
(a)
To find: The expression of contrast for each of the treatments in terms of their respective means.
(a)
Answer to Problem 49E
Solution: The expression of contrast for the experiment including the treatment of Placebo verses average of two low dose treatment is given below:
The expression of contrast for the experiment including the treatment of difference between high A and low A verses high B and low B is given below:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The average of means of low A and low B treatment is
Null hypotheses represent that there is no difference in the Placebo treatment and average of low A and low B treatment, which is represented as below:
Hence, on equating
The difference of means of low A and high A treatment is
Null hypotheses represent that there is no difference in the difference of low A and high A treatment and difference of high B and low B treatment, which is represented as below:
Hence, on equating
The coefficients of contrast for the contrast
The coefficients of contrast for the contrast
(b)
To find: The sample and standard error for each of the contrast.
(b)
Answer to Problem 49E
Solution: The sample of contrast
The standard error for the contrast
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The value of contrast
The value of contrast
Standard error can be calculated by using the formula given below:
Pooled standard deviation can be calculated as given below:
For the first contrast, the standard error
For the second contrast, the standard error
Interpretation: Therefore, it can be concluded that for the first contrast, the estimated value of standard deviation is 2.1353 and for the second contrast, the estimated value of standard deviation is 3.487.
(c)
To test: The significance test for each of the contrast and summarize the obtained results.
(c)
Answer to Problem 49E
Solution: The test statistic for contrast of the experiment including the treatment of Placebo verses average of two low dose treatment is 0.0414 and the test statistics for contrast for the experiment including the treatment of difference between high A and low A verses high B and low B is 0.2540. For the first contrast, the result is significant but for the second contrast the result is insignificant.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: Test statistic can be calculated by using following formula, which is mentioned below:
To calculate the test statistic for first contrast, the value of
The total
The degree of freedom for contrast can be obtained as shown below:
The P-value can also be calculated by the software Microsoft Excel by using the following command:
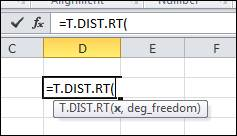
Insert the values of x and degree of freedom, which are –1.8264 and 20, respectively. After this, press enter and the output is shown below in the snapshot:
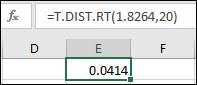
Hence, the P- value is obtained as 0.0414, which is less than the significance level 0.05, so the decision is to reject the null hypothesis.
To calculate the test statistic for second contrast, the value of
The P-value can also be calculated by the software Microsoft Excel by using the following command:

Insert the values of x and degree of freedom, which is 0.6739 and 20, respectively. After this, press enter and the output is shown below in the snapshot:
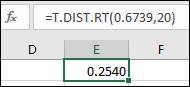
Hence, the P- value is obtained as 0.2540, which is greater than the significance level 0.05, so the decision is to accept the null hypothesis.
Conclusion: Therefore, it can be concluded that the result is significant for the first contrast and the result is not significant for the second contrast.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics: w/CrunchIt/EESEE Access Card
- John and Mike were offered mints. What is the probability that at least John or Mike would respond favorably? (Hint: Use the classical definition.) Question content area bottom Part 1 A.1/2 B.3/4 C.1/8 D.3/8arrow_forwardThe details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. What is the simple moving average root mean square error? Round to two decimal places. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Question content area bottom Part 1 A. 207.13 B. 20.12 C. 14.39 D. 0.21arrow_forwardThe details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. If the smoothing constant is assumed to be 0.7, and setting F1 and F2=A1, what is the exponential smoothing sales forecast for week 7? Round to the nearest whole number. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Question content area bottom Part 1 A. 80 clocks B. 60 clocks C. 70 clocks D. 50 clocksarrow_forward
- The details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. Calculate the value of the simple moving average mean absolute percentage error. Round to two decimal places. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Part 1 A. 14.39 B. 25.56 C. 23.45 D. 20.90arrow_forwardThe accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Year Fossil Fuels Production Fossil Fuels Consumption Total Energy Consumption1949 28.748 29.002 31.9821950 32.563 31.632 34.6161951 35.792 34.008 36.9741952 34.977 33.800 36.7481953 35.349 34.826 37.6641954 33.764 33.877 36.6391955 37.364 37.410 40.2081956 39.771 38.888 41.7541957 40.133 38.926 41.7871958 37.216 38.717 41.6451959 39.045 40.550 43.4661960 39.869 42.137 45.0861961 40.307 42.758 45.7381962 41.732 44.681 47.8261963 44.037 46.509 49.6441964 45.789 48.543 51.8151965 47.235 50.577 54.0151966 50.035 53.514 57.0141967 52.597 55.127 58.9051968 54.306 58.502 62.4151969 56.286…arrow_forwardThe accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Year Fossil Fuels Production Fossil Fuels Consumption Total Energy Consumption1949 28.748 29.002 31.9821950 32.563 31.632 34.6161951 35.792 34.008 36.9741952 34.977 33.800 36.7481953 35.349 34.826 37.6641954 33.764 33.877 36.6391955 37.364 37.410 40.2081956 39.771 38.888 41.7541957 40.133 38.926 41.7871958 37.216 38.717 41.6451959 39.045 40.550 43.4661960 39.869 42.137 45.0861961 40.307 42.758 45.7381962 41.732 44.681 47.8261963 44.037 46.509 49.6441964 45.789 48.543 51.8151965 47.235 50.577 54.0151966 50.035 53.514 57.0141967 52.597 55.127 58.9051968 54.306 58.502 62.4151969 56.286…arrow_forward
- The accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Develop line charts for each variable and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). What is the line chart for the variable Fossil Fuels Production?arrow_forwardThe accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Year Fossil Fuels Production Fossil Fuels Consumption Total Energy Consumption1949 28.748 29.002 31.9821950 32.563 31.632 34.6161951 35.792 34.008 36.9741952 34.977 33.800 36.7481953 35.349 34.826 37.6641954 33.764 33.877 36.6391955 37.364 37.410 40.2081956 39.771 38.888 41.7541957 40.133 38.926 41.7871958 37.216 38.717 41.6451959 39.045 40.550 43.4661960 39.869 42.137 45.0861961 40.307 42.758 45.7381962 41.732 44.681 47.8261963 44.037 46.509 49.6441964 45.789 48.543 51.8151965 47.235 50.577 54.0151966 50.035 53.514 57.0141967 52.597 55.127 58.9051968 54.306 58.502 62.4151969 56.286…arrow_forwardFor each of the time series, construct a line chart of the data and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). Month PercentApr 1972 4.97May 1972 5.00Jun 1972 5.04Jul 1972 5.25Aug 1972 5.27Sep 1972 5.50Oct 1972 5.73Nov 1972 5.75Dec 1972 5.79Jan 1973 6.00Feb 1973 6.02Mar 1973 6.30Apr 1973 6.61May 1973 7.01Jun 1973 7.49Jul 1973 8.30Aug 1973 9.23Sep 1973 9.86Oct 1973 9.94Nov 1973 9.75Dec 1973 9.75Jan 1974 9.73Feb 1974 9.21Mar 1974 8.85Apr 1974 10.02May 1974 11.25Jun 1974 11.54Jul 1974 11.97Aug 1974 12.00Sep 1974 12.00Oct 1974 11.68Nov 1974 10.83Dec 1974 10.50Jan 1975 10.05Feb 1975 8.96Mar 1975 7.93Apr 1975 7.50May 1975 7.40Jun 1975 7.07Jul 1975 7.15Aug 1975 7.66Sep 1975 7.88Oct 1975 7.96Nov 1975 7.53Dec 1975 7.26Jan 1976 7.00Feb 1976 6.75Mar 1976 6.75Apr 1976 6.75May 1976…arrow_forward
- Hi, I need to make sure I have drafted a thorough analysis, so please answer the following questions. Based on the data in the attached image, develop a regression model to forecast the average sales of football magazines for each of the seven home games in the upcoming season (Year 10). That is, you should construct a single regression model and use it to estimate the average demand for the seven home games in Year 10. In addition to the variables provided, you may create new variables based on these variables or based on observations of your analysis. Be sure to provide a thorough analysis of your final model (residual diagnostics) and provide assessments of its accuracy. What insights are available based on your regression model?arrow_forwardI want to make sure that I included all possible variables and observations. There is a considerable amount of data in the images below, but not all of it may be useful for your purposes. Are there variables contained in the file that you would exclude from a forecast model to determine football magazine sales in Year 10? If so, why? Are there particular observations of football magazine sales from previous years that you would exclude from your forecasting model? If so, why?arrow_forwardStat questionsarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





