
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
The two most important reactions of alcohols are their acid-catalyzed dehydration to give
Concept Introduction:
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 22P
True.
Explanation of Solution
Alcohols are organic compounds containing -OH group. It undergoes in the presence of acid to form an alkene. Dehydration is the removal of water from alcohol.
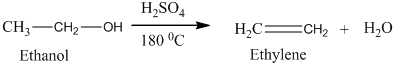
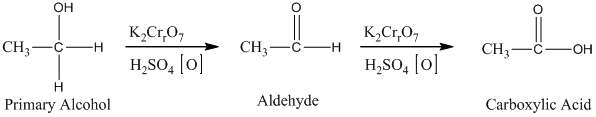
Alcohols undergo oxidation to yield aldehyde, ketone, and carboxylic acid. The primary alcohol in an acid catalyzed oxidation gives an aldehyde and further acid catalyzed oxidation gives a corresponding acid.
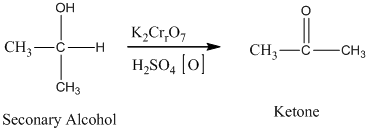
The secondary alcohol in an acid catalyzed oxidation fives a ketone.
Therefore, this statement is True.
(b)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
The acidity of alcohols is comparable to that of water.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 22P
True.
Explanation of Solution
The strength of an acid can be measured by the acid dissociation constant Ka while the pKa value is logarithmic value of the acid dissociation constant. So, the alcohol has the nearly same pKa value as of water.
Therefore, this statement is True.
(c)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
Water-insoluble alcohols and water-insoluble phenols react with string bases to give water soluble salts.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 22P
False.
Explanation of Solution
Alcohol is a water-soluble compound. It is soluble in water because of the hydrogen bonding between oxygen and hydrogen atoms of water and alcohol molecules. Phenol is also water soluble because of hydrogen bonding. Water-soluble alcohol and water-insoluble phenol react with string bases to form water-soluble salt.
Therefore, this statement is False.
(d)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
Acid catalyzed dehydration of cyclohexanol gives cyclohexene.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 22P
False.
Explanation of Solution
Acid-catalyzed dehydration of cyclohexanol gives corresponding alkene. In the presence of sulfuric acid, cyclohexanol gives cyclohexene.
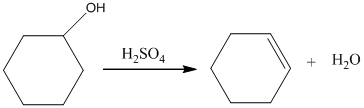
Therefore, this statement is False.
(e)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
When the acid-catalyzed dehydration of an alkene can yield isomeric alkenes, the alkene with the greater number of hydrogens in the carbons of the double bond generally predominates.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 22P
False.
Explanation of Solution
Acid-catalyzed dehydration of an alcohol gives an isomeric alkene. The isomeric alkene, which has a lower number of hydrogen atoms in the double bond, has a grater yield. Hence, when butanol undergoes an acid-catalyzed dehydration, 2-butene is the major product.
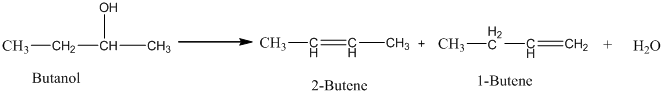
Therefore, this statement is False.
(f)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
The acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-butanol gives predominantly 1-butene.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 22P
False.
Explanation of Solution
An acid catalyzed dehydration of butanol gives predominantly 2-butene. The yield of 1-butene is approximately because in the acid-catalyzed dehydration reaction of an alcohol, the major product has the lower number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms with double bonds. Thus, 2-Butene is the major product.
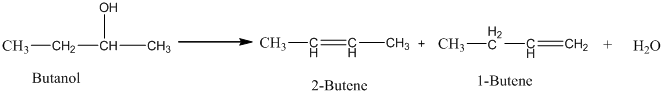
Therefore, this statement is False.
(g)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
The oxidation of a primary alcohol gives either an aldehyde or a carboxylic acid depending on experimental conditions.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 22P
True.
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation of the primary alcohols gives either aldehyde or carboxylic acid, depending on the experimental condition. For illustration, the primary alcohol in an acid catalyzed oxidation gives an aldehyde and further acid catalyzed oxidation gives a corresponding acid.
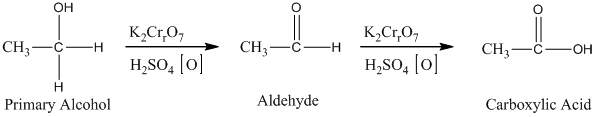
Therefore, this statement is True.
(h)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
The oxidation of a secondary alcohol gives a carboxylic acid.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 22P
False.
Explanation of Solution
The secondary alcohol in an acid-catalyzed oxidation gives ketone. The oxidation of the secondary alcohol gives ketone in the presence of potassium chromate as an oxidizing agent. It does not produce carboxylic acid because it lacks a hydrogen atom.
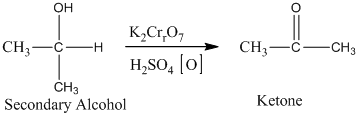
Therefore, this statement is false.
(i)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
Acetic acid, CH3 COOH, can be prepared from ethylene, CH2 =CH2, by treatment of ethylene with H2 O/H2 SO4, followed by treatment with K2 Cr2 O7 /H2 SO4.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 22P
True.
Explanation of Solution
Ethylene undergoes acid catalyzed hydration to produce ethanol. This, ethanol, in further treatment with potassium dichromate, undergoes oxidation to form acetic acid. The reaction is.
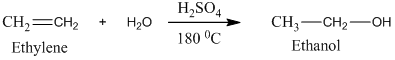
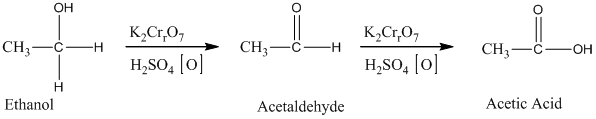
Therefore, this statement is True.
(j)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
Treatment of propene, CH3 CH=CH2, with H2 O/H2 SO4, followed by treatment with K2 Cr2 O7 /H2 SO4 gives propanoic acid.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 22P
False.
Explanation of Solution
The hydration of propene with water in the presence of sulfuric acid produces propanol. It is a secondary alcohol. Propanol undergoes oxidation in the presence of potassium chromate and produces propanone. There is no hydrogen atom present in propanone. So, it does not produce propanoic acid in oxidation.
Therefore, this statement is false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
- Predict the product of this organic reaction: IZ + HO i P+H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ :arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: 0 O ----- A + KOH ? CH3-CH2-C-O-CH2-C-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. X ⑤ èarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O CH3 + H2O + HCI A A? CH3-CH2-C-N-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forward
- What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ HO-C-CH2-CH3 0= CH3 CH3 —CH, C−NH—CH CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. €arrow_forward个 CHEM&131 9267 - $25 - Intro to Mail - Hutchison, Allison (Student x Aktiv Learnin https://app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + Na2Cr2O7 Acetone, H2SO4 Type here to search Dryng OH W Prarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: OH + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ Sarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: CH3-C-O-CH2-CH2-C-CH3 + H₂O ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. :☐ darrow_forwardDE d. Draw an arrow pushing mechanism for the following IN O CI N fo 人 P Polle DELL prt sc home end ins F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: + H₂O H* ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Predict the major organic products of the reaction below and draw them on right side of the arrow. If there will be no significant reaction, check the box below the drawing area instead. C Cl CH, OH There will be no significant reaction. + pyridine G Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? H R+ H2O Δ OH 0= CH3-CH-O-CH3 + CH3-C-OH Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. dyarrow_forwardYou are trying to determine whether the following organic reaction can be done in a single synthesis step. If so, add any missing reagents or conditions in the drawing area below. If it isn't possible to do this reaction in a single synthesis step, check the box below the drawing area instead. Note for advanced students: if you have a choice of reagents to add, you should choose the least reactive and most economical reagents possible. Cl It isn't possible to do this reaction in a single synthesis step. + T OHarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

