
Concept explainers
Determine what state this substance is in at 1 atm and 298 K by referring to its phase diagram.
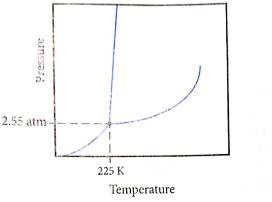
a) Solid
b) Li quid
c) Gas
d) All three states in equilibrium
Interpretation: The state of a substance at
Concept introduction: A phase diagram represents what phases exist at equilibrium and the phase transformation that one can expect on changing one of the parameters of the system
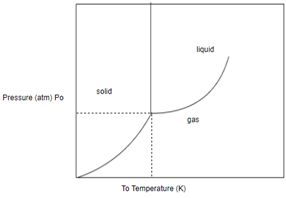
In order to determine the phase of a substance, draw a horizontal line corresponding to given pressure and a vertical line corresponding to given temperature. The point of intersection of these two horizontal and vertical lines gives the idea in which phase the given material exist.
To determine: what state this substance is at
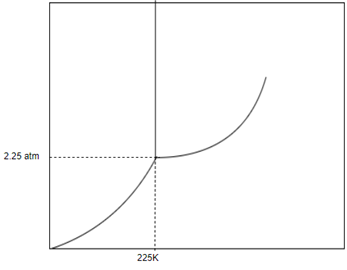
Answer to Problem 1SAQ
Solution: The phase of this substance at
Explanation of Solution
Given, Pressure
Temperature
And following phase diagram
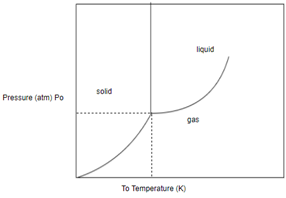
Draw horizontal and vertical line corresponding to given temperature and pressure.
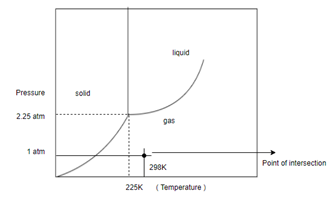
From above diagram it becomes clear that point of intersection is in gas phase so this substance at
Phase of any substance is function of both temperature and pressure.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties, Books a la Carte Edition & Modified MasteringChemistry with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for Chemistry: Structure and Properties Package
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardLet's see if you caught the essentials of the animation. What is the valence value of carbon? a) 4 b) 2 c) 8 d) 6arrow_forwardA laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forward
- A laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forwardThe number of microstates corresponding to each macrostate is given by N. The dominant macrostate or configuration of a system is the macrostate with the greatest weight W. Are both statements correct?arrow_forwardFor the single step reaction: A + B → 2C + 25 kJ If the activation energy for this reaction is 35.8 kJ, sketch an energy vs. reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction. Be sure to label the following on your diagram: each of the axes, reactant compounds and product compounds, enthalpy of reaction, activation energy of the forward reaction with the correct value, activation energy of the backwards reaction with the correct value and the transition state. In the same sketch you drew, after the addition of a homogeneous catalyst, show how it would change the graph. Label any new line "catalyst" and label any new activation energy.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





