
Hamilton Company’s
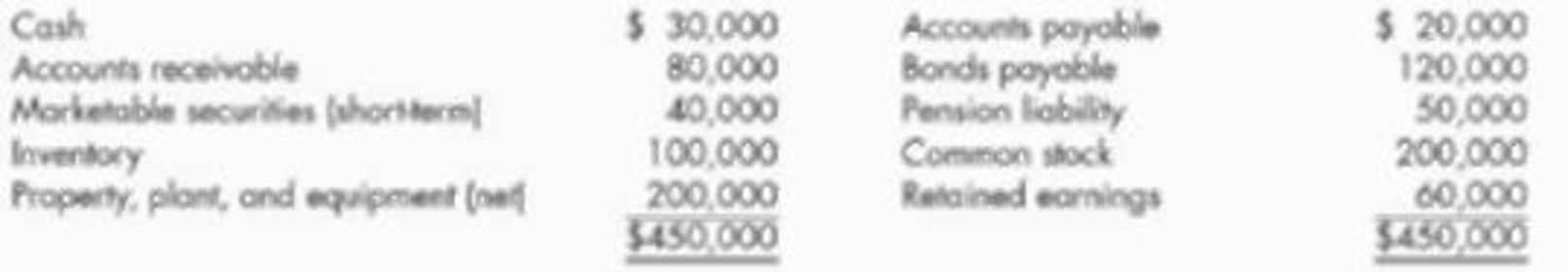
Korbel Company is considering purchasing Hamilton (a privately held company) and discovers the following about Hamilton:
- a. No allowance for doubtful accounts has been established. A $10,000 allowance is considered appropriate.
- b. Marketable securities are valued at cost. The current market value is $60,000.
- c. The LIFO inventory method is used. The FIFO inventory of $140,000 would be used if the company is acquired.
- d. Land, included in property, plant, and equipment, which is recorded at its cost of $50,000, is worth $120,000. The remaining property, plant, and equipment is worth 10% more than its
depreciated cost. - e. The company has an unrecorded trademark that is worth $70,000.
- f. The company’s bonds are currently trading for $130,000.
- g. The pension liability is understated by $40,000.
Required:
- 1. Compute the amount of
goodwill if Korbel agrees to pay $500,000 cash for Hamilton. - 2. Next Level What are the reasons that the book value of Hamilton’s net identifiable assets differ from their market value?
- 3. Prepare the
journal entry to record the acquisition on the books of Korbel assuming Hamilton is liquidated. - 4. If Korbel agrees to pay only $400,000 cash, how much goodwill exists?
- 5. If Korbel pays only $400,000 cash, prepare the journal entry to record the acquisition on its books, assuming Hamilton is liquidated.
1.
Calculate the amount of goodwill of Company H.
Explanation of Solution
Goodwill: Goodwill is the good reputation developed by a company over years. This is recorded as an intangible asset, and is quantified when other company acquires. Goodwill should be recorded only when one company is acquired by another company. Goodwill value would be impaired, if the book value of goodwill is less than fair market value.
Calculate the amount of goodwill of Company H:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Amount willing to pay | $500,000 |
| Less: Identifiable net assets | $415,000 |
| Goodwill | $85,000 |
Table (1)
Compute the identifiable net assets:
| Assets | Amount ($) |
| Cash | $30,000 |
| Accounts receivable (net) (1) | 70,000 |
| Marketable securities (short-term) | 60,000 |
| Inventory | 140,000 |
| Land | 120,000 |
| Plant Property &Equipment (2) | 165,000 |
| Trademark | 70,000 |
| Total assets (a) | $655,000 |
| Liabilities | |
| Accounts payable | 20,000 |
| Bonds payable | 130,000 |
| Pension liability | 90,000 |
| Total liabilities (b) | $240,000 |
| Identifiable net assets | 415,000 |
Table (2)
Working note (1):
Compute the accounts receivable (net):
Working note (2):
Compute the plant, property and equipment (net):
2.
State the reason for the difference in the book value of Company H’s identifiable net assets from the market value.
Explanation of Solution
Identifiable intangibles: The identifiable intangibles are the intangible assets that can be easily separated from the company, and it would be sold, transferred, licensed, rented or exchanged. Examples: trademarks, patents, copyrights, franchises, customer lists and relationships, non-compete agreements, and licenses.
The book value of H Company’s identifiable net assets differs from its market value for the following reason:
- Some of the assets of Company H are listed on the balance sheet at amounts other than their market value. For instance: The marketable securities are listed at cost and not at a fair value, likewise the inventory is valued using LIFO, instead of FIFO. The land is reported at cost but not at its market value, if it would have reported at its market value, then the cost would be much higher. Equipment is reported at depreciated cost while its market value is much higher.
- Company H has a valuable internally developed trademark that is not recorded.
- An unidentifiable intangible asset (goodwill) exists. However, it is not reported on H Company’s books.
3.
Prepare journal entry for the given transaction.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry in the books of Company K assume that Company H has been liquidated.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 30,000 | |||
| Accounts Receivable | 70,000 | |||
| Marketable Securities | 60,000 | |||
| Inventory | 140,000 | |||
| Land | 120,000 | |||
| Property, Plant, and Equipment | 165,000 | |||
| Trademark | 70,000 | |||
| Goodwill | 85,000 | |||
| Accounts Payable | 20,000 | |||
| Bonds Payable | 130,000 | |||
| Pension Liability | 90,000 | |||
| Cash | 500,000 | |||
| (To record the acquisition of company H) |
Table (3)
4.
Compute the amount of goodwill that exist, when Company K agrees pay only $400,000 cash.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the amount of goodwill that exist, when Company K agrees pay only $400,000 cash
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Amount willing to pay | $400,000 |
| Less: Identifiable net assets | 415,000 |
| Goodwill | (15,000) |
Table (4)
5.
Prepare journal entry for the given transaction.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry in the books of Company K assume that Company H had paid only $400,000.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 30,000 | |||
| Accounts Receivable | 70,000 | |||
| Marketable Securities | 60,000 | |||
| Inventory | 140,000 | |||
| Land | 120,000 | |||
| Property, Plant, and Equipment | 165,000 | |||
| Trademark | 70,000 | |||
| Accounts Payable | 20,000 | |||
| Bonds Payable | 130,000 | |||
| Pension Liability | 90,000 | |||
| Cash | 400,000 | |||
| Gain on purchase of Company H | 15,000 | |||
| (To record the gain on acquisition of company H) |
Table (5)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
