
Concept explainers
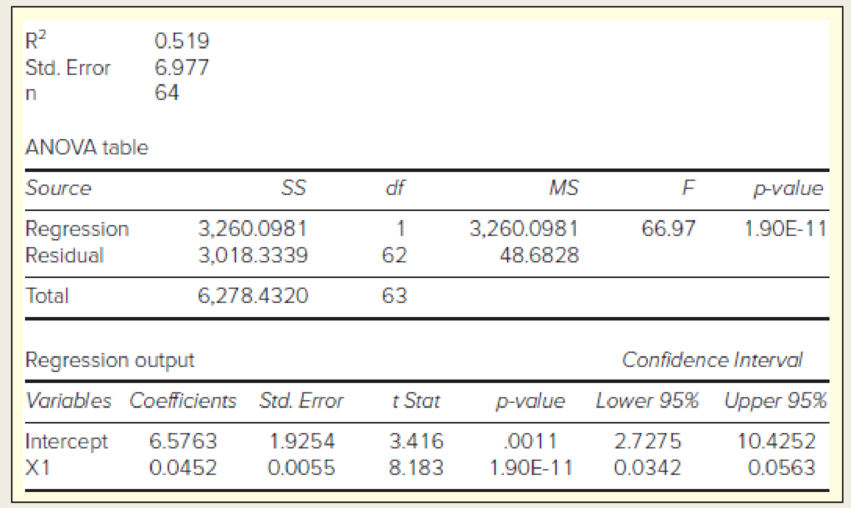
In the following regression, X = total assets ($ billions), Y = total revenue ($ billions), and n = 64 large banks. (a) Write the fitted regression equation. (b) State the degrees of freedom for a two-tailed test for zero slope, and use Appendix D to find the critical value at α = .05. (c) What is your conclusion about the slope? (d) Interpret the 95 percent confidence limits for the slope. (e) Verify that F= t2 for the slope. (f) In your own words, describe the fit of this regression.
a.
Write the fitted regression equation.
Answer to Problem 62CE
The regression equation is,
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
An output of a regression is given. The X variable is the total assets and Y be the total revenue.
Regression:
Suppose
Where,
The total sum of squares is denoted as,
The regression sum of squares is denoted as,
The error sum of squares is denoted as,
From the regression the fitted line is denoted as,
From the output,
Hence, the regression equation is,
b.
Find the degrees of freedom for the two-tailed test for zero slope.
Find the critical value at 0.05 level of significanceusing Appendix D.
Answer to Problem 62CE
The degrees of freedom for the two-tailed test for zero slop is62.
The critical value at 0.05 level of significanceis 2.000.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Critical value:
Here from the output, the sample size,
The degrees of freedom is,
For two tailed test, the critical value for t-test will be,
From the Appendix D: STUDENT’S t CRITICAL VALUES:
- • Since 62 is not in the table, so locate the value 60in the column of degrees of freedom.
- • Locate the 0.025 in level of significance.
- • The intersecting value that corresponds to the degrees of freedom 60 with level of significance 0.025 is 2.000.
Thus, the critical-valueusing Appendix D is 2.000.
c.
Make a conclusion about the slope.
Explanation of Solution
Let
Hypotheses:
Null hypothesis:
That is, the slope is zero.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, the slope is not equal to zero.
Decision rule:
If
If
From the output, the t-statistics is 8.183 and from part (b), the critical value at 0.05 level of significanceis 2.000.
Conclusion:
Here the t-statistics is greater than the critical value at 0.05 level of significance.
That is,
Hence, by the decision rule reject the null hypothesis.
That is, the slope is significantly different from zero.
d.
Interpret the 95% confidence interval for the slope.
Explanation of Solution
The 95% confidence interval for the slope,
Where,
From the output, the 95% confidence interval of the slope is (0.0342, 0.0563).
Interpretation:
From the confidence interval it can be concluded that there is 95% confident that the slope will lie between 0.0342 and 0.0563.
e.
Verify
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From the output the F statistic is 66.97.
For the slope the t-statistic is 8.183.
Hence, it can be concluded that
f.
Describe the fit of the regression.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From the output, the R-squared value is 0.519.
The coefficient of determination (
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Applied Statistics in Business and Economics
- AP1.1 You look at real estate ads for houses in Sarasota, Florida. Many houses range from $200,000 to $400,000 in price. The few houses on the water, however, have prices up to $15 million. Which of the following statements best describes the distribution of home prices in Sarasota? The distribution is most likely skewed to the left, and the mean is greater than the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the left, and the mean is less than the median. The distribution is roughly symmetric with a few high outliers, and the mean is approximately equal to the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the right, and the mean is greater than the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the right, and the mean is less than the median.arrow_forwardDuring busy political seasons, many opinion polls are conducted. In apresidential race, how do you think the participants in polls are generally selected?Discuss any issues regarding simple random, stratified, systematic, cluster, andconvenience sampling in these polls. What about other types of polls, besides political?arrow_forwardPlease could you explain why 0.5 was added to each upper limpit of the intervals.Thanksarrow_forward
- 28. (a) Under what conditions do we say that two random variables X and Y are independent? (b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) = E(X)E(Y); (e) Show by a counter example that the converse of (ii) is not necessarily true.arrow_forward1. Let X and Y be random variables and suppose that A = F. Prove that Z XI(A)+YI(A) is a random variable.arrow_forward30. (a) What is meant by the term "product measur"? ANDarrow_forward
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





