
To label: The different types of muscle fibers given in Figure 13.1.
Introduction: Muscles are composed of a group of muscle fibers. Fibers of skeletal muscles are classified into three types based on the speed of contraction and the mode of ATP production. They are slow oxidative (SO), fast oxidative (FO) and fast glycolytic (FG).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
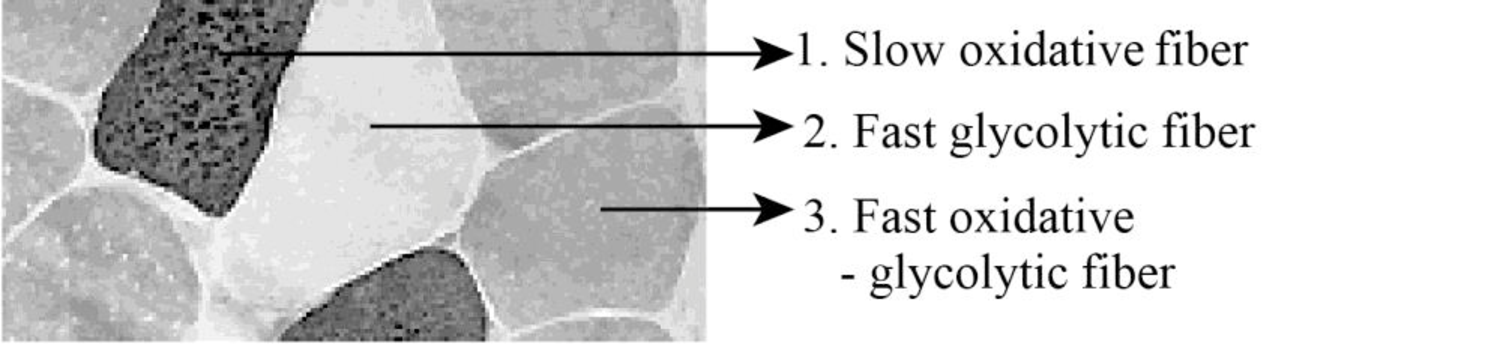
Fig1: The different types of muscle fibers: slow oxidative, fast glycolytic, and fast oxidative glycolytic fibers
Explanation of Solution
The SO fibers contract gradually as well as use aerobic
1. Slow oxidative fibers: The diameter of these fibers is small than other types of fibers. High content of myoglobin is present. Numerous mitochondria and blood capillaries are present in this group. These fibers appear red in color.
2. Fast glycolytic fibers: These fibers are large in size and so they possess the largest diameter. These fibers contain relatively low levels of myoglobin. These fibers possess less number of mitochondria and blood capillaries. They appear in pale white color.
3. Fast oxidative-glycolytic fiber: The diameter of these fibers is greater than slow fibers and lesser than the fast glycolytic fibers. These fibers contain a large amount of myoglobin content. Numerous mitochondria and blood capillaries are present in this group. They appear in pink or red color.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion with WileyPLUS Blackboard Card Set
- series of two-point crosses were carried out among six loci (a, b, c, d, e and f), producing the following recombination frequencies. According to the data below, the genes can be placed into how many different linkage groups? Loci a and b Percent Recombination 50 a and c 14 a and d 10 a and e 50 a and f 50 b and c 50 b and d 50 b and e 35 b and f 20 c and d 5 c and e 50 c and f 50 d and e 50 d and f 50 18 e and f Selected Answer: n6 Draw genetic maps for the linkage groups for the data in question #5. Please use the format given below to indicate the genetic distances. Z e.g. Linkage group 1=P____5 mu__Q____12 mu R 38 mu 5 Linkage group 2-X_____3 mu__Y_4 mu sanightarrow_forwardWhat settings would being able to isolate individual bacteria colonies from a mixed bacterial culture be useful?arrow_forwardCan I get a handwritten answer please. I'm having a hard time understanding this process. Thanksarrow_forward
- Biology How many grams of sucrose would you add to 100mL of water to make a 100 mL of 5% (w/v) sucrosesolution?arrow_forwardWhich marker does this DNA 5ʹ AATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGC 3ʹ show?arrow_forwardThe Z value of LOD for two genes is 4, what does it mean for linkage and inheritance?arrow_forward
- Biology How will you make a 50-ul reaction mixture with 2uM primer DNA using 10 uM primer DNA stocksolution and water?arrow_forwardBiology You’re going to make 1% (w/v) agarose gel in 0.5XTBE buffer 100 ml. How much agarose are you goingto add to 100 ml of buffer? The volume of agaroseis negligible.arrow_forwardBiology How will you make a 50-ul reaction mixture with0.2 mM dNTP using 2-mM dNTP stock solution andwater?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





