Concept explainers
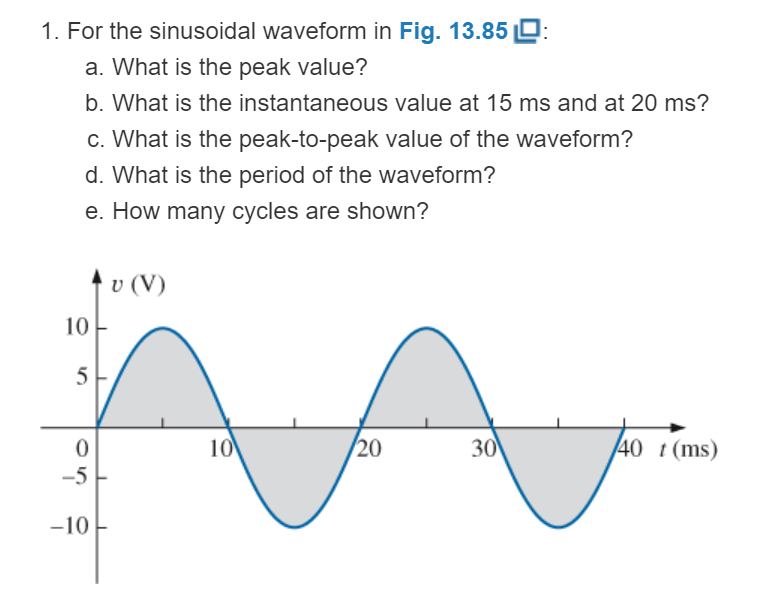
For the sinusoidal waveform in Fig. 13.85:
a. What is the peak value?
b. What is the instantaneous value at 15 ms and at 20 ms?
c. What is the peak-to-peak value of the waveform?
d. What is the period of the waveform?
e. How many cycles are shown?
(a)
Peak value of sinusoidal signal.
Answer to Problem 1P
The peak value is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Peak value is the maximum value of an alternating quantity over one cycle duration.
So peak value is
Conclusion:
Thus, peak value is
(b)
Instantaneous value at
Answer to Problem 1P
The Instantaneous value at
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Instantaneous value is the valueof an alternating quantity at a particular value of time in a cycle.
So Instantaneous value at
Conclusion:
Thus, Instantaneous value at
(c)
Peak-to-peak value of sinusoidal signal.
Answer to Problem 1P
The peak-to-peak value of sinusoidal signal is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Peak to peak value is the difference in the value of positive peak and negative peak of a waveform.
Write the expression for peak to peak value.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, Peak-to-peak value of sinusoidal signal is
(d)
Value of period of the waveform.
Answer to Problem 1P
The value of period of the wave form is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Period is the time taken by a waveform to complete its one cycle.
Waveform completes its one cycle in
Conclusion:
Thus, value of period of the wave form is
(e)
Value of number of cycles.
Answer to Problem 1P
The value of total number of cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
There is
Conclusion:
Thus, value of total number of cycle is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Introductory Circuit Analysis
- Q3. a) The frequency response method enables the study of the steady-state response of a system G(s). What type of inputs are used for frequency response? If the system is linear and stable, how does the output differ from the input? Compare the main characteristics of two types frequency response plots. b) Consider the control system shown in Figure Q3. Controller E(s) R(s) Desired output C(s) Plant G(s) Y(s) Actual output 3(s + 3) C(s) = k G(s) = = s(s - 1)(s + 10) Figure Q3. Closed-loop system. (i) Considering definitions in the study of bounded-input bounded-output stability, is G(s) stable? Classify the poles and zeros of G(s). (ii) G(s) defined in Figure Q3 is a system completely characterised by its transfer function. Explain why this is the case. (iii) Obtain the closed-loop transfer function P(s) = Y(s)/R(s) of the system. (iv) Based on your result for the previous question [Question 3b)-(iii)], use the Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion to determine suitable values of gain K…arrow_forwardPlease, I want the solution in two ways: Method 1 (without the Smith chart): Method 2 (using the Smith chart): A short circuit stub of length 0.04λ is used to match a 50 Ω lossless line to a load ZL = RL + j30 Ω. Use Smith chart to find:(a) The distance between the stub and the load.(b) The value of RL .arrow_forwardTHE FIRST PAGE OF THIS QUESTION SECTION BELOW IS THE FIRST IMAGE UPLOADED, WHICH SHOWS A digital synchronous sequential circuit and then comes the questions below:1B) Suppose the flip-flops are 74F74 devices and the AND gates are 74F08 devices. Let maxtpd,D=9ns, maxtsu,D=3ns, and maxtpd,AND=6ns. What is the maximum clock frequency at which the circuit can operate reliably? 2) Compare serial transmission and parallel transmission and discuss their advantages and disadvantages. 3) Explain briefly how the slave can protect itself from being overwhelmed by the master in I2 4) A hypothetical logic family has the following specifications. VOH=4.6V VIH=4.0V VOL=0.5V VIL=1.0V IOH=-1mA IIH=50μA IOL=8mA IIL=-0.6mA (4a) What are the noise margins? (4b) What is the fan-out capability?…arrow_forward
- THE FIRST PAGE OF THIS QUESTION SECTION BELOW IS THE FIRST IMAGE UPLOADED, WHICH SHOWS A digital synchronous sequential circuit and then comes the questions below:1B) Suppose the flip-flops are 74F74 devices and the AND gates are 74F08 devices. Let maxtpd,D=9ns, maxtsu,D=3ns, and maxtpd,AND=6ns. What is the maximum clock frequency at which the circuit can operate reliably? 2) Compare serial transmission and parallel transmission and discuss their advantages and disadvantages. 3) Explain briefly how the slave can protect itself from being overwhelmed by the master in I2 4) A hypothetical logic family has the following specifications. VOH=4.6V VIH=4.0V VOL=0.5V VIL=1.0V IOH=-1mA IIH=50μA IOL=8mA IIL=-0.6mA (4a) What are the noise margins? (4b) What is the fan-out capability?…arrow_forwardI need help on this question a) Find y(t) =yh(t) +yp(t) in time domainIs the system over-damped, under-damped, or critical?arrow_forwardGiven f(t)=a sin(ßt) a = 10 & ß = 23 Find the Laplace Transform using the definition F(s) = ∫f(t)e-stdtarrow_forward
- = Calculate Avf, Zif, and Zof for the amplifier circuit,Assume he = 50, hie 1.1k2, and identical transistors? 150kQ Vs 5002 HH +25v 10k +6 · 47ΚΩ 47k2 4.7k0} 33 ΚΩ 4.7ΚΩ 10k w 4.7kQ HH Voarrow_forwardFor the four-pole filter in Fig. (2), determine the capacitance values required to produce a critical frequency of 2680 Hz if all the resistors in the RC low-pass circuits are 1.8 K. Also select values for the feedback resistors to get a Butterworth response. Note: For a Butterworth response, the damping factor must be 1.848 for the first stage and 0.765 for the second stage. (2) Re Res ww " = 11arrow_forwardFor the circuit shown in Fig. 2.20, the transistors are identica' and have the following parameters: hje=50, hie = 1.1K, hr =0, and hoe = 0. Calculate Auf, Rif and Rof. Ans: 45.4; 112 KN; 129N. HH 150k 47k R 25 V 10k 47k 4.7k 5μF 33k 4.7k 50µF 50µF 4.7k 4.7k R₁ Roj R1000arrow_forward
- A triangular wave is applied to the input of Fig. (3). Determine what the output should be and sketch its waveform in relation to the input. 10μs. 0 5μs 15 μs 0.001 μF R₁ w 2.2karrow_forwardA three-phase, 480-V, 60-Hz, 6-pole, Y-connected induction motor has its speed controlled by slip power. The circuit parameters are given: Rs=0.06 ohms, Rr=0.05 ohms, Xs=0.2 ohms, Xr=0.3 ohms and Xm=6 ohms. The turn ratio of the rotor to stator winding is n=0.8. The no-load losses of the motor are equal to 150 W. The rotor and stator cupper losses are equal to 249.21 W. The slip power losses are estimated to 8000W. The load torque is 173.61 N.m. at 700 rpm. The efficiency is equal to: Select one: a. 71.5% b. None of these c. 81.5% d. 91.5% Question 2 Consider a 3-phase, 460-V, 100-hp, 0.88 power factor lagging, 4-pole, 1728 RPM, 60 Hz, Y-connected induction motor. The operating slip is equal to: Select one: a. 0.05 b. 0.01 c. 0.04 d. None of these Question 3 A 3 phase, 10 kW, 1750 rpm, Y- connected 460 V, 60 Hz, 4 poles, Y-connected induction motor has the following parameters: Rs = 0.5 Ohms, Rr = 0.3 Ohms, Xs = 0.9 Ohms, Xr = 0.9 Ohms, Xm = 25 Ohms. The no load…arrow_forwardelectric plants do for hand writingarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





