
Concept explainers
(a)
Find whether the block will slide in the slot if it is released in the position corresponding to
Find the magnitude and the direction of the friction force exerted on the block immediately after it is released.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The radius of semicircular slot is
The angular velocity
The weight
The coefficient of static friction
The coefficient of kinetic friction
Calculation:
Write the general equation of mass of block B (m).
Here, g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Write the general equation (a) of acceleration in curved path.
Here, v is the velocity in the curved path.
Find the horizontal distance (d) between line of origin to block E using the equation:
Substitute 10 in. for r.
Find the distance (D) between edge AD and block E using the equation:
Substitute
Find the radius
Substitute
Write the equation velocity of block E
Find the equation of acceleration of block E.
Substitute
Substitute
Assume that the block is at rest with respect to the plate.
Sketch the free body diagram of block E as shown in Figure 1.
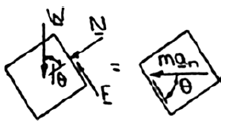
Here, F is the friction force and N is the normal force.
Refer Figure 1.
Apply Newton’s law of equation along x-axis (Consider forces along x-axis is negative).
Substitute
Apply Newton’s law of equation along y-axis (Consider forces along x-axis is negative).
Substitute
Find the normal force (N) when
Substitute
Substitute 0.8 lb for W,
Find the maximum friction force
Substitute 0.35 for
Find the friction force (F) using Equation (1):
Substitute
Substitute 0.8 lb for W,
The friction force on the system is less than the maximum friction force. Therefore, the block does not slide in the slot.
Thus, the friction force exerted on the block immediately after it is released is
(b)
Find whether the block will slide in the slot if it is released in the position corresponding to
Find the magnitude and the direction of the friction force exerted on the block immediately after it is released.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Find the normal force (N) when
Substitute
Substitute 0.8 lb for W,
Find the maximum friction force
Substitute 0.35 for
Find the friction force (F) using Equation (1):
Substitute
Substitute 0.8 lb for W,
The friction force in the system is greater than the maximum friction force. Therefore the block will slide downward in the slot.
The sliding leads to kinetic equation.
Find the magnitude and the direction of the friction force (F) exerted on the block immediately after it is released using the equation:
Substitute 0.25 for
Thus, the friction force exerted on the block immediately after it is released is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Homework#5arrow_forwardQuestion 1: Beam Analysis Two beams (ABC and CD) are connected using a pin immediately to the left of Point C. The pin acts as a moment release, i.e. no moments are transferred through this pinned connection. Shear forces can be transferred through the pinned connection. Beam ABC has a pinned support at point A and a roller support at Point C. Beam CD has a roller support at Point D. A concentrated load, P, is applied to the mid span of beam CD, and acts at an angle as shown below. Two concentrated moments, MB and Mc act in the directions shown at Point B and Point C respectively. The magnitude of these moments is PL. Moment Release A B с ° MB = PL Mc= = PL -L/2- -L/2- → P D Figure 1: Two beam arrangement for question 1. To analyse this structure, you will: a) Construct the free body diagrams for the structure shown above. When constructing your FBD's you must make section cuts at point B and C. You can represent the structure as three separate beams. Following this, construct the…arrow_forwardA differential element on the bracket is subjected to plane strain that has the following components:, Ɛx = 300 × 10-6, Ɛy = 150 × 10-6, Ɛxy = -750 x 10-6. Use the strain-transformation equations and determine the normal strain Ɛx in the X/ direction on an element oriented at an angle of 0 = 40°. Note, a positive angle, 0, is counter clockwise. x Enter your answer in micro strain to a precision of two decimal places. eg. if your answer is 300.15X106, please enter 300.15.arrow_forwardIf the 50 mm diameter shaft is made from brittle material having an ultimate strength of σult=595 MPa for both tension and compression, determine the factor of safety of the shaft against rupture. The applied force, F, is 140 kN. The applied torque T, is 5.0 kN⚫m. Enter your answer to a precision of two decimal places. T Farrow_forwardЗіс 1 mH 10 Ω m 16 cos 2.5 × 104 A Lic 592 10 Ω 1 μFarrow_forwardHomework#5arrow_forwardHomework#5arrow_forwardOxygen (molar mass 32 kg/kmol) expands reversibly in a cylinder behind a piston at a constant pressure of 3 bar. The volume initially is 0.01 m3 and finally is 0.03 m3; the initial temperature is 17°C. Calculate the work input and the heat supplied during the expansion. Assume oxygen to be an ideal gas and take cp = 0.917 kJ/kg K. For 1 bonus mark explain why (using your understanding of thermodynamics) that oxygen is used in this context rather than water vapour.arrow_forwardHydrodynamic Lubrication Theory Q1: Convert this equations into Python by 1- ah ap a h³ ap 1..ah = ax 12μ ax ay 12μ ay 2 ax Where P=P(x, y) is the oil film pressure. 2- 3μU (L² ε sin P= C²R (1+ cos 0)³ Q2: prove that |h(0) = C(1+ cos 0) ?arrow_forward### To make a conclusion for a report of an experiment on rockets, in which the openrocket software was used for the construction and modeling of two rockets: one one-stage and one two-stage. First rocket (single-stage) reached a maximum vertical speed of 200 m/s and a maximum height of 1000 m The second rocket (two-stage) reached a maximum vertical speed of 250 m/s and a maximum height of 1800 m To make a simplified conclusion, taking into account the efficiency of the software in the study of rocketsarrow_forwardWhat is the difference between saturated liquid and compressed liquid? What is the difference between the critical point and the triple pointarrow_forwardWhat is quality? Does it have any meaning in the superheated vapour region? What is the difference between saturated vapor and superheated vapour? What is the difference between saturated liquid and compressed liquid? What is the difference between the critical point and the triple point?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





