
(a)
Interpretation:
Sulfur belongs to group of the periodic table, along with . The element has an
Sulfur has three allotropes: Rhombic, Monoclinic and amorphous.
Sulfur is a non- metal which exists in different crystal structure known as allotropes. The stable form at room temperature is called rhombic sulfur and when this is heated slowly above about it converts into monoclinic sulfur.
Only difference between the rhombic and monoclinic types is the arrangement of the molecules in space.
Concept introduction:
Phase diagram represent change in state of substance with change in pressure and temperature.
There are some common line between solid state, liquid state and gaseous state. The line are known as sublimation curve common line between solid state and gaseous state condensation curve (common region between liquid and gas) and meeting curve (common region between solid and liquid state)
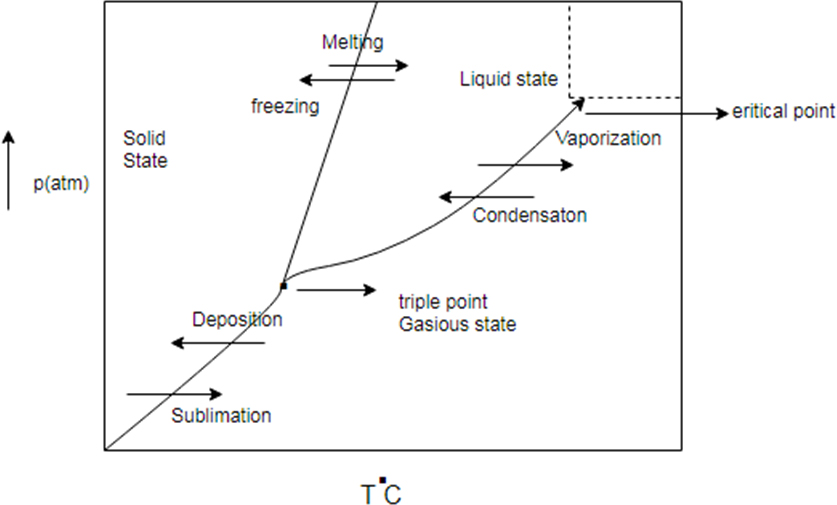
Generic phase diagram and conversion between states
To determine:
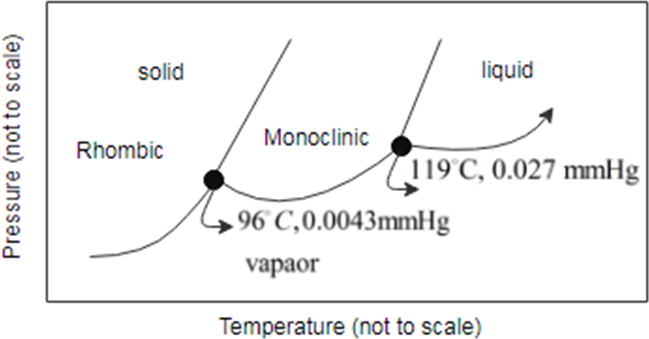
Consider the phase diagram for sulfur shown here. The rhombic and monoclinic are two solid with different structures.
a. The pressure below which solid sulfur sublimes
(b)
Interpretation:
Sulfur belongs to group of the periodic table, along with . The element has an atomic number of and atomic mass of , four oxidation states
Sulfur has three allotropes: Rhombic, Monoclinic and amorphous (no shape plastic).
Sulfur is a non- metal which exists is different crystal structure known as allotropes. The stable form at room temperature is called rhombic sulfur and when this is heated slowly above about it converts into monoclinic sulfur.
Only difference between the rhombic and monoclinic types is the arrangement of the molecules in space.
Concept Interdiction:
Phase diagram represents change in state of substance with change in pressure and temperature.
There are some common line between solid state, liquid state and gaseous state. The line are known as sublimation curve common line between solid state and gaseous state condensation curve (common region between liquid and gas) and melting curve (common region between solid and liquid state)
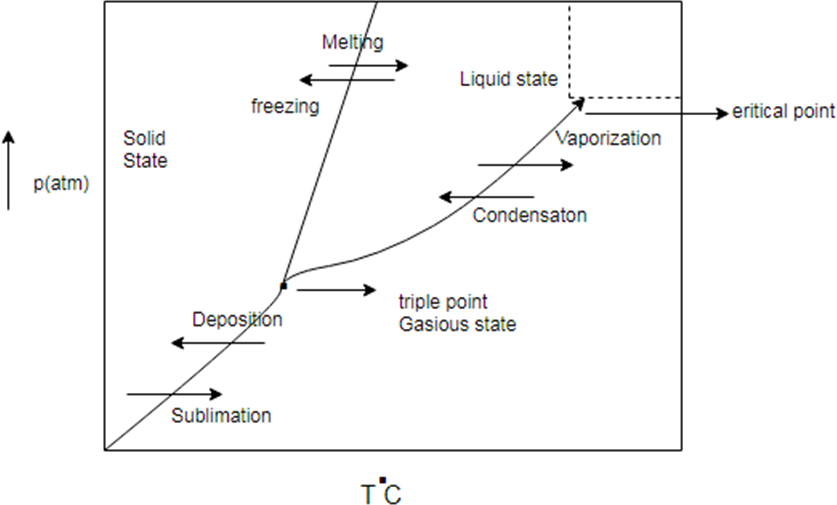
Generic phase diagram and conversion between states
To determine: between the two solid states of sulfur which is denser
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties, Books a la Carte Edition & Modified MasteringChemistry with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for Chemistry: Structure and Properties Package
- 5. A solution of sucrose is fermented in a vessel until the evolution of CO2 ceases. Then, the product solution is analyzed and found to contain, 45% ethanol; 5% acetic acid; and 15% glycerin by weight. If the original charge is 500 kg, evaluate; e. The ratio of sucrose to water in the original charge (wt/wt). f. Moles of CO2 evolved. g. Maximum possible amount of ethanol that could be formed. h. Conversion efficiency. i. Per cent excess of excess reactant. Reactions: Inversion reaction: C12H22O11 + H2O →2C6H12O6 Fermentation reaction: C6H12O6 →→2C2H5OH + 2CO2 Formation of acetic acid and glycerin: C6H12O6 + C2H5OH + H₂O→ CH3COOH + 2C3H8O3arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solution. How many carbons and hydrogens are in the structure?arrow_forward13. (11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B 2°C. +2°C. cleavage Bond A •CH3 + 26.← Cleavage 2°C. + Bond C +3°C• CH3 2C Cleavage E 2°C. 26. weakest bond Intact molecule Strongest 3°C 20. Gund Largest argest a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. C Weakest bond A Produces Most Bond Strongest Bond Strongest Gund produces least stable radicals Weakest Stable radical b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. 13°C. formed in bound C cleavage ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. • CH3 methyl radical Formed in Gund A Cleavage c.…arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





