
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The reagent that has to be used to convert 1-pentyne to pentane has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:

Hydrogenation reaction is one of the reactions that alkynes undergo. Addition of hydrogen is the hydrogenation reaction. This can be accomplished by using hydrogen molecule and metal catalyst. Hydrogenation reaction is also known as reduction reaction.
When an alkyne undergoes hydrogenation reaction with hydrogen and catalyst such as platinum, the final product obtained will be
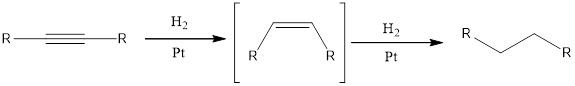
Under the above conditions, the alkene cannot be isolated. This is because the alkene is more reactive than the alkyne towards hydrogenation.
If the alkene has to be obtained from alkyne means, then a partially deactivated catalyst like Lindlar’s catalyst or sodium in liquid ammonia can be used. Partially deactivated catalyst is known as poisoned catalyst. When the alkyne is reduced using Lindlar’s catalyst, the alkene product obtained will be having cis configuration. If the alkyne is reduced using sodium in liquid ammonia means the alkene obtained will be having trans configuration.
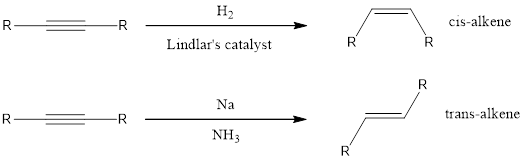
(b)
Interpretation:
The reagent that has to be used to convert 1-pentyne to 2-hexyne has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Alkynes are the compounds that contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms. The carbon atom present in the triple bond is

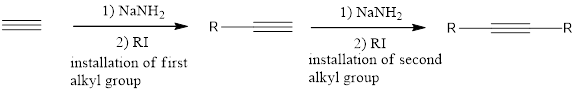
The terminal alkynes can be deprotonated upon treatment with a strong base such as sodium amide to give an alkynide ion. Alkynide ions are very strong nucleophiles and can take part in

If the starting alkyne is acetylene, then the installation of the alkyl groups has to be done one at one time. This means that one group is installed on one side and then the second substitution takes place in next step.
(c)
Interpretation:
The reagent that has to be used to convert 1-pentyne to 3-heptyne has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Alkynes are the compounds that contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms. The carbon atom present in the triple bond is

The terminal alkynes can be deprotonated upon treatment with a strong base such as sodium amide to give an alkynide ion. Alkynide ions are very strong nucleophiles and can take part in

If the starting alkyne is acetylene, then the installation of the alkyl groups has to be done one at one time. This means that one group is installed on one side and then the second substitution takes place in next step.

(d)
Interpretation:
The reagent that has to be used to convert 1-pentyne to cis-4-octene has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Alkynes are the compounds that contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms. The carbon atom present in the triple bond is

The terminal alkynes can be deprotonated upon treatment with a strong base such as sodium amide to give an alkynide ion. Alkynide ions are very strong nucleophiles and can take part in

If the starting alkyne is acetylene, then the installation of the alkyl groups has to be done one at one time. This means that one group is installed on one side and then the second substitution takes place in next step.

Hydrogenation reaction is one of the reactions that alkynes undergo. Addition of hydrogen is the hydrogenation reaction. This can be accomplished by using hydrogen molecule and metal catalyst. Hydrogenation reaction is also known as reduction reaction.
When an alkyne undergoes hydrogenation reaction with hydrogen and catalyst such as platinum, the final product obtained will be alkane. The intermediate formed in the hydrogenation reaction is alkene and this is further reduced to alkane.

Under the above conditions, the alkene cannot be isolated. This is because the alkene is more reactive than the alkyne towards hydrogenation.
If the alkene has to be obtained from alkyne means, then a partially deactivated catalyst like Lindlar’s catalyst or sodium in liquid ammonia can be used. Partially deactivated catalyst is known as poisoned catalyst. When the alkyne is reduced using Lindlar’s catalyst, the alkene product obtained will be having cis configuration. If the alkyne is reduced using sodium in liquid ammonia means the alkene obtained will be having trans configuration.
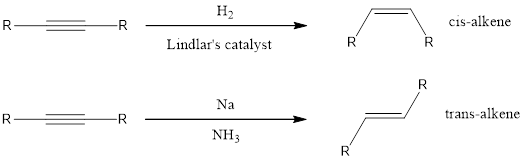
(e)
Interpretation:
The reagent that has to be used to convert 1-pentyne to cis-4-octene has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Alkynes are the compounds that contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms. The carbon atom present in the triple bond is

The terminal alkynes can be deprotonated upon treatment with a strong base such as sodium amide to give an alkynide ion. Alkynide ions are very strong nucleophiles and can take part in

If the starting alkyne is acetylene, then the installation of the alkyl groups has to be done one at one time. This means that one group is installed on one side and then the second substitution takes place in next step.

Hydrogenation reaction is one of the reactions that alkynes undergo. Addition of hydrogen is the hydrogenation reaction. This can be accomplished by using hydrogen molecule and metal catalyst. Hydrogenation reaction is also known as reduction reaction.
When an alkyne undergoes hydrogenation reaction with hydrogen and catalyst such as platinum, the final product obtained will be alkane. The intermediate formed in the hydrogenation reaction is alkene and this is further reduced to alkane.

Under the above conditions, the alkene cannot be isolated. This is because the alkene is more reactive than the alkyne towards hydrogenation.
If the alkene has to be obtained from alkyne means, then a partially deactivated catalyst like Lindlar’s catalyst or sodium in liquid ammonia can be used. Partially deactivated catalyst is known as poisoned catalyst. When the alkyne is reduced using Lindlar’s catalyst, the alkene product obtained will be having cis configuration. If the alkyne is reduced using sodium in liquid ammonia means the alkene obtained will be having trans configuration.
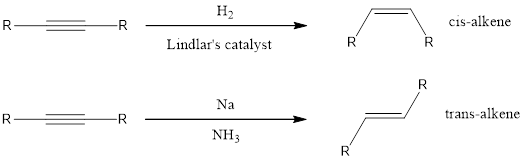
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-NEXTGEN+BOX (1 SEM.)
- 22arrow_forwardPLEASE READ!!! I DONT WANT EXAMPLES, I DONT WANT WORDS OR PARAGRAPHS FOR THE MECHANISM!!! THANKS First image: QUESTION 6. I have to show, with ARROWS and STRUCTURES, the mechanism of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primary. I also tried to draw the mechanism, tell me what to change. Please note that its an AMIDE thats formed not an AMINE the nitrogen has ONE hydrogen and one Phenyl-C-Phenyl. I already asked for this mechanism and got as a final product ...-NH2 not whats shown on the picture, thank you Ths second part. QUESTION 3. I just need a way to synthesize the lactone A, I already started please continue from where I left it Second image: I simply need the products, substrates or reagents, thank youarrow_forwardIndicate how to prepare a 10% sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution to a slightly alkaline pH.arrow_forward
- CH, CH CH₂ CH₂ Phytyl side chain 5. What is the expected order of elution of compounds A-D below from a chromatography column packed with silica gel, eluting with hexane/ethyl acetate? C D OHarrow_forwardPlease analze my gel electrophoresis column of the VRK1 kinase (MW: 39.71 kDa). Attached is the following image for the order of column wells and my gel.arrow_forward2.0arrow_forward
- Write the electron configuration of an atom of the element highlighted in this outline of the Periodic Table: 1 23 4 5 6 7 He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn Hint: you do not need to know the name or symbol of the highlighted element! ☐arrow_forwardCompare these chromatograms of three anti-psychotic drugs done by HPLC and SFC. Why is there the difference in separation time for SFC versus HPLC? Hint, use the Van Deemter plot as a guide in answering this question. Why, fundamentally, would you expect a faster separation for SFC than HPLC, in general?arrow_forwardA certain inorganic cation has an electrophoretic mobility of 5.27 x 10-4 cm2s-1V-1. The same ion has a diffusion coefficient of 9.5 x 10-6cm2s-1. If this ion is separated from cations by CZE with a 75cm capillary, what is the expected plate count, N, at an applied voltage of 15.0kV? Under these separation conditions, the electroosmotic flow rate was 0.85mm s-1 toward the cathode. If the detector was 50.0cm from the injection end of the capillary, how long would it take in minutes for the analyte cation to reach the detector after the field was applied?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





