
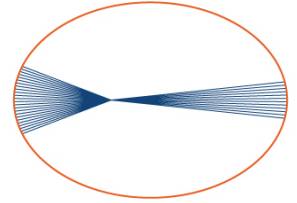
Kepler's first law states that the planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus. The closest point of a planetary orbit to the Sun is called the perihelion (for Earth, it currently occurs around January 3) and the farthest paint is called the aphelion (for Earth. it currently occurs around July 4). Kepler's second law states that planets sweep out equal areas of their elliptical orbits in equal times. Thus, the two arcs indicated in the following figure are swept out in equal times. At what lime of year is Earth moving fastest in its orbit? When is it moving slowest?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Calculus Volume 2
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Graphical Approach To College Algebra
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- Business discussarrow_forwardSpam filters are built on principles similar to those used in logistic regression. We fit a probability that each message is spam or not spam. We have several variables for each email. Here are a few: to_multiple=1 if there are multiple recipients, winner=1 if the word 'winner' appears in the subject line, format=1 if the email is poorly formatted, re_subj=1 if "re" appears in the subject line. A logistic model was fit to a dataset with the following output: Estimate SE Z Pr(>|Z|) (Intercept) -0.8161 0.086 -9.4895 0 to_multiple -2.5651 0.3052 -8.4047 0 winner 1.5801 0.3156 5.0067 0 format -0.1528 0.1136 -1.3451 0.1786 re_subj -2.8401 0.363 -7.824 0 (a) Write down the model using the coefficients from the model fit.log_odds(spam) = -0.8161 + -2.5651 + to_multiple + 1.5801 winner + -0.1528 format + -2.8401 re_subj(b) Suppose we have an observation where to_multiple=0, winner=1, format=0, and re_subj=0. What is the predicted probability that this message is spam?…arrow_forwardConsider an event X comprised of three outcomes whose probabilities are 9/18, 1/18,and 6/18. Compute the probability of the complement of the event. Question content area bottom Part 1 A.1/2 B.2/18 C.16/18 D.16/3arrow_forward
- I need help making sure that I explain this part accutartly.arrow_forwardPlease help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction decompostion on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forwardJohn and Mike were offered mints. What is the probability that at least John or Mike would respond favorably? (Hint: Use the classical definition.) Question content area bottom Part 1 A.1/2 B.3/4 C.1/8 D.3/8arrow_forward
- Please help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forwardEvaluate F³ - dr where ♬ = (4z, -4y, x), and C' is given by (t) = (sin(t), t, cos(t)), 0≤t≤ñ .arrow_forwardThe details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. What is the simple moving average root mean square error? Round to two decimal places. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Question content area bottom Part 1 A. 207.13 B. 20.12 C. 14.39 D. 0.21arrow_forward
- 5:00 PM Sat May 3 deltamath.com DeltaMath Given: ABBC and D is the midpoint of AC. Prove: ABD ≈ ACBD. ← Back to Home Deltamath Regents Review Week 3 Due: May 9 at 8:00 PM Grade: 97% Step Statement AB ≈ BC Reason 1 Given D is the midpoint of AC 2 BD BD 3 ADDC Calculating Volume (Mixed) Volume of Oblique Solids Volume, Density, and Unit 5 4 AABC is an isosceles triangle ZAZC Conversions (Level 1) Triangle Congruence Criteria try ZAD =/ DC Basic Triangle Proofs (Congruence Only - No CPCTC) Triangle Proofs (Reasons Only) Calculator Aseret Martinez Domi... Log Out Reflexive Property A midpoint divides a segment into two congruent segments The triangle has two congruent sides In a triangle, angles opposite of congruent sides are congruent An angle bisector divides an angle into two congruent angles B * A Ꭰ Note: the segment AC is a straight segment. 86%arrow_forwardEvaluate the following expression and show your work to support your calculations. a). 6! b). 4! 3!0! 7! c). 5!2! d). 5!2! e). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forwardLANDMARKS Stonehenge is a British landmark made of huge stones arranged in a circular pattern that reflects the movements of Earth and the moon. The diagram shows that the angle formed by the north/south axis and the line aligned from the station stone to the northmost moonrise position measures 23.5°. a. Find measure of arc BC. b. Is arc ABC semicircle? Explain. c. If the circle measures about 100 feet across, approximately how far would you walk around the circle from point B to point sarsen circle B station stone trilithons horseshoe 71° 23.5° farthest north moonrise Sarrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,  Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





