
General, Organic, and Biochemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781260506198
Author: Denniston, Katherine
Publisher: MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 13, Problem 13.73QP
(a)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The product of the oxidation of pentanal has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The oxidation of
The general equation for the oxidation of an aldehyde to a
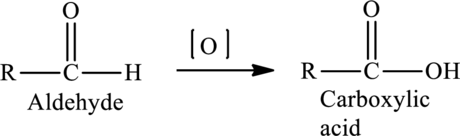
(b)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The product of the oxidation of hexanal has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The product of the oxidation of heptanal has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The product of the oxidation of octanal has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
* Hint: Think back to Chem 1 solubility rules.
Follow Up Questions for Part B
12. What impact do the following disturbances to a system at equilibrium have on k, the rate constant
for the forward reaction? Explain. (4 pts)
a) Changing the concentration of a reactant or product. (2 pts)
b) Changing the temperature of an exothermic reaction. (2 pts)
of
Draw TWO general chemical equation to prepare Symmetrical and non-Symmetrical ethers
Draw 1 chemical reaction of an ether
Please help me with the following questions for chemistry.
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biochemistry
Ch. 13.1 - Which member in each of the following pairs will...Ch. 13.1 - Which member in each of the following pairs will...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.3QCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.4QCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.1PPCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.2PPCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.3PPCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.4PPCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.5QCh. 13.2 - Write the condensed formula for each of the...
Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.7QCh. 13.2 - Write the condensed formula for each of the...Ch. 13.3 - Draw the structure of the aldehyde synthesized...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.10QCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.5PPCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.6PPCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.7PPCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.8PPCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.11QCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.12QCh. 13.4 - Identify each of the following structures as a...Ch. 13.4 - Identify each of the following structures as a...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.9PPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.15QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.16QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.17QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.18QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.19QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.20QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.21QPCh. 13 - Why do hydrocarbons have lower boiling points than...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.23QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.24QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.25QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.26QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.27QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.28QPCh. 13 - Draw each of the following using condensed...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.30QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.31QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.32QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.33QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.34QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.35QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.36QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.37QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.38QPCh. 13 - Give the IUPAC name for each of the following...Ch. 13 - Give the IUPAC name for each of the following...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.41QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.42QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.43QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.44QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.45QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.46QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.47QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.48QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.49QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.50QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.51QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.52QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.53QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.54QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.55QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.56QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.57QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.58QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.59QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.60QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.61QPCh. 13 - An unknown has been determined to be one of the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.63QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.64QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.65QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.66QPCh. 13 - Which of the following compounds would be expected...Ch. 13 - Write an equation representing the reaction of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.69QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.70QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.71QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.72QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.73QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.74QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.75QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.76QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.77QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.78QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.79QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.80QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.81QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.82QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.83QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.84QPCh. 13 - Prob. 1MCPCh. 13 - Prob. 2MCPCh. 13 - Prob. 3MCPCh. 13 - Prob. 4MCPCh. 13 - Prob. 6MCPCh. 13 - Prob. 7MCPCh. 13 - Prob. 8MCPCh. 13 - Design a synthesis for each of the following...Ch. 13 - Prob. 10MCPCh. 13 - Prob. 12MCP
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- + C8H16O2 (Fatty acid) + 11 02 → 8 CO2 a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? H2o CO₂ c. Which reactant is the electron donor? Futty acid d. Which reactant is the electron acceptor? e. Which of the product is now reduced? f. Which of the products is now oxidized? 02 #20 102 8 H₂O g. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? 2 h. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forward→ Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + 1FAD + 1ADP 2CO2 + CoA + 3NADH + 1FADH2 + 1ATP a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? c. Which reactant is the electron donor? d. Which reactants are the electron acceptors? e. Which of the products are now reduced? f. Which product is now oxidized? g. Which process was used to produce the ATP? h. Where was the energy initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? i. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? j. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. OCH 3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) Br (Choose one) Explanation Check NO2 (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Aarrow_forward
- For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Cl O donating O withdrawing ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects O Explanation Check O electron-rich O electron-deficient similar to benzene X © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects NH2 ○ donating NO2 Explanation Check withdrawing no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating O withdrawing O no resonance effects O donating O withdrawing O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Ono resonance effects O electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene olo 18 Ar 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation Check Х (Choose one) OH (Choose one) OCH3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- Assign R or S to all the chiral centers in each compound drawn below porat bg 9 Br Brarrow_forwarddescrive the energy levels of an atom and howan electron moces between themarrow_forwardRank each set of substituents using the Cahn-Ingold-Perlog sequence rules (priority) by numbering the highest priority substituent 1.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY