
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605521
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: RENT PEARS
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.2, Problem 4FP
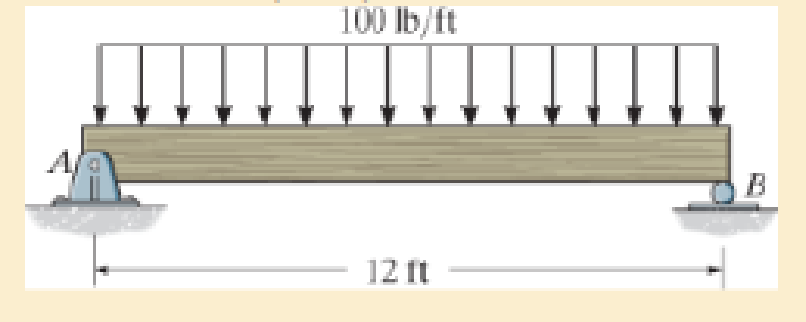
Determine the maximum deflection of the simply supported beam. The beam is made of wood having a modulus of elasticity of Ew = 1.5(103) ksi and a rectangular cross section of width b = 3 in. and height h = 6 in.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule13:57
Students have asked these similar questions
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Chapter 12 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope of end A of the cantilevered...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope of the simply supported beam...Ch. 12.2 - An L2 steel strap having a thickness of 0.125 in....Ch. 12.2 - The L2 steel blade of the band saw wraps around...Ch. 12.2 - A picture is taken of a man performing a pole...Ch. 12.2 - A torque wrench is used to tighten the nut on a...
Ch. 12.2 - The pipe can be assumed roller supported at its...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve for...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the solid...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.3 - The shaft supports the two pulley loads shown....Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve, the...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve and...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the maximum deflection of the...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 45PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 46PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 47PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 48PCh. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection at A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 11FPCh. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection at C. El is...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 54PCh. 12.4 - The composite simply supported steel shaft is...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 60PCh. 12.4 - Determine the slope at A and the maximum...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the displacement of the 20-mm-diameter...Ch. 12.4 - The two force components act on the tire of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at B and deflection at C. El...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 79PCh. 12.5 - The W10 15 cantilevered beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A992...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A992...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, B, and...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - The beam has a constant E1I1 and is supported by...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the reaction at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller B. EI is...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller B. EI is...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller support B if...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the journal bearing...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.9 - The rim on the flywheel has a thickness t, width...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the moment developed in each corner....Ch. 12 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve. Use...Ch. 12 - Draw the bending-moment diagram for the shaft and...Ch. 12 - Determine the moment reactions at the supports A...Ch. 12 - Specify the slope at A and the maximum deflection....Ch. 12 - Determine the maximum deflection between the...Ch. 12 - Determine the slope at B and the deflection at C....Ch. 12 - Determine the reactions, then draw the shear and...Ch. 12 - El is constant.Ch. 12 - Using the method of superposition, determine the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
For each of the following E-R diagrams from Chapter 2 C: Transform the diagram to a relational schema that show...
Modern Database Management
The current source in the circuit shown generates the current pulse
Find (a) v (0); (b) the instant of time gr...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
What output will be produced by the following code?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
The ________ object is assumed to exist and it is not necessary to include it as an object when referring to it...
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
What sequence of events do you think would be required to move the contents of one memory cell in a computer to...
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
In Exercises 49 through 54, find the value of the given function.
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- [Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forwardcan you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forwardcan you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors.arrow_forward
- hi can you please help me in finding the stress intensity factor using a k-calcluator for the scenario attathced in the images.arrow_forwardHi, can you please help me .Identify and justify suitable analytical techniques of the scenario below, bearing in mind the kinds of information being handled to reach a conclusion (methodology). A child swing set was discovered to have failed at the fixing at the top of the chains connecting the seat to the top of the swing set. A 12 mm threaded steel bolt, connecting the shackle to the top beam, failed at the start of the threaded region on the linkage closest to the outside side of the swing set . The linkage and bolts were made of electro galvanised mild steel . The rigid bar chain alternatives and fixings were of the same material and appeared to be fitted in accordance with guidelines. The yield strength of the steel used is 260 MPa and the UTS is 380 MPa. The bolt that failed was threaded using a standard thread with a pitch (distance between threads) of 1.75 mm and a depth of approximately 1.1 mm. The swing set in question had been assigned to ‘toddlers’ with the application of…arrow_forwardHi, can you please define and calculate the failure mode of the linkage that failed on the swing (images added) : A child swing set was discovered to have failed at the fixing at the top of the chains connecting the seat to the top of the swing set. A 12 mm threaded steel bolt, connecting the shackle to the top beam, failed at the start of the threaded region on the linkage closest to the outside side of the swing set . The linkage and bolts were made of electro galvanised mild steel . The rigid bar chain alternatives and fixings were of the same material and appeared to be fitted in accordance with guidelines. The yield strength of the steel used is 260 MPa and the UTS is 380 MPa. The bolt that failed was threaded using a standard thread with a pitch (distance between threads) of 1.75 mm and a depth of approximately 1.1 mm. The swing set in question had been assigned to ‘toddlers’ with the application of a caged-type seat. However, the location was within the play area not…arrow_forward
- Page 11-68. The rectangular plate shown is subjected to a uniaxial stress of 2000 psi. Compute the shear stress and the tensile developed on a plane forming an angle of 30° with the longitud axis of the member. (Hint: Assume a cross-sectional area of unity) 2000 psi 2000 psi hparrow_forward11-70. A shear stress (pure shear) of 5000 psi exists on an element. (a) Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses caused in the element due to this shear. (b) Sketch the element showing the planes on which the maximum tensile and compressive stresses act.arrow_forward11-20. An aluminum specimen of circular cross section, 0.50 in. in diameter, ruptured under a tensile load of 12,000 lb. The plane of failure was found to be at 48° with a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the specimen. (a) Compute the shear stress on the failure plane. (b) Compute the maximum tensile stress. (c) Compute the tensile stress on the failure plane. hparrow_forward
- A long flat steel bar 13 mm thick and 120 mm wide has semicircular grooves as shown and carries a tensile load of 50 kN Determine the maximum stress if plate r= 8mm r=21mm r=38mmarrow_forwardProblem 13: F₁ = A =250 N 30% Determine the moment of each of the three forces about point B. F₂ = 300 N 60° 2 m -3 m B 4 m F3=500 Narrow_forward3 kN 3 kN 1.8 kN/m 80 mm B 300 mm D an 1.5 m-1.5 m--1.5 m- PROBLEM 5.47 Using the method of Sec. 5.2, solve Prob. 5.16 PROBLEM 5.16 For the beam and loading shown, determine the maximum normal stress due to bending on a transverse section at C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY