
Concept explainers
The equilibrium constant for the reaction
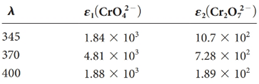
Four solutions were preparedby dissolving 4.00 × 10-4, 3.00 × 10-4, 2.00 × 10-4,and 1.00 × 10-4 moles of K2 Cr2 O7 in water and diluting to 1.00 L with a pH 5.60 buffer. Derive theoretical absorbance values (1.00-cm cells) for each solution and plot the data for (a) 345 nm, (b) 370 nm, and (c) 400 nm.
(a)
Interpretation:
The theoretical absorbance value for 345 nm should be derived and the data should be plotted.
Concept introduction:
The relationship between absorbance and concentration of absorbance is linear. If the incident light
In the case of no absorbing sample, all the light gets passed and the value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equilibrium constant is
The given reaction is
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction is
The formula to determine pH is:
Therefore
For the given reaction the expression for the equilibrium constant can be written as
The equilibrium concentration of dichromate is
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the second solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the third solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the fourth solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below:
Now take the values in excel and plot to get the graph:
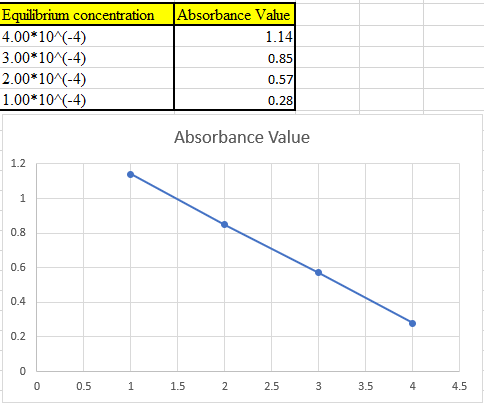
(b)
Interpretation:
The theoretical absorbance value for 370 nm should be derived and the data should be plotted.
Concept introduction:
The relationship between absorbance and concentration of absorbance is linear. If the incident light
In the case of no absorbing sample, all the light gets passed and the value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equilibrium constant is
The given reaction is
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction is
The formula to determine pH is:
Therefore
For the given reaction the expression for the equilibrium constant can be written as
The equilibrium concentration of dichromate is
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the second solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the third solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the fourth solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
Now take the values in excel and plot to get the graph:
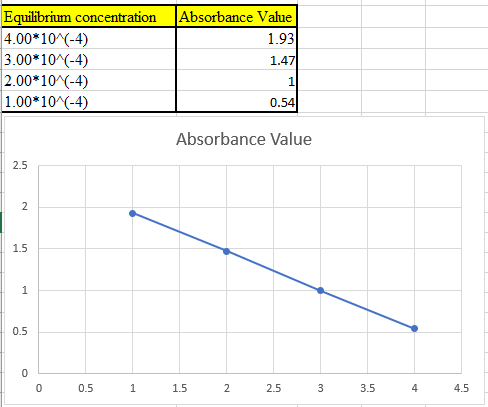
(c)
Interpretation:
The theoretical absorbance value for 400 nm should be derived and the data should be plotted.
Concept introduction:
The relationship between absorbance and concentration of absorbance is linear. If the incident light
In the case of no absorbing sample, all the light gets passed and the value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equilibrium constant is
The given reaction is
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction is
The formula to determine pH is:
Therefore
For the given reaction the expression for the equilibrium constant can be written as
The equilibrium concentration of dichromate is
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the second solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the third solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the fourth solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
Theoretical absorbance value of first solution can be calculated as below
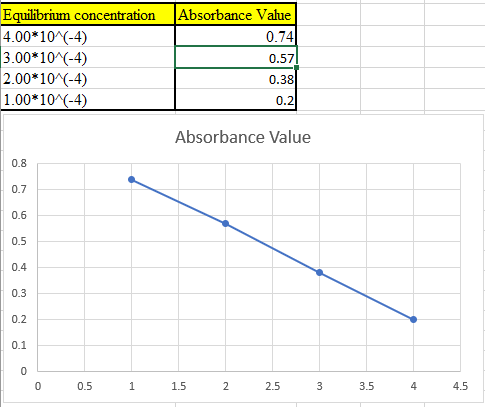
Now take the values in excel and plot to get the graph:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
PRINCIPLES OF INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS
- Indicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Galactose with hydroxylamine.arrow_forward
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





