
Concept explainers
Obtain the Thevenin equivalent circuit for the circuit in Fig. 13.83 at terminals a-b.
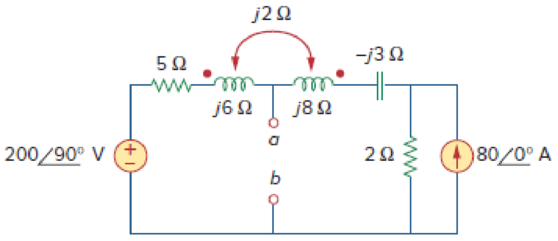
Calculate the Thevenin equivalent to the circuit at terminals a-b.
Answer to Problem 14P
TheThevenin equivalent circuit parameters are
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 13.83 in the textbook for the circuit with coupled coils.
Consider that the value of the source voltage.
Calculation:
Calculate the Thevenin voltage.
Modify the Figure 13.83 by converting the current source
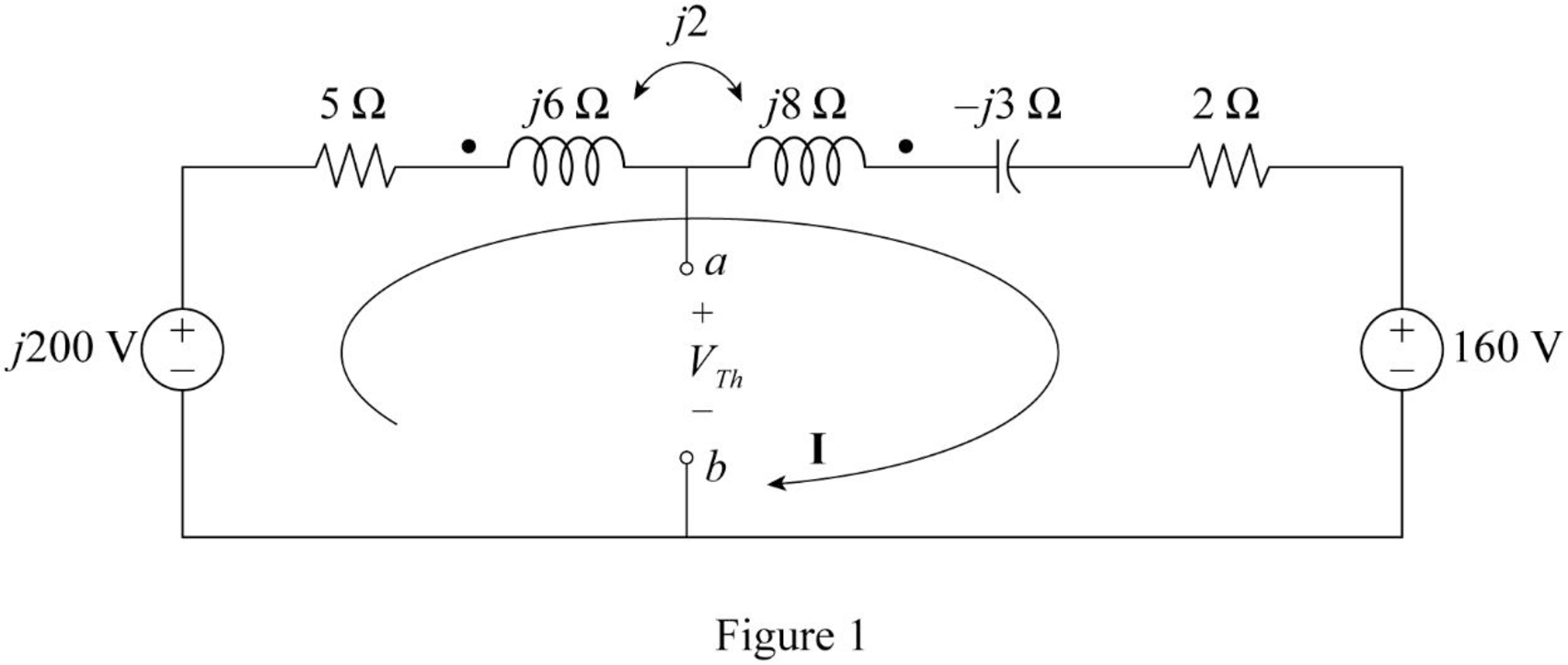
Consider that the two coils are connected series aiding.
Substitute
Apply Kirchhoff's voltage law to the loop 1 contains current
Substitute
Re-arrange the equation.
From Figure 1, consider the following expression using Kirchhoff's voltage law.
Re-arrange the Equation.
Substitute Equation (1) in (2).
Simplify the equation as follows.
To obtain Thevenin impedance
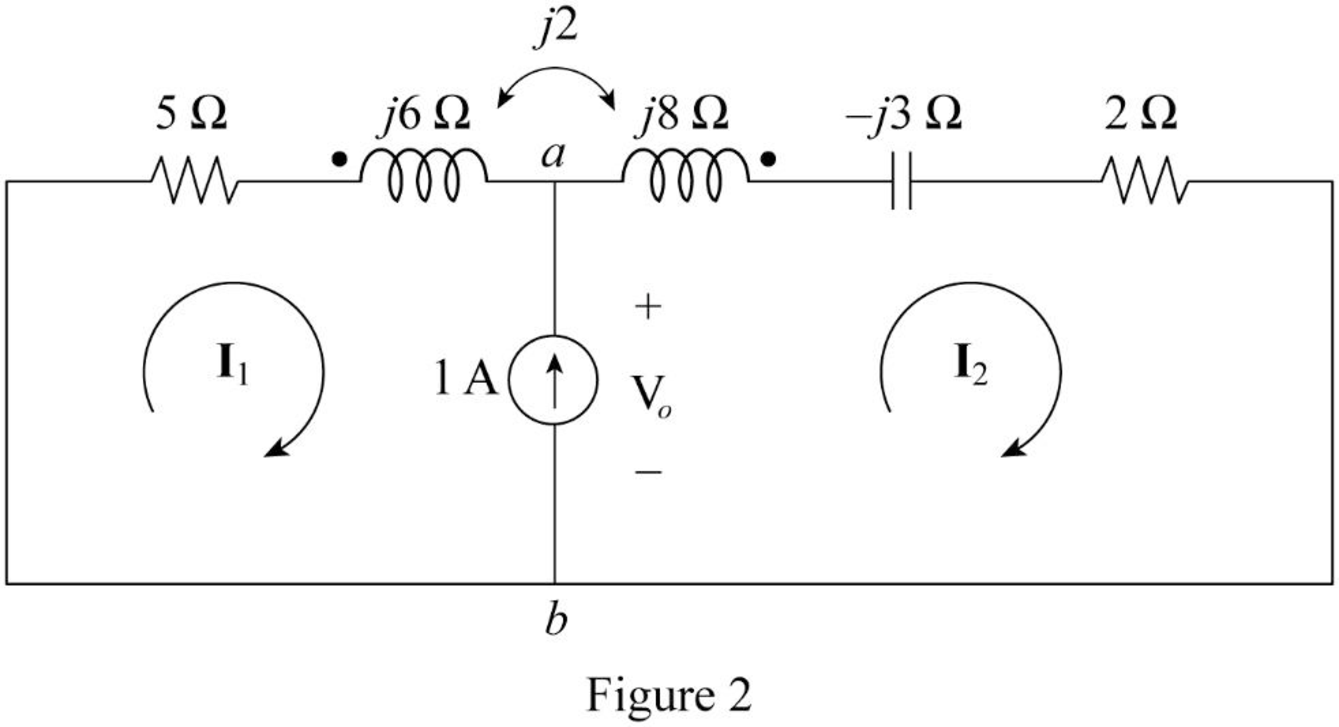
In Figure 2, consider that the loops 1 and 2 contain the currents
Write the Kirchhoff's voltage law expression to Figure 2 using super mesh analysis.
From Figure 2, write the current expression.
Substitute
Apply Kirchhoff's voltage law to the loop 1 contains current
Re-arrange the equation.
Substitute Equation (4) in (5).
Write the expression for Thevenin’s equivalent impedance.
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the Thevenin equivalent circuit parameters are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EE 98: Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits - With Connect Access
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
- P5. Although all fuses possess a thermal element that melts resulting in an open circuit, describe the difference between an "expulsion" and a "current limiting" fuse.arrow_forwardExpert only, don't use Artificial intelligence or screen shot it solvingarrow_forwardSolve this. find the initial conditions ic(0-) and vc(0-) the switch opens at t=0 so it's closed at t=0- dont copy the response from previous because it's wrong. please solve in great detail explaining everything step by step. now the way i thought about it is Getting millman voltage (1/3)-2 / (1/3)+(1/2) and it's the same as Vc as both are nodal voltages but i wasn't sure if correct. because i didnt take into consideration all voltages (Vc here) even though it's the same so i'm quite confused. please explain to me if i'm correct and if not tell me why and where my thinking was flawed. thank youarrow_forward
- 3. Consider the RL circuit with a constant voltage source shown in the diagram below. The values of the resistor, inductor, and input voltage are R = 100, L = 100 mH, and Vo = 12V, respectively. Vo - Ti(t) R w When the switch closes at time t = 0, the current begins to flow as a function of time. It follows from Kirchoff's voltage law that the current is described by the differential equation di(t) L dt + Ri(t) = Vo⋅arrow_forward4. Consider the RL circuit with a sinusoid voltage source shown in the diagram below. The values of the resistor, inductor, input voltage amplitude and frequency are R = 5, L = 50mH, and Vo = 10 V, respectively. The input voltage frequency w is variable. Assume that the circuit has reached steady state. Voejwt + ↑i(t) R سيد The input voltage can be described using the complex sinusoid function V(t) = Voejwt The current is given by a sinusoid with same the frequency was the input voltage, but a different magnitude and different phase. The physical voltage and current are obtained by taking the real part. In complex form, the current is given by i(t) Vo ejwt R1+jw/ The differential equation that describes the current follows from Kirchoff's voltage law, and is given by di(t) L + Ri(t) = Voejwt dtarrow_forward2. (4 marks) Use the real and imaginary parts of ĉejut, where ñ = a + jb = e³, to show that: c cos(wt) = acos(wt) – bsin(wt), csin(wt) = a sin(wt) + bcos(wt). Describe the relations between a, b, c, and o.arrow_forward
- Compute the thevenin equivalent between the two terminals a-b zeq and veq show all your steps and explain clearly what you did.arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardconpute the thevenin equivalent between the terminals a and b Veq and Zeq note that the voltage source has 5e^j0 V the other values if not clear are -8j 8 20 and 5ohmsarrow_forward-calculate theoretical voltage and current values in Figure 1.3 and record them in Table 1.1. Calculate-all- voltage and current values as peak-to-peak. Table 1.1: Calculated Values of RC-Circuit ZTotale in (p-to-p)¤ VR-(p-to-p)¤ Vc-(p-to-p)¤ R(2) X-(2) mag (mA) angled mag (V) angled mag-(V) angle Freq. (Hz) X (N)- ρα ρα 500x 4000x ρα ρα ρα ρα ρα ρα ρα ραarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





