
Mechanics of Materials (Custom)
16th Edition
ISBN: 9781323178867
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.2, Problem 12.15P
A torque wrench is used to tighten the nut on a bolt. If the dial indicates that a torque of 60 lb-ft is applied when the bolt is fully tightened determine the force P acting at the handle and the distance s the needle moves along the scale. Assume only the portion AB of the beam distorts cross section is square having dimensions of 0.5 in. by 0.5 in. E = 29(103) ksi.
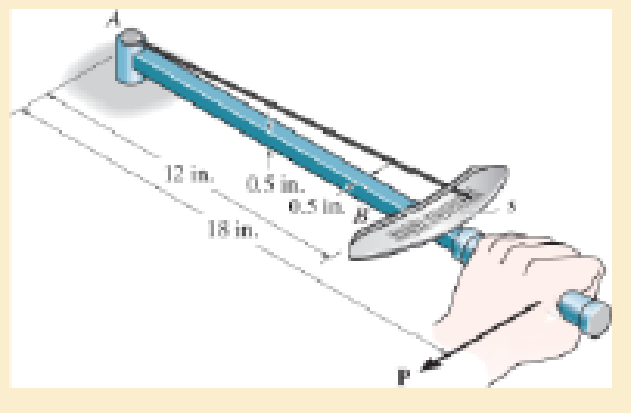
Prob. 12–15
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Qf, Qa,Qm, Qcon,Qfg, Qbd, Qref,Qloss ( meaning, formula, percentage, and importance of higher value na qf, qa etc)
The beam is supported by a fixed support at point C and a roller at point A. It also has an internal hinge at point B. The beam supports a point load at point D, a moment at point A and a distributed load on segment BC.
a. calculate the support reactions at points A and C
b. calculate the internal resultant loadings (N, V, M) at points E and F, which lies in the middle between points A and D
P = 4 kip
Ma = 5 kip-ft
w1 = 3 kip/ft and w2 = 4 kip/ft
a = 3 ft
From the image of the pyramid, I want to find what s1 hat, s2 hat, and s3 hat are. I think s3 hat is just equal to e3 hat right? What about the others?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (Custom)
Ch. 12.2 - In each case, determine the internal bending...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope of end A of the cantilevered...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope of the simply supported beam...Ch. 12.2 - An L2 steel strap having a thickness of 0.125 in....Ch. 12.2 - The L2 steel blade of the band saw wraps around...Ch. 12.2 - A picture is taken of a man performing a pole...
Ch. 12.2 - El is constant. Prob. 124Ch. 12.2 - Determine the deflection of end C of the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the elastic curve for the cantilevered...Ch. 12.2 - The A-36 steel beam has a depth of 10 in. and is...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve for...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Draw the bending-moment diagram for the shaft and...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the beam and...Ch. 12.2 - The simply supported shaft has a moment of inertia...Ch. 12.2 - A torque wrench is used to tighten the nut on a...Ch. 12.2 - The pipe can be assumed roller supported at its...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve for...Ch. 12.2 - The bar is supported by a roller constraint at B,...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the deflection at B of the bar in Prob....Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the solid...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the elastic curve for the cantilevered...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - The floor beam of the airplane is subjected to the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.2 - The beam is made of a material having a specific...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope at end B and the maximum...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.3 - The shaft is supported at A by a journal bearing...Ch. 12.3 - The shaft supports the two pulley loads shown....Ch. 12.3 - The beam is made of a ceramic material. If it is...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve, the...Ch. 12.3 - The beam is subjected to the load shown. Determine...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve, the...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve and...Ch. 12.3 - The shaft supports the two pulley loads. Determine...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the maximum deflection of the...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the slope at A and the deflection of end...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the maximum deflection in region AB of...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.42PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.43PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.44PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.45PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.46PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.47PCh. 12.3 - Determine the value of a so that the displacement...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the displacement at C and the slope at...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equations of the slope and elastic...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection at A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.11FPCh. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection at C. El is...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection at C. El is...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the deflection of end B of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.54PCh. 12.4 - The composite simply supported steel shaft is...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.56PCh. 12.4 - Prob. 12.57PCh. 12.4 - Determine the deflection at C and the slope of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.60PCh. 12.4 - Determine the position a of the roller support B...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.62PCh. 12.4 - Determine the slope and the deflection of end B of...Ch. 12.4 - The two A-36 steel bars have a thickness of 1 in....Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at A and the displacement at...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the deflection at C and the slopes at...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection within region AB....Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at A and the maximum...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at C and the deflection at B....Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at A and the maximum...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the displacement of the 20-mm-diameter...Ch. 12.4 - The two force components act on the tire of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.73PCh. 12.4 - The rod is constructed from two shafts for which...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.75PCh. 12.4 - Determine the slope at point A and the maximum...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the position a of roller support B in...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at B and deflection at C. El...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.79PCh. 12.4 - Prob. 12.80PCh. 12.4 - Prob. 12.81PCh. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection of the beam. El...Ch. 12.5 - The W10 15 cantilevered beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.5 - The W10 15 cantilevered beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A992...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A992...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.5 - The W8 48 cantilevered beam is made of A-36 steel...Ch. 12.5 - The beam supports the loading shown. Code...Ch. 12.5 - The W24 104 A-36 steel beam is used to support...Ch. 12.5 - The W8 48 cantilevered beam is made of A-36 steel...Ch. 12.5 - The rod is pinned at its end A and attached to a...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12.94PCh. 12.5 - The pipe assembly consists of three equal-sized...Ch. 12.5 - The assembly consists of a cantilevered beam CS...Ch. 12.5 - Determine the smallest force F required to attract...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12.98PCh. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, B, and...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the moment reactions at the supports A...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the support A and B. EI...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at roller support A and...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the moment reactions at the supports A...Ch. 12.7 - The beam has a constant E1I1 and is supported by...Ch. 12.7 - The beam is supported by a pin at A, a roller at...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the moment reactions at the supports A...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the reaction at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the vertical reaction at the journal...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the reactions at the supports. EI is...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the vertical reaction at the journal...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller B. EI is...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller B. EI is...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller support B if...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the journal bearing...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B....Ch. 12.9 - The beam is used to support the 20-kip load....Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B....Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B....Ch. 12.9 - Before the uniform distributed load is applied to...Ch. 12.9 - The fixed supported beam AB is strengthened using...Ch. 12.9 - The beam has a constant E1I1, and is supported by...Ch. 12.9 - The beam is supported by the bolted supports at...Ch. 12.9 - Each of the two members is made from 6061-T6...Ch. 12.9 - The beam is made from a soft linear elastic...Ch. 12.9 - The beam AB has a moment of inertia I = 475 in4...Ch. 12.9 - The rim on the flywheel has a thickness t, width...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the moment developed in each corner....Ch. 12 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve. Use...Ch. 12 - Draw the bending-moment diagram for the shaft and...Ch. 12 - Determine the moment reactions at the supports A...Ch. 12 - Specify the slope at A and the maximum deflection....Ch. 12 - Determine the maximum deflection between the...Ch. 12 - Determine the slope at B and the deflection at C....Ch. 12 - Determine the reactions, then draw the shear and...Ch. 12 - El is constant.Ch. 12 - Using the method of superposition, determine the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 1. A tube rotates in the horizontal ry plane with a constant angular velocity w about the z-axis. A particle of mass m is released from a radial distance R when the tube is in the position shown. This problem is based on problem 3.2 in the text. R m 2R Figure 1 x a) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the tube is frictionless. b) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the coefficient of friction between the sides of the tube and the particle is = k = p. c) For the case where the tube is frictionless, what is the radial speed at which the particle leaves the tube? d) For the case where there is friction, derive a differential equation that would allow you to solve for the radius of the particle as a function of time. I'm only looking for the differential equation. DO NOT solve it. 1 e) If there is no friction, what is the angle of the tube when the particle exits? • Hint: You may need to solve a differential equation for the last part. The "potentially useful…arrow_forwardQuestion 2. A smooth uniform sphere of mass m and radius r is squeezed between two massless levers, each of length 1, which are inclined at an angle with the vertical. A mechanism at pivot point O ensures that the angles & remain the same at all times so that the sphere moves straight upward. This problem is based on Problem 3-1 in the text. P P r Figure 2 a) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is no friction. b) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is a coefficient of friction between the sphere and the right lever of μ. c) If a force P is applied between the ends of the levers (shown in the diagram), and there is no friction, what is the acceleration of the sphere when = 30°arrow_forwardIf you had a matrix A = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] and a matrix B = [1 2 3], how would you cross multiply them i.e. what is the cross product of AxB. what would be the cross product of a dyadic with a vector?arrow_forward
- Problem 3: The inertia matrix can be written in dyadic form which is particularly useful when inertia information is required in various vector bases. On the next page is a right rectangular pyramid of total mass m. Note the location of point Q. (a) Determine the inertia dyadic for the pyramid P, relative to point Q, i.e., 7%, for unit vectors ₁₁, 2, 3.arrow_forwardCan you solve for v? Also, what is A x uarrow_forwardThe external loads on the element shown below at the free end are F = 1.75 kN, P = 9.0 kN, and T = 72 Nm. The tube's outer diameter is 50 mm and the inner diameter is 45 mm. Given: A(the cross-sectional area) is 3.73 cm², Moment inertial I is 10.55 cm4, and J polar moment inertial is 21.1 cm4. Determine the following. (1) The critical element(s) of the bar. (2) Show the state of stress on a stress element for each critical element. -120 mm- Farrow_forward
- A crate weighs 530 lb and is hung by three ropes attached to a steel ring at A such that the top surface is parallel to the xy plane. Point A is located at a height of h = 42 in above the top of the crate directly over the geometric center of the top surface. Use the dimensions given in the table below to determine the tension in each of the three ropes. 2013 Michael Swanbom ↑ Z C BY NC SA b x B у D Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 30 in b 43 in с 4.5 in The tension in rope AB is lb The tension in rope AC is lb The tension in rope AD is lbarrow_forwardThe airplane weighs 144100 lbs and flies at constant speed and trajectory given by 0 on the figure. The plane experiences a drag force of 73620 lbs. a.) If = 11.3°, determine the thrust and lift forces required to maintain this speed and trajectory. b.) Next consider the case where is unknown, but it is known that the lift force is equal to 7.8 times the quantity (Fthrust Fdrag). Compute the resulting trajectory angle - and the lift force in this case. Use the same values for the weight and drag forces as you used for part a. Уллу Fdrag 10. Ө Fthrust cc 10 2013 Michael Swanbom BY NC SA Flift Fweight The lift force acts in the y' direction. The weight acts in the negative y direction. The thrust and drag forces act in the positive and negative x' directions respectively. Part (a) The thrust force is equal to lbs. The lift force is equal to Part (b) The trajectory angle is equal to deg. The lift force is equal to lbs. lbs.arrow_forwardThe hoist consists of a single rope and an arrangement of frictionless pulleys as shown. If the angle 0 = 59°, determine the force that must be applied to the rope, Frope, to lift a load of 4.4 kN. The three-pulley and hook assembly at the center of the system has a mass of 22.5 kg with a center of mass that lies on the line of action of the force applied to the hook. e ΘΕ B CC 10 BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Fhook Note the figure may not be to scale. Frope = KN HO Fropearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Strain energy and strain energy density introduced; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m14sqLGg4BQ;License: Standard youtube license