
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The molar mass of the compound is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The freezing point is the temperature at which both the solid and liquid phases coexist in equilibrium. It is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the substance in the liquid state becomes equal to the vapor pressure in a solid state.
The formula to calculate the change in freezing point is as follows:
ΔTf=ikfm (1)
Here,
ΔTf is the change in freezing point.
i is van’t Hoff factor.
kf is the freezing point depression constant.
m is the molality of the solution.
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.128P
89.9 g/mol is the molar mass of the compound.
Explanation of Solution
The formula to calculate the change in freezing point is as follows:
ΔTf=Tf(solvent)−Tf(solution) (2)
Substitute 0°C for Tf(solvent) and −0.201°C for Tf(solution) in equation (2).
ΔTf=0°C−(−0.201°C)=0.201°C
The solute is a nonvolatile non-electrolyte so its van’t Hoff factor is 1.
Rearrange equation (1) to calculate the molarity of the solution as follows:
m=ΔTfikf (3)
Substitute 1 for i, 0.201°C for ΔTf, 1.86°C/m for kb in equation (3).
m=0.201°C(1)(1.86°C/m)=0.1080645 m
The density of the solution is calculated as follows:
Density of solution(ρ)=Mass (M)of solutionVolume (V)of solution (4)
Rearrange equation (4) to calculate the mass of the solution as follows:
Mass of solution=(Density of solution)(Volume of solution) (5)
Substitute 25 mL for the volume of solution and 1 g/mL for the density of the solution in equation (5) to calculate the mass of water.
Mass of water=(25 mL)(1 g1 mL)(1 kg103 g)=0.0250 kg
The formula to calculate the molality of the solution is as follows:
Molality=amount (mol) of solute mass (kg) of solvent (6)
Rearrange equation (6) to calculate the moles of solute as follows:
Amount of solute=(Molality)(mass of solvent) (7)
Substitute 0.1080645 m for the molality and 0.0250 kg for the mass of solvent in equation (7) to calculate the amount of solute.
Amount of solute=(0.1080645 m)(0.0250 kg)=0.0027016 mol
The formula to calculate the number of moles is as follows:
Number of moles=Given massMolar mass (8)
Rearrange equation (8) to calculate the molar mass as follows:
Molar mass=Given massNumber of moles (9)
Substitute 0.243 g for the given mass and 0.0027016 mol for the number of moles in equation (9).
Molar mass=0.243 g0.0027016 mol=89.946698 g/mol≈89.9 g/mol.
(b)
Interpretation:
The empirical and the molecular formula of the compound are to be determined.
Concept introduction:
An empirical formula gives the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element present in a molecule. The molecular formula tells the exact number of atoms of each element present in a molecule.
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.128P
The empirical and molecular formula of the compound is C2H5O and C4H10O2.
Explanation of Solution
Consider the mass of the compound to be 100 g. The mass of carbon is 53.31 g, the mass of hydrogen is 11.18 g.
The formula to calculate the mass of the compound is as follows:
Mass of compound=Mass of C+Mass of H+Mass of O (10)
Rearrange equation (10) to calculate the mass of oxygen as follows:
Mass of O=Mass of compound−(Mass of C+Mass of H) (11)
Substitute 100 g for the mass of the compound, 53.31 g for the mass of carbon and 11.18 g for the mass of hydrogen in equation (11).
Mass of O=100 g−(53.31 g+11.18 g)=35.51 g
The formula to calculate the moles of the compound is as follows:
Moles of compound=Given massMolar mass (12)
Substitute 53.31 g for the given mass and 12.01 g/mol for the molar mass in equation (12) to calculate the moles of carbon.
Moles of C=(53.31 g)(1 mol12.01 g)=4.43880 mol
Substitute 11.18 g for the given mass and 1.008 g/mol for the molar mass in equation (12) to calculate the moles of hydrogen.
Moles of H=(11.18 g)(1 mol1.008 g)=11.09127 mol
Substitute 35.51 g for the given mass and 16 g/mol for the molar mass in equation (12) to calculate the moles of oxygen.
Moles of O=(35.51 g)(1 mol16 g)=2.219375 mol
Write the amount of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as subscripts of their symbols to obtain a preliminary formula as follows:
C4.43880H11.09127O2.219375
The smallest subscript is 2.219375. Therefore, divide each subscript by 2.219375 as follows:
C4.438802.219375H11.091272.219375O2.2193752.219375→C2H5O
The subscripts are in the whole number. Hence, the empirical formula of the compound is C2H5O.
The expression to calculate the empirical formula mass of C2H5O is as follows:
Empirical formula mass of C2H5O=(2)(M of C)+(5)(M of H)+(1)(M of O) (13)
Substitute 12.01 g/mol for M of C, 1.008 g/mol for M of H, and 16.00 g/mol for M of O in equation (13) as follows:
Empirical formula mass of C2H5O=(2)(12.01 g/mol)+(5)(1.008 g/mol)+(1)(16.00 g/mol)=45.06 g/mol.
The molar mass of the compound is 89.9 g/mol that is double its empirical mass. So the molecular formula of the compound is C4H10O2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structures for the compound that forms hydrogen bonds and one that does not form hydrogen bonds are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is basically a simplified representation of the structure of any molecule or atom. Lewis structure shows the bonding between the atoms and the lone pairs of electrons as dot.
The steps to draw the Lewis structure of any molecule are as follows:
1. Write the letter
2. Count the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. In case of charged molecules subtract the positive charge from the total number of valence electrons and add the negative charge to the total number of valence electrons.
3. Assign two electrons between two atoms and join them via a single bond. Place the remaining valence electrons as lone pairs such that octet of each element is achieved. Use multiple bonds to complete the octet.
(c)
Answer to Problem 13.128P
The Lewis structure of the compound that forms hydrogen bonds is as follows:
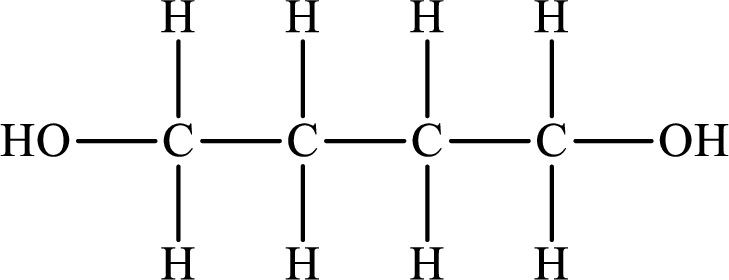
The Lewis structure of the compound that does not form hydrogen bonds is as follows:
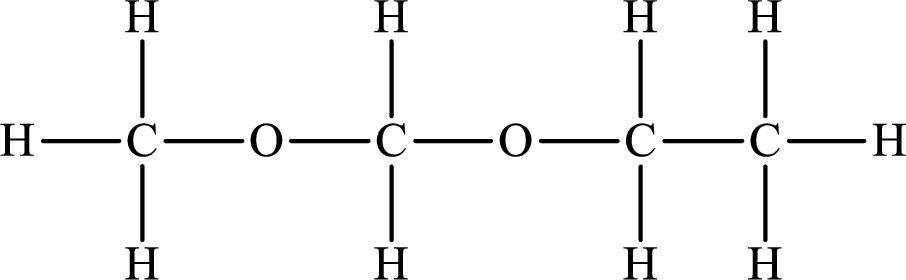
Explanation of Solution
The compound will form hydrogen bonds with the electronegative element is present at the end positions. But no hydrogen bonding occurs when the electronegative element is placed in between the other elements.
So the Lewis structure of the compound that forms hydrogen bonds is as follows:
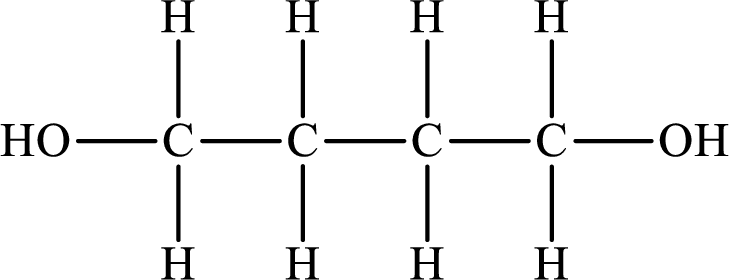
The Lewis structure of the compound that does not form hydrogen bonds is as follows:
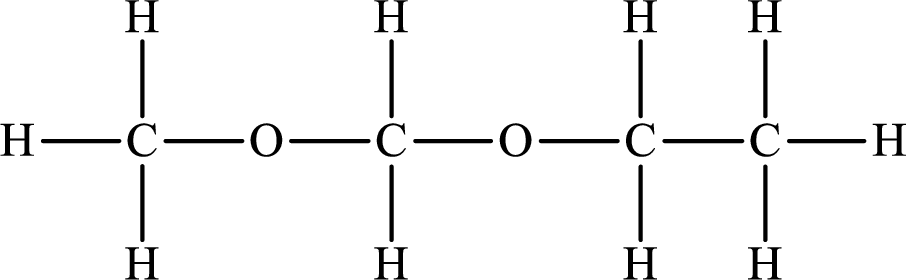
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
CHEMISTRY:MOLECULAR NATURE...-ALEKS 360
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





