
Concept explainers
Draw the enol tautomers for each of the following compounds. If the compound has more than one enol tautomer, indicate which one is more stable.
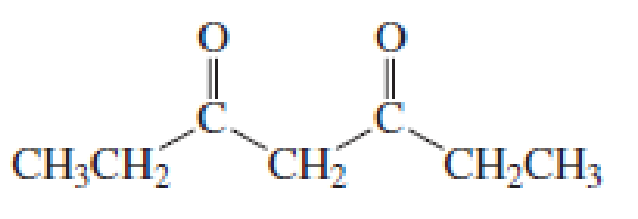
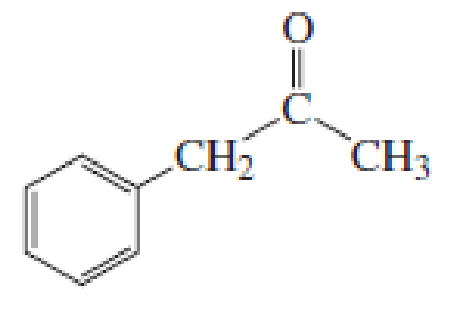
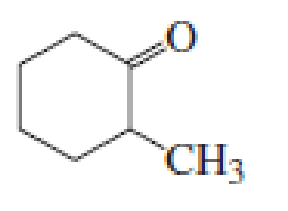
(a)
Interpretation:
The enol tautomer of the given compound has to be drawn and more stable structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Tautomerism is the ability of a molecule to exist in more than one chemical form.
Tautomers are formed by the migration of a hydrogen atom, accompanied by the switching of a single and neighboring double bond.
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.
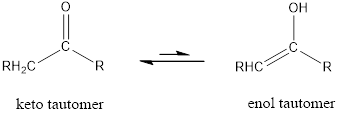
Enol tautomer is much less stable than the keto tautomer.
Enol tautomer is more stable when enol tautomer is aromatic or when the double bonds are conjugated.
Resonance is an electron displacement effect for stabilizing a molecule through delocalization of bonding electrons in the pi orbital.
Delocalized electrons stabilize a compound. The extra stability gains from having delocalized electrons are called resonance stabilization or resonance energy.
Explanation of Solution
Given keto tautomer is,
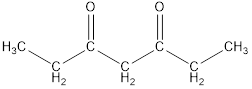
The only difference in keto-enol tautomer is the location of hydrogen and double bond.
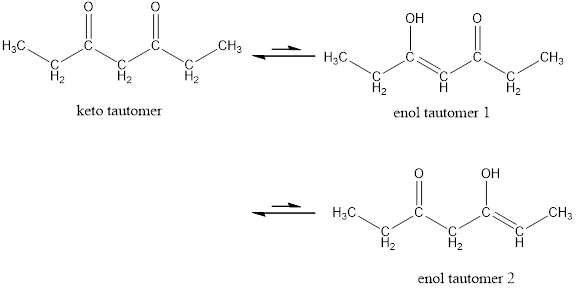
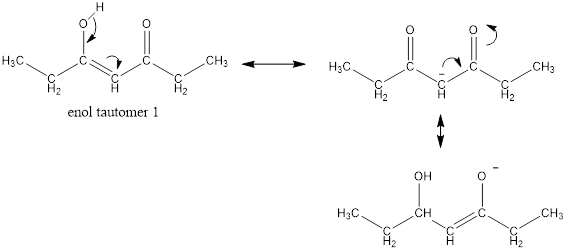
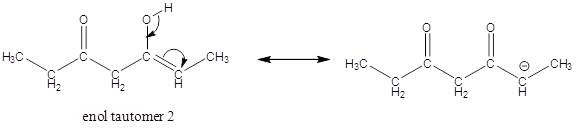
Enol tautomer 1 is more stable than enol tautomer 2.
Enol tautomer 1 can undergo delocalization and are more stable.
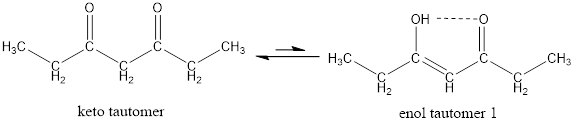
Thus enol tautomer 1 is more stable since it has more resonance structures and also possess intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
(b)
Interpretation:
The enol tautomer of the given compound has to be drawn and more stable structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Tautomerism is the ability of a molecule to exist in more than one chemical form.
Tautomers are formed by the migration of a hydrogen atom, accompanied by the switching of a single and neighboring double bond.
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.

Enol tautomer is much less stable than the keto tautomer.
Enol tautomer is more stable when enol tautomer is aromatic or when the double bonds are conjugated.
Resonance is an electron displacement effect for stabilizing a molecule through delocalization of bonding electrons in the pi orbital.
Delocalized electrons stabilize a compound. The extra stability gains from having delocalized electrons are called resonance stabilization or resonance energy.
Explanation of Solution
Given keto tautomer is,
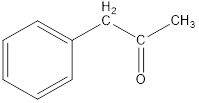
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.
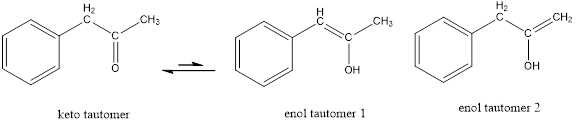
These tautomers undergo resonance and are shown below,
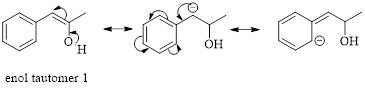
Enol tautomer 1 can undergo delocalization. Enol tautomer 1 is more stable than enol tautomer 2.
The enol tautomer 1 is more stable because there is a conjugation between the double bond and benzene ring. No such conjugation is possible in the enol tautomer 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The enol tautomer of the given compound has to be drawn and more stable structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Tautomerism is the ability of a molecule to exist in more than one chemical form.
Tautomers are formed by the migration of a hydrogen atom, accompanied by the switching of a single and neighboring double bond.
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.

Enol tautomer is much less stable than the keto tautomer.
Enol tautomer is more stable when enol tautomer is aromatic or when the double bonds are conjugated.
Explanation of Solution
Given keto tautomer is,
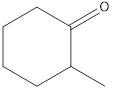
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.
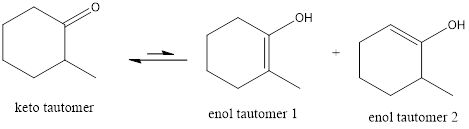

The alkene double bond formed by tautomer 1 is tetra-substituted which is stable than tautomer 2.
Hence, enol tautomer 1 is more stable.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? *see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardThe answer here says that F and K have a singlet and a doublet. The singlet and doublet are referring to the H's 1 carbon away from the carbon attached to the OH. Why don't the H's two carbons away, the ones on the cyclohexane ring, cause more peaks on the signal?arrow_forward
- Draw the Birch Reduction for this aromatic compound and include electron withdrawing groups and electron donating groups. *See attachedarrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardBlocking Group are use to put 2 large sterically repulsive group ortho. Show the correct sequence toconnect the reagent to product with the highest yield possible. * see imagearrow_forward
- Elimination-Addition: What molecule was determined to be an intermediate based on a “trapping experiment”? *please solve and see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor”. **see attachedarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
