Jupiter based on the fact that I0...Ch. 13 - Astronomical observatrions of our Milky Way galaxy...Ch. 13 - (a) In order to keep a small satellite from...Ch. 13 - The Moon and Earth rotate about their common...Ch. 13 - The Sun orbits the Milky Way galaxy once each...Ch. 13 - A geosynchronous Earth satellite is one that has...Ch. 13 - Calculate the mass of the Sun based on data for...Ch. 13 - I0 orbits Jupiter with an average radius of...Ch. 13 - The “mean” orbital radius listed for astronomical...Ch. 13 - The perihelion of Halley’s comet is 0.586 AU and...Ch. 13 - The perihelion of the comet Legerkvist is 2.61 AU...Ch. 13 - What is the ratio of the speed at perihelion to...Ch. 13 - Eros has an elliptical orbit about the Sun, with a...Ch. 13 - What is the difference between the force on a...Ch. 13 - If the Sun were to collapse into a black hole, the...Ch. 13 - Consider Figure 13.23 in Tidal Forces. This...Ch. 13 - What is the Schwarzschild radius for the black...Ch. 13 - What would be the Schwarzschild radius, in light...Ch. 13 - A neutron star is a cold, collapsed star with...Ch. 13 - (a) How far from the center of Earth would the net...Ch. 13 - How far from the center of the Sun would the net...Ch. 13 - Calculate the values of g at Earth’s surface for...Ch. 13 - Suppose you can communicate with the inhabitants...Ch. 13 - (a) Suppose that your measured weight at the...Ch. 13 - A body of mass 100 kg is weighed at the North Pole...Ch. 13 - Find the speed needed to escape from the solar...Ch. 13 - Consider the previous problem and include the fact...Ch. 13 - A comet is observed 1.50 AU from the Sun with a...Ch. 13 - An asteroid has speed 15.5km/s when it is located...Ch. 13 - Space debris left from old satellites and their...Ch. 13 - A satellite of mass 1000 kg is in circular orbit...Ch. 13 - After Cares was promoted to a dwarf planet, we now...Ch. 13 - (a) Using the data in the previous problem for the...Ch. 13 - What is the orbital velocity of our solar system...Ch. 13 - (a) Using the information in the previous problem,...Ch. 13 - Circular orbits in Equation 13.10 for conic...Ch. 13 - Show that for eccentricity equal to one in...Ch. 13 - Using the technique shown in Satellite Orbits and...Ch. 13 - Given the perihelion distance, p , and aphelion...Ch. 13 - Comet P/1999 R1 has a perihelion of 0.0570 AU and...Ch. 13 - A tunnel is dug through the center of a perfectly...Ch. 13 - Following the technique used in Gravitation Near...Ch. 13 - Show that the areal velocity for a circular orbit...Ch. 13 - Show that the period of orbit for two masses, m1...Ch. 13 - Show that for small changes in height h, such that...Ch. 13 - Using Figure 13.9, carefull sketch a free body...Ch. 13 - (a) Show that tidal force on a small object of...Ch. 13 - Find the Hohmann transfer velocities,...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
87. Fill in the blanks.
a.
b.
c.
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Compare each of the mechanisms listed here with the mechanism for each of the two parts of the acid-catalyzed h...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Using the South Atlantic as an example, label the beginning of the normal polarity period C that began 2 millio...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Match each of the following items with all the terms it applies to:
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
53. This reaction was monitored as a function of time:
A plot of In[A] versus time yields a straight ...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- simple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forwardAn L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forward
- A long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forwardDiscuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forward
- Explain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forwardA 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forward
- For each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.arrow_forwardWhen violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60 cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away. Part A How wide is the slit? ΟΙ ΑΣΦ ? D= 2.7.10-8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining marrow_forwardTwo complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9781938168284
Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:OpenStax

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Gravitational Force (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pxp1Z91S5uQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY