
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer
(b)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
(c)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of
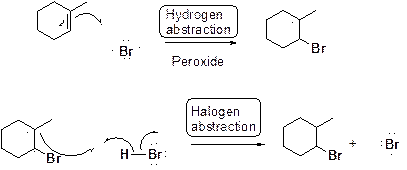
(d)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
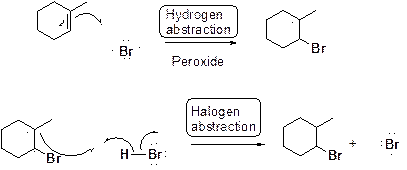
(e)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
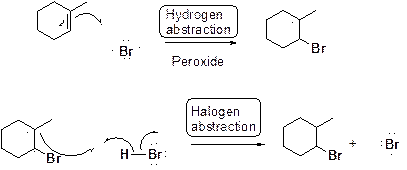
(f)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
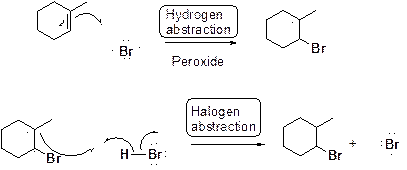
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

