
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds cyclohexane and
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The cyclohexane gives only a single peak for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the
Explanation of Solution
The compounds cyclohexane and
The structure of
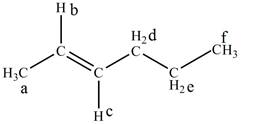
Figure 1
The structure of the cyclohexane along with its all equivalent protons peak data is shown below.
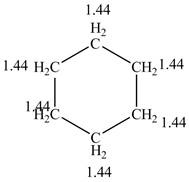
Figure 2
The cyclohexane gives only a single peak for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the
(b)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The structure of
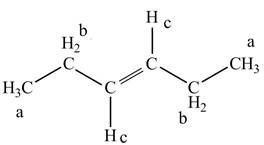
Figure 3
The structure of the
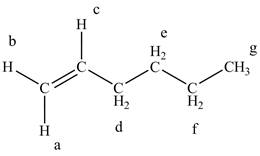
Figure 4
The
(c)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The two compounds
The structure of
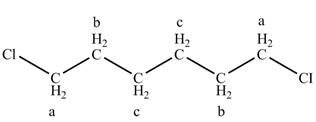
Figure 5
The structure of the
There is one signal at high chemical value at
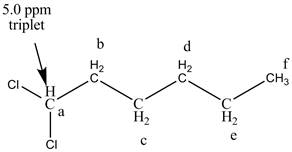
Figure 6
The structure of the
There are two signals at high chemical shift value for the compound. One at
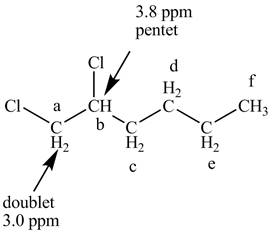
Figure 7
The
(d)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The only signal that is different in both the compounds is for the single hydrogen of methane group attached directly to the oxygen. Also, the splitting of the protons methyl groups into doublet occurs for isopropyl group while in
The structure of
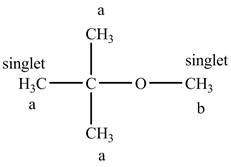
Figure 8
The structure of the isopropyl methyl ether is given below along with three sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
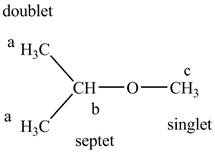
Figure 9
The
(e)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Both compounds are distinguished on the basis of the number of NMR signals.
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The structure of
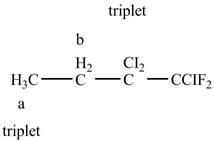
Figure 10
The structure of the
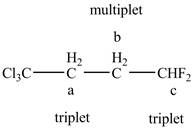
Figure 11
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM +SG +SAPLING >IP<
- Draw the structure of serine at pH 6.8. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : d كarrow_forwardTake a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH H H H OH OH OH CH2OH H H H H OH H H OH H OH Is this a reducing sugar? yes α β ロ→ロ no ☑ yes Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. O no 0+0 If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. ☐arrow_forwardAnswer the questions in the table below about this molecule: H₂N-CH₂ -C—NH–CH–C—NH–CH—COO- CH3 CH CH3 What kind of molecule is this? 0= CH2 C If you said the molecule is a peptide, write a description of it using 3-letter codes separated ☐ by dashes. polysaccharide peptide amino acid phospolipid none of the above Хarrow_forward
- Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: CH₂OH C=O HO H H -OH H OH CH₂OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ Х S '☐arrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution 22.30 Predict all possible products formed from the following nucleophilic substitution reactions. (a) (b) 9 1. NaOH 2. HCI, H₂O CI NH₁(!) +NaNH, -33°C 1. NaOH 2. HCl, H₂Oarrow_forwardSyntheses 22.35 Show how to convert toluene to these compounds. (a) -CH,Br (b) Br- -CH3 22.36 Show how to prepare each compound from 1-phenyl-1-propanone. 1-Phenyl-1-propanone ہتی. Br. (b) Br (racemic) 22.37 Show how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid. 22.38 Show reagents and conditions to bring about the following conversions. (a) 9 NH2 8 CO₂H NH2 CO₂Et (d) NO2 NH2 S NH₂ NO2 CHS CHarrow_forward
- ive the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all rant stereochemistry. [10 only] A. B. NaN3 1. LiAlH4, ether Br 2. H₂O CH3 HNO3 H₂/Pt H₂SO ethanol C. 0 0 CH3CC1 NaOH NHCCH AICI H₂O . NH₂ CH3CH2 N CH2CH3 + HCI CH₂CH 3 1. LIAIH, THE 2. H₂Oarrow_forwardCalculate the stoichiometric amount of CaCl2 needed to convert all of the CuSO4 into CuCl2.arrow_forwardH CH تنی Cl 1. NaCN, DMF 2. LIAIH4, ether H₂O pyridine N NH₂ 5 CH H 1 HNO, H₂SO 2. Nal NH2 Br Br HNO₂ CuCl H₂SO HCI CH3 H3C NN HSO KCN CuCN 1. HNO₂, H₂SO O₂N NH2 2. OH ཀ་ལས། །ས་ཅན་ :i་དེ་མ་མ་སེ་ NH₂ CH3 1. HNO₂, H₂SO4 2. H3PO₂ 1 HNO2, H2SO4 2. Nalarrow_forward
- ive the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all rant stereochemistry. [10 only] A. B. NaN3 1. LiAlH4, ether Br 2. H₂O CH3 HNO3 H₂/Pt H₂SO ethanol C. 0 0 CH3CC1 NaOH NHCCH AICI H₂O . NH₂ CH3CH2 N CH2CH3 + HCI CH₂CH 3 1. LIAIH, THE 2. H₂Oarrow_forwardIf a pharmacy chain sold 65 million 500-mg tablets of aspirin, how many US tons of aspirin does this represent? Report your answer to 2 significant figures.arrow_forwardHere are the options: reducing a monosaccharide a non reducing disaccharide amylopectin cellulose 1,4' beta- glycosidearrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

