
Concept explainers
Dwayne Cole, owner of a Florida firm that manufactures display cabinets, develops an 8-month aggregate plan. Demand and capacity (in units) are
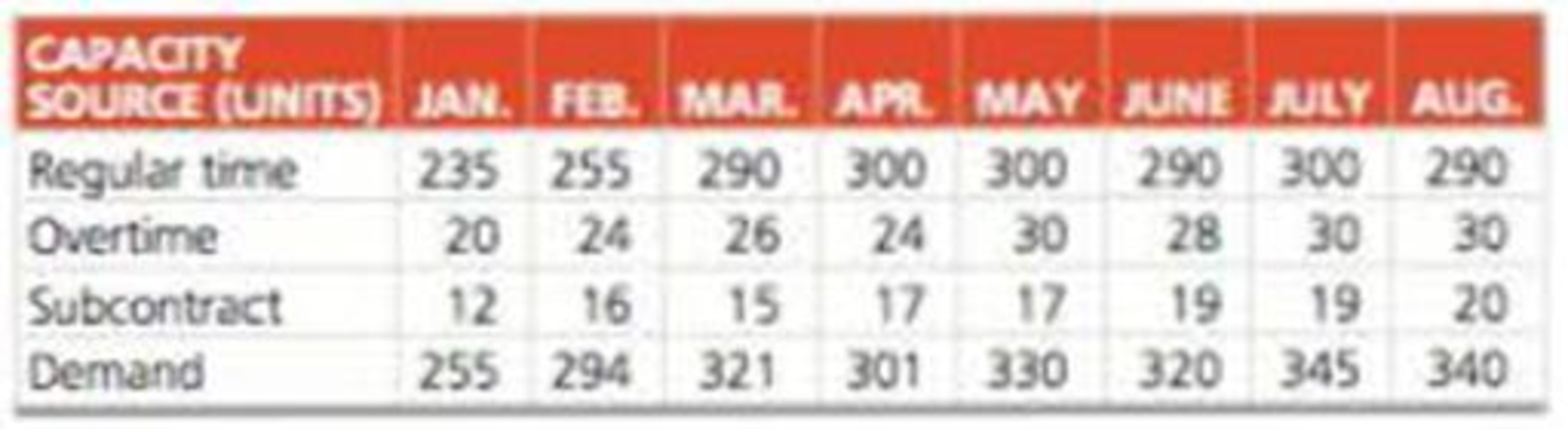
The cost of producing each unit is $1,000 on regular time, $1,300 on overtime, and $1,800 on a subcontract. Inventory carrying cost is $200 per unit per month. There is no beginning or ending inventory in stock, and no backorders are permitted from period to period.
Let the production (workforce) vary by using regular time first, then overtime, and then subcontracting.
a) Set up a production plan that minimizes cost by producing exactly what the demand is each month. This plan allows no backorders or inventory. What is this plan’s cost?
b) Through better planning, regular time production can be set at exactly the same amount, 275 units, per month. If demand cannot be met there is no cost assigned to shortages and they will not be filled. Does this alter the solution?
c) If overtime costs per unit rise from $1,300 to $1,400, will your answer to (a) change? What if overtime costs then fall to $1,200?
a)
To determine: The total cost of the plan.
Introduction: The aggregate plan is the output of sales and operations planning. The major concern of aggregate planning is the production time and quantity for the intermediate future. Aggregate planning would encompass a time prospect of approximately 3 to 18 months.
Answer to Problem 19P
The total cost of the plan is $2,608,300.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Regular time cost per unit is given as $1,000, overtime cost is $1,300, and subcontract cost is $1,800 per unit. The capacity and demand are given as follows:
| Month | Demand | Regular time capacity | Overtime capacity | Subcontract capacity |
| Initial | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| January | 255 | 235 | 20 | 12 |
| February | 294 | 255 | 24 | 16 |
| March | 321 | 290 | 26 | 15 |
| April | 301 | 300 | 24 | 17 |
| May | 330 | 300 | 30 | 17 |
| June | 320 | 290 | 28 | 19 |
| July | 345 | 300 | 30 | 19 |
| August | 340 | 290 | 30 | 20 |
Calculate the total cost:
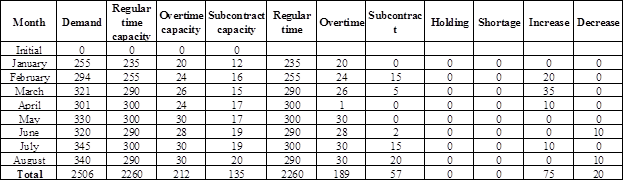
Table 1
Working note:
Demand, regular time capacity, overtime capacity, and subcontract capacity are given.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of January:
It is given that the demand for the month of January is 255 units. 235 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 235). Remaining 20 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 20). Hence, regular time unit is 235 units and overtime unit is 20 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of February:
It is given that the demand for the month of February is 294 units. 255 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 255). From the remaining 39 units, 24 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 24) and 15 units would be produced using subcontract (as the subcontract capacity is 16). Hence, regular time unit is 255 units, overtime unit is 24 units, and subcontract unit is 15 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of March:
It is given that the demand for the month of March is 321 units. 290 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 290). From the remaining 31 units, 26 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 26) and 5 units would be produced using subcontract (as the subcontract capacity is 15). Hence, regular time unit is 290 units, overtime unit is 26 units, and subcontract unit is 5 units.
Note: The procedure continues for all months.
Increase or decrease for the month of January:
There would be no increase or decrease for the month of January as there is no period compare.
Increase or decrease for the month of February:
Production in the month of January is 235 units and production in the month of February is 255 units. There is an increase of 20 units. Hence, there would be 20 units increase in February.
Increase or decrease for the month of March:
Production in the month of February is 255 units and production in the month of March is 290 units. There is an increase of 35 units. Hence, there would be 35 units increase in March.
Increase or decrease for the month of April:
Production in the month of March is 290 units and production in the month of April is 300 units. There is an increase of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units increase in April.
Increase or decrease for the month of May:
Production in the month of April is 300 units and production in the month of May is 300 units. As there is no change in the production units, there would not be any increase or decrease.
Increase or decrease for the month of June:
Production in the month of May is 300 units and production in the month of June is 290 units. There is a decrease of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units decrease in June.
Increase or decrease for the month of July:
Production in the month of June is 290 units and production in the month of July is 300 units. There is an increase of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units increase in July.
Increase or decrease for the month of August:
Production in the month of July is 300 units and production in the month of August is 290 units. There is a decrease of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units decrease in August.
Summary of the table:
| Type | Units | Cost |
| Regular time | 2,260 | $2,260,000 |
| Overtime | 189 | $245,700 |
| Subcontract | 57 | $102,600 |
| Holding | 0 | 0 |
| Shortage | 0 | 0 |
| Increase | 75 | 0 |
| Decrease | 20 | 0 |
| $2,608,300 |
Table 2
Working note:
Total units of regular time, overtime, subcontract, shortage, holding, increase, and decrease were calculated in theTable 1.
Calculate the regular time cost:
Regular time cost is calculated by multiplying regular time unit and the given regular time cost per unit. Hence, the regular time cost is $2,260,000.
Calculate the overtime cost:
Overtime cost is calculated by multiplying overtime unit and the given overtime cost per unit. Hence, the overtime cost is $245,700.
Calculate the subcontract cost:
Subcontract cost is calculated by multiplying subcontract unit and the given subcontract cost per unit. Hence, the subcontract cost is $102,600.
Calculate the increase and decrease cost:
As there is no increase or decrease cost per unit, it would remain 0.
Calculate the total cost:
Total cost is calculated by adding regular time cost, overtime cost, subcontract cost, holding cost, shortage cost, increase cost, and decrease cost.
Hence, the total cost of the plan is $2,608,300.
b)
To determine: The total cost of the plan.
Introduction: The aggregate plan is the output of sales and operations planning. The major concern of aggregate planning is the production time and quantity for the intermediate future. Aggregate planning would encompass a time prospect of approximately 3 to 18 months.
Answer to Problem 19P
The total cost of the plan is $2,585,100.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Regular time cost per unit is given as $1,000, overtime cost is $1,300, and subcontract cost is $1,800 per unit. The capacity and demand are given as follows:
| Month | Demand | Regular time capacity | Overtime capacity | Subcontract capacity |
| Initial | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| January | 255 | 275 | 20 | 12 |
| February | 294 | 275 | 24 | 16 |
| March | 321 | 275 | 26 | 15 |
| April | 301 | 275 | 24 | 17 |
| May | 330 | 275 | 30 | 17 |
| June | 320 | 275 | 28 | 19 |
| July | 345 | 275 | 30 | 19 |
| August | 340 | 275 | 30 | 20 |
Calculate the total cost:
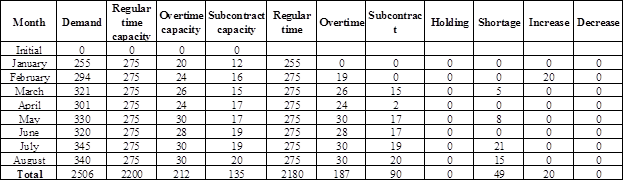
Table 3
Working note:
Demand, regular time capacity, overtime capacity, and subcontract capacity are given.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of January:
It is given that the demand for the month of January is 255 units. Whole 255 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 275). Hence, regular time unit is 255 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of February:
It is given that the demand for the month of February is 294 units. 275 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 275). Remaining 19 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 24). Hence, regular time unit is 275 units and overtime unit is 19 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of March:
It is given that the demand for the month of March is 321 units. 275 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 290). From the remaining 46 units, 26 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 26) and 15 units would be produced using subcontract (as the subcontract capacity is 15). Hence, regular time unit is 275 units, overtime unit is 26 units, and subcontract unit is 15 units. Remaining 5 units is a shortage.
Note: The procedure continues for all months.
Increase or decrease for the month of January:
There would be no increase or decrease for the month of January as there is no period compare.
Increase or decrease for the month of February:
Production in the month of January is 255 units and production in the month of February is 275 units. There is an increase of 20 units. Hence, there would be 20 units increase in February.
Increase or decrease from the month of March to August:
As the production for regular time remains the same, there would be no increase or decrease from the month of March to August.
Summary of the table:
| Type | Units | Cost |
| Regular time | 2,180 | $2,180,000 |
| Overtime | 187 | $243,100 |
| Subcontract | 90 | $162,000 |
| Holding | 0 | 0 |
| Shortage | 49 | 0 |
| Increase | 20 | 0 |
| Decrease | 0 | |
| $2,585,100 |
Table 4
Working note:
Total units of regular time, overtime, subcontract, shortage, holding, increase, and decrease were calculated in theTable 3.
Calculate the regular time cost:
Regular time cost is calculated by multiplying regular time unit and the given regular time cost per unit. Hence, the regular time cost is $2,180,000.
Calculate the overtime cost:
Overtime cost is calculated by multiplying overtime unit and the given overtime cost per unit. Hence, the overtime cost is $243,100.
Calculate the subcontract cost:
Subcontract cost is calculated by multiplying subcontract unit and the given subcontract cost per unit. Hence, the subcontract cost is $162,000.
Calculate the increase and decrease cost:
As there is no increase or decrease cost per unit, it would remain 0.
Calculate the total cost:
Total cost is calculated by adding regular time cost, overtime cost, subcontract cost, holding cost, shortage cost, increase cost, and decrease cost.
Hence, the total cost of the plan is $2,585,100.
c)
To determine: The total cost of the plan, if the overtime increased to $1,400.
Introduction: The aggregate plan is the output of sales and operations planning. The major concern of aggregate planning is the production time and quantity for the intermediate future. Aggregate planning would encompass a time prospect of approximately 3 to 18 months.
Answer to Problem 19P
The total cost of the plan is $2,627,200.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Regular time cost per unit is given as $1,000, overtime cost is $1,400, and subcontract cost is $1,800 per unit. The capacity and demand are given as follows:
| Month | Demand | Regular time capacity | Overtime capacity | Subcontract capacity |
| Initial | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| January | 255 | 235 | 20 | 12 |
| February | 294 | 255 | 24 | 16 |
| March | 321 | 290 | 26 | 15 |
| April | 301 | 300 | 24 | 17 |
| May | 330 | 300 | 30 | 17 |
| June | 320 | 290 | 28 | 19 |
| July | 345 | 300 | 30 | 19 |
| August | 340 | 290 | 30 | 20 |
Calculate the total cost:
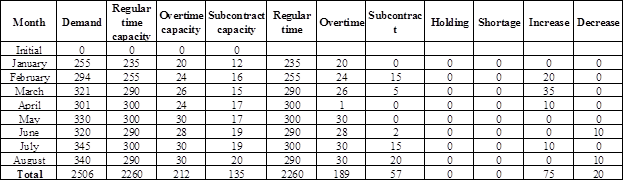
Table 5
Working note:
Demand, regular time capacity, overtime capacity, and subcontract capacity are given.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of January:
It is given that the demand for the month of January is 255 units. 235 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 235). Remaining 20 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 20). Hence, regular time unit is 235 units and overtime unit is 20 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of February:
It is given that the demand for the month of February is 294 units. 255 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 255). From the remaining 39 units, 24 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 24) and 15 units would be produced using subcontract (as the subcontract capacity is 16). Hence, regular time unit is 255 units, overtime unit is 24 units, and subcontract unit is 15 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of March:
It is given that the demand for the month of March is 321 units. 290 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 290). From the remaining 31 units, 26 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 26) and 5 units would be produced using subcontract (as the subcontract capacity is 15). Hence, regular time unit is 290 units, overtime unit is 26 units, and subcontract unit is 5 units.
Note: The procedure continues for all months.
Increase or decrease for the month of January:
There would be no increase or decrease for the month of January as there is no period compare.
Increase or decrease for the month of February:
Production in the month of January is 235 units and production in the month of February is 255 units. There is an increase of 20 units. Hence, there would be 20 units increase in February.
Increase or decrease for the month of March:
Production in the month of February is 255 units and production in the month of March is 290 units. There is an increase of 35 units. Hence, there would be 35 units increase in March.
Increase or decrease for the month of April:
Production in the month of March is 290 units and production in the month of April is 300 units. There is an increase of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units increase in April.
Increase or decrease for the month of May:
Production in the month of April is 300 units and production in the month of May is 300 units. As there is no change in the production units, there would not be any increase or decrease.
Increase or decrease for the month of June:
Production in the month of May is 300 units and production in the month of June is 290 units. There is a decrease of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units decrease in June.
Increase or decrease for the month of July:
Production in the month of June is 290 units and production in the month of July is 300 units. There is an increase of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units increase in July.
Increase or decrease for the month of August:
Production in the month of July is 300 units and production in the month of August is 290 units. There is a decrease of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units decrease in August.
Calculate the total cost if the overtime cost per unit increased to $1,400:
| Type | Units | Cost |
| Regular time | 2,260 | $2,260,000 |
| Overtime | 189 | $264,600 |
| Subcontract | 57 | $102,600 |
| Holding | 0 | 0 |
| Shortage | 0 | 0 |
| Increase | 75 | 0 |
| Decrease | 20 | 0 |
| $2,627,200 |
Table 6
Working note:
Total units of regular time, overtime, subcontract, shortage, holding, increase, and decrease were calculated in theTable 5.
Calculate the regular time cost:
Regular time cost is calculated by multiplying regular time unit and the given regular time cost per unit. Hence, the regular time cost is $2,260,000.
Calculate the overtime cost:
Overtime cost is calculated by multiplying overtime unit and the given overtime cost per unit. Hence, the overtime cost is $264,600.
Calculate the subcontract cost:
Subcontract cost is calculated by multiplying subcontract unit and the given subcontract cost per unit. Hence, the subcontract cost is $102,600.
Calculate the increase and decrease cost:
As there is no increase or decrease cost per unit, it would remain 0.
Calculate the total cost:
Total cost is calculated by adding regular time cost, overtime cost, subcontract cost, holding cost, shortage cost, increase cost, and decrease cost.
Hence, the total cost of the plan is $2,627,200.
Calculate the total cost if the overtime cost per unit increased to $1,200:
| Type | Units | Cost |
| Regular time | 2,260 | $2,260,000 |
| Overtime | 189 | $226,800 |
| Subcontract | 57 | $102,600 |
| Holding | 0 | 0 |
| Shortage | 0 | 0 |
| Increase | 75 | 0 |
| Decrease | 20 | 0 |
| $2,589,400 |
Table 7
Working note:
Total units of regular time, overtime, subcontract, shortage, holding, increase, and decrease were calculated in theTable 6.
Calculate the regular time cost:
Regular time cost is calculated by multiplying regular time unit and the given regular time cost per unit. Hence, the regular time cost is $2,260,000.
Calculate the overtime cost:
Overtime cost is calculated by multiplying overtime unit and the given overtime cost per unit. Hence, the overtime cost is $264,600.
Calculate the subcontract cost:
Subcontract cost is calculated by multiplying subcontract unit and the given subcontract cost per unit. Hence, the subcontract cost is $102,600.
Calculate the increase and decrease cost:
As there is no increase or decrease cost per unit, it would remain 0.
Calculate the total cost:
Total cost is calculated by adding regular time cost, overtime cost, subcontract cost, holding cost, shortage cost, increase cost, and decrease cost.
Hence, the total cost of the plan is $2,589,400.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- Elaborate on the need for and the benefits of an effective supply chain management (SCM) system in the context of a globalized and networked economy. In your answer, explain how organizations like Dell and Hewlett-Packard leverage supply chain networks to maintain competitiveness, and analyse the impact of globalization, technological advancements, and business environment changes on supply chain structures. Additionally, evaluate the key components of SCM, including distribution network configuration, inventory management, and cash-flow management, and discuss how these components contribute to creating an effective and integrated supply chain. (15) 3.2. Critically evaluate the requirements for effective inventory management within an organization. In your answer, discuss the importance of inventory accounting systems, the role of cost information (holding, ordering, and shortage costs), and the significance of classification systems like ABC analysis. Additionally, analyse how…arrow_forwardAssess the role of EDI in ensuring supply chain security and data integrity. How does EDI contribute to reducing vulnerabilities in supply chain operations, and what best practices should organizations adopt to maintain a secure and reliable EDI system? (10) 1.3. Examine how the adoption of modern EDI systems influences the strategic decision-making process in supply chain management. How does EDI provide supply chain managers with actionable insights, and what are the implications of these insights for long-term supply chain planning? (10) 1.4. Evaluate the potential challenges and risks associated with the modernization of EDI systems in supply chain management. How can organizations effectively manage these challenges to ensure successful EDI implementation and ongoing optimization? (10)arrow_forwardAnalyse the impact of integrating EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) with API (Application Programming Interface) on supply chain management, particularly focusing on how this integration enhances information flow and operational efficiency. Consider the challenges that might arise from this integration in terms of managing legacy systems alongside modern applications.arrow_forward
- 1) View the video What is Operations Management (14.01 minutes, Ctrl+Click on the link); what are your key takeaways (tie to one or more of the topics discussed in Chapters 1 and/or 2) after watching this video. (https://www.viddler.com/embed/d01189e1) Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs. 2) View the video What McDonald’s is serving up at its new CosMc’s Chain (3.42 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), and answer the following questions: (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k7ojpUzE8q4) i) From a strategic perspective, why do you think McDonald’s is opting for this new chain rather than trying to launch the new menu in its existing restaurants? ii) What factors do you think in McDonald’s external and internal environments are driving its decision to open the CosMc’s locations? iii) How do you think this format will improve McDonald’s profit margin as compared to its regular fast-food restaurants? Note: As a…arrow_forwardSince the end of World War II, globalization has steadily increased with rapid expansion around the turn of the 21st century. What are some of the forces driving globalization and international business? What are some of the challenges of engaging in international business compared to doing business in your home country?arrow_forwardPS.53 Brother I.D. Ricks is a faculty member at BYU-Idaho whose grandchildren live in Oklahoma and California. He and his wife would like to visit their grandchildren at least once a year in these states. They currently have one vehicle with well over 100,000 miles on it, so they want to buy a newer vehicle with fewer miles and that gets better gas mileage. They are considering two options: (1) a new subcompact car that would cost $18,750 to purchase or (2) a used sedan that would cost $12,750.They anticipate that the new subcompact would get 37 miles per gallon (combined highway and around town driving) while the sedan would get 26 miles per gallon. Based on their road tripping history they expect to drive 13,000 miles per year. For the purposes of their analysis they are assuming that gas will cost $2.93 per gallon.Question: How many miles would the Ricks need to drive before the cost of these two options would be the same? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) (Hint:…arrow_forward
- Choose one major approach to job design, and then discuss how best that approach can be utilized in either your current or previous employer, including a discussion of its strengths and weaknesses.arrow_forwardThe results of your four plans will provide an indicative EOQ value. State this value and discuss in a precise manner, why it is not the exact, true value. Additional calculations in the form of plans E, F etc. may also assist your explanation of the EOQ and can be includedarrow_forwardi). Complete the table assuming a Level production plan. ii) Comment on your results and explain whether at this stage, you consider a Level plan is a suitable approach for this particular business. Your comment should include reference to a calculated ‘fill rate’.arrow_forward
- In the following sawtooth inventory profile diagram, two inventory plans with different order quantities (Q) and different frequencies of delivery are shown; order quantity for Plan A = 200 units and Plan B = 50 units. i). Total demand (D) is 350 units, the holding cost per unit (Ch) is equal to (£0.8) and the ordering cost per order (Co) is (£12.5). Calculate the total costs for each plan and state which one is more preferable along with the reason why. ii). There is a stark difference in the composition of the total costs of Plans A and B. Explain this difference and why it occurs. Use the breakdown of costs for each plan to help illustrate your answer.arrow_forwardi). Complete the table for a Chase production plan. ii). Explain whether a Level or Chase plan is more suitable for the demand pattern experienced by this particular business, which incidentally relies on highly skilled workers in the production process. Assume a starting workforce of 7 and that fractional workers are permissible. You should support your answer with numerical data derived from Table 3. In comparing the costs, state any other assumptions made.arrow_forwardi). Complete for a Chase production plan. ii). Explain whether a Level or Chase plan is more suitable for the demand pattern experienced by this particular business, which incidentally relies on highly skilled workers in the production process. Assume a starting workforce of 7 and that fractional workers are permissible.arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing




