
(a)
Draw the influence lines for the horizontal and vertical reactions at support A and the member forces in members BC, CM, and ML.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Influence line for the vertical reaction at A.
The influence line ordinate of
Apply 1 kip at D.
Find the vertical reaction at support A.
The reaction is determined by applying a 1-kip load at successive panel points.
Apply 1 kip load at C.
Draw the free body diagram as shown in Figure 1.
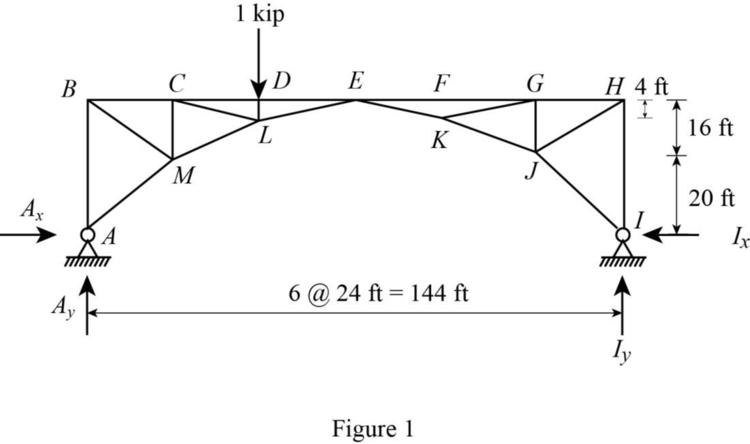
Refer Figure 1.
Consider moment equilibrium at I.
Thus, the influence line ordinate of vertical reaction at A is 0.667.
Similarly find the influence line ordinate of
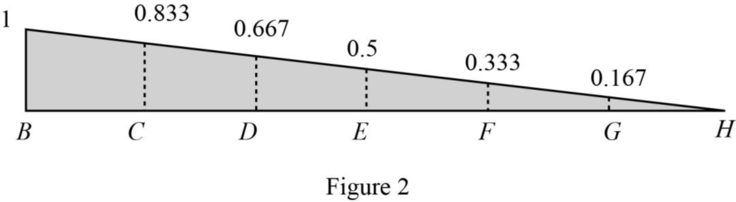
| Points | x (ft) | Influence line ordinate of |
| B | 0 | 1 |
| C | 24 | 0.833 |
| D | 48 | 0.667 |
| E | 72 | 0.5 |
| F | 96 | 0.333 |
| G | 120 | 0.167 |
| H | 144 | 0 |
Draw the influence line ordinate of
Influence line for the horizontal reaction at A.
The influence line ordinate of
Apply 1 kip at D.
Find the horizontal reaction at support A.
The reaction is determined by applying a 1-kip load at successive panel points.
Apply 1 kip load at C.
Draw the free body diagram as shown in Figure 3.
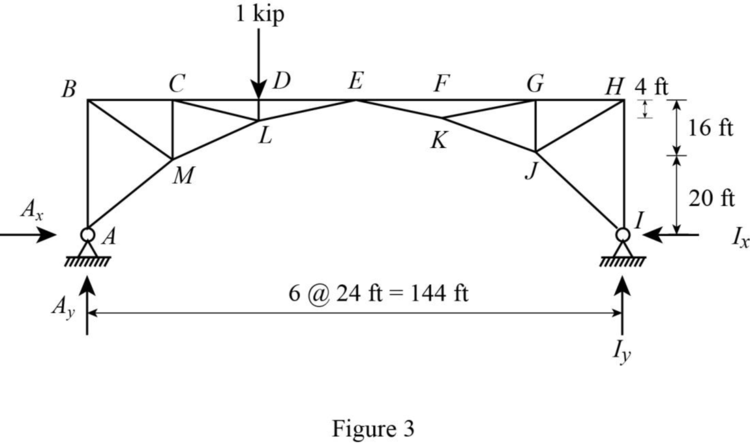
Refer Figure 4.
Consider moment equilibrium at E.
Thus, the influence line ordinate of horizontal reaction at A is 0.667.
Similarly find the influence line ordinate of
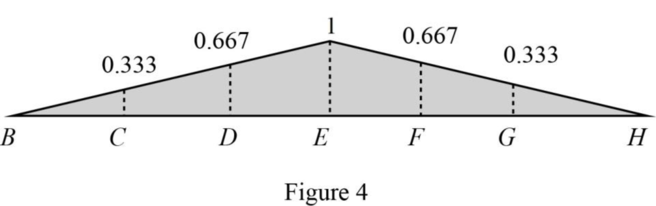
| Points | x (ft) | Influence line ordinate of |
| B | 0 | 0 |
| C | 24 | 0.333 |
| D | 48 | 0.667 |
| E | 72 | 1 |
| F | 96 | 0.667 |
| G | 120 | 0.333 |
| H | 144 | 00 |
Draw the influence line ordinate of
Influence line for the force in member BC.
Find the force
The influence line ordinate of
Apply 1 kip at C and consider a section passes through members BC, CM, and ML.
Sketch the free body diagram of the section as in Figure 5.
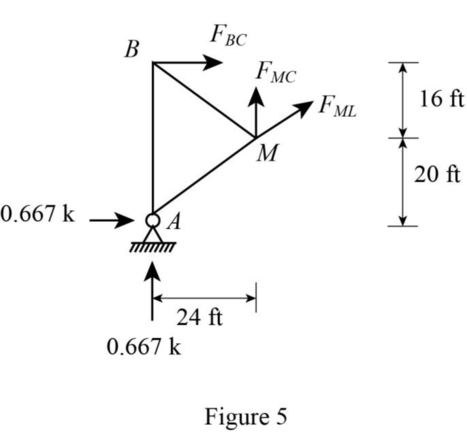
Refer Figure 5.
Find the member force BC.
Consider moment equilibrium at M.
Thus, the influence line ordinate of member force BC at D is ‑0.167.
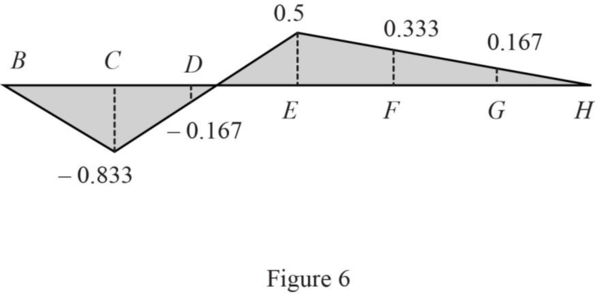
Similarly find the influence line ordinate of
| Points | x (ft) | Influence line ordinate of |
| B | 0 | 0 |
| C | 24 | ‑0.833 |
| D | 48 | ‑0.167 |
| E | 72 | 0.5 |
| F | 96 | 0.333 |
| G | 120 | 0.167 |
| H | 144 | 0 |
Draw the influence line ordinate of
Influence line for the force in member ML.
Find the force
The influence line ordinate of
Apply 1 kip at C and consider a section passes through members BC, CM, and ML.
Sketch the free body diagram of the section as in Figure 7.
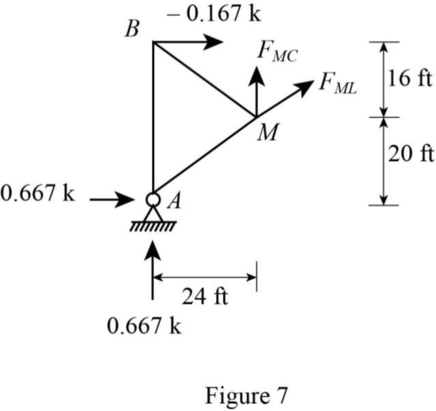
Refer Figure 7.
The slope of member ML is 24 ft horizontal and 12 ft vertical.
Find the member force ML.
Consider horizontal equilibrium equation.
Thus, the influence line ordinate of member force ML at D is ‑0.56.
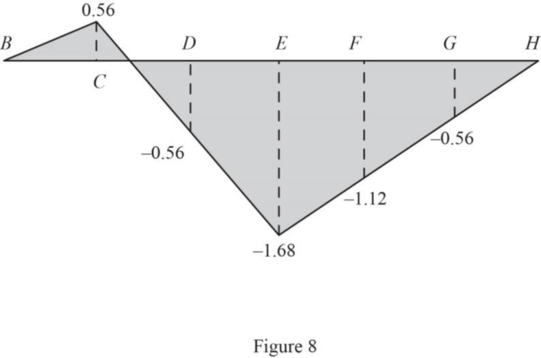
Similarly find the influence line ordinate of
| Points | x (ft) | Influence line ordinate of |
| B | 0 | 0 |
| C | 24 | 0.56 |
| D | 48 | ‑0.56 |
| E | 72 | ‑1.68 |
| F | 96 | ‑1.12 |
| G | 120 | ‑0.56 |
| H | 144 | 0 |
Draw the influence line ordinate of
Influence line for the force in member CM.
Find the force
The influence line ordinate of
Apply 1 kip at C and consider a section passes through members BC, CM, and ML.
Sketch the free body diagram of the section as in Figure 9.
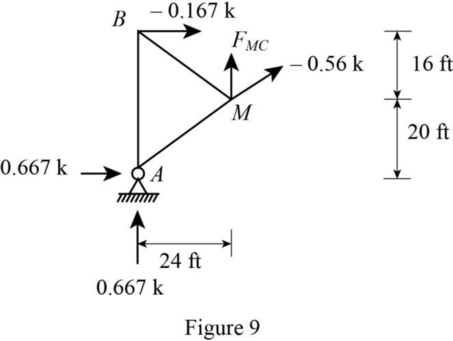
Refer Figure 9.
The slope of member ML is 24 ft horizontal and 12 ft vertical.
Find the member force CM.
Consider vertical equilibrium equation.
Thus, the influence line ordinate of member force CM at D is ‑0.416.
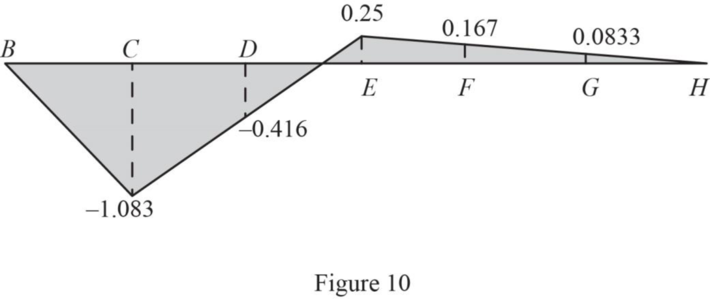
Similarly find the influence line ordinate of
| Points | x (ft) | Influence line ordinate of |
| B | 0 | 0 |
| C | 24 | ‑1.083 |
| D | 48 | ‑0.416 |
| E | 72 | 0.25 |
| F | 96 | 0.167 |
| G | 120 | 0.083 |
| H | 144 | 0 |
Draw the influence line ordinate of
(b)
Find the forces (compression and tension) in bars CM and ML produced by the dead load.
(b)
Answer to Problem 40P
The dead load force in member CM is
The dead load force in member ML is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The uniform dead load,
Calculation:
Refer Figure 11.
Sketch the influence line diagram of member CM as in Figure 11.
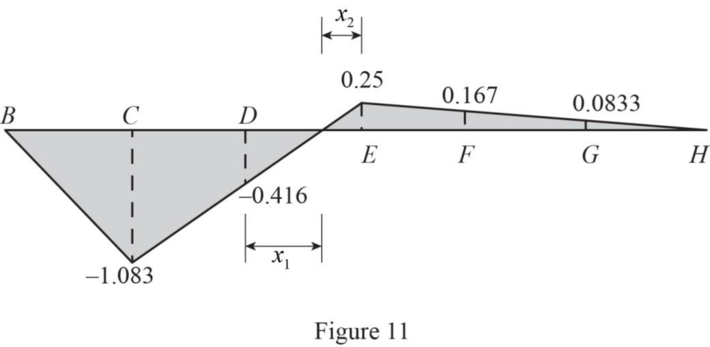
Refer Figure 11.
Find the length
Find the length
Refer Figure 11.
Find the dead load force in member CM using the equation.
Therefore, the dead load force in member CM is
Refer Figure 9.
Sketch the influence line diagram of member ML as in Figure 12.
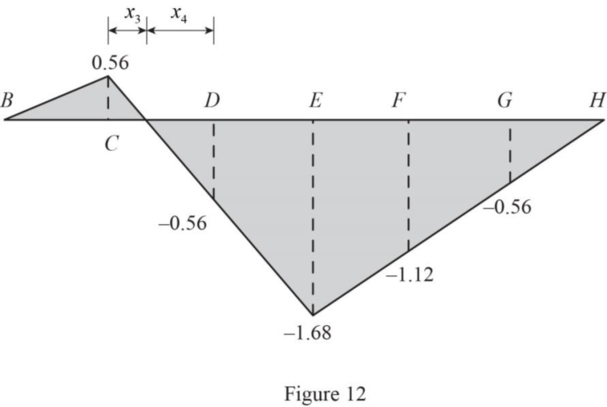
Refer Figure 12.
Find the length
Find the length
Refer Figure 11.
Find the dead load force in member CM using the equation.
Therefore, the dead load force in member ML is
(c)
Find the forces (compression and tension) in bars CM due to live load.
(c)
Answer to Problem 40P
The maximum compression force in member CM due to live load is
The maximum tension force in member CM due to live load is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The uniform live load,
The concentrated live load, P is 20 k.
Calculation:
Refer Figure 11.
Sketch the influence line diagram of member CM as in Figure 13.
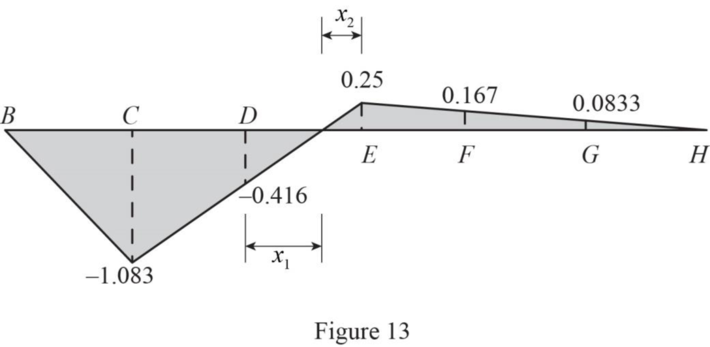
Refer Figure 13.
Find the maximum compression force in member CM using the equation.
Therefore, the maximum compression force in member CM due to live load is
Find the maximum tension force in member CM using the equation.
Therefore, the maximum tension force in member CM due to live load is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
- 2. Use method of sections to determine all member forces in the figure below 1.3 m 15 kN N 10 E 9 E 8 E 7 6 E 1.7arrow_forwardUse method of sections to solve all member forces for the diagram dont mind the question down therearrow_forwardThe following data show spot speeds collected at a section of highway located in a residential area before and after an increase in speed enforcement activities. (All speeds are in mi/h.) Before After Before After 44 27 34 21 38 36 35 21 36 23 32 37 41 40 26 26 36 40 38 33 28 32 41 23 32 27 31 24 38 31 36 23 33 22 36 26 44 35 29 23 36 27 31 20 33 18 38 22 40 25 31 26 39 31 33 32 38 33 41 35 Using the student's t-test, determine whether there was a statistically significant difference in the average speeds at a significance level of a = 0.05 (the 95-percent confidence level.) O Yes, there was a statistically significant difference in the average speeds. ○ No, there was not a statistically significant difference in the average speeds. Also report, for both the before and after cases, the mean speed, standard deviation, 85th-percentile speed, and percentage of traffic exceeding the posted speed limit of 30 mi/h. (Enter all speeds and standard deviations in mi/h. Round your 85th-percentile…arrow_forward
- Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the moment distribution method. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200 GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forward||| = 1% 11. LTE2 Voi) Vol) 1. LTE1 SEARCH 8 VYT bartleby.com/dashboard ASK √x MATH SOLV affected resale value at year 5, would that affect perceived value-in-use? How exactly? There is an error in submission of question Check it out! See if this is the solution you're looking for VIEW FULL SOLUTION Not what you're looking for? Keep submitting your original question SUBMIT QUESTIONarrow_forward. The average soil weights for a clay are the following: 2,050 pounds in Loose CY, 2,675pounds in Bank CY, and 2,835 pounds in Compacted CY What is the swell percentage for theclay?arrow_forward
- A traffic count taken between 7:00 a.m. and 2:00 p.m. on a rural highway found the following hourly volumes. Time 7:00-8:00 a.m. Hourly volume 332 8:00-9:00 a.m. 311 9:00-10:00 a.m. 263 10:00-11:00 a.m. 273 11:00 a.m.-12:00 p.m. 289 12:00-1:00 p.m. 1:00-2:00 p.m. 286 265 If these data were collected on a Tuesday in February, estimate the AADT (in veh/day) on this section of highway. Assume that the expansion factors given in this table, this table, and this table apply. veh/dayarrow_forwardA project schedule has been updated. The activity placement of spread footing concretewas originally scheduled to begin as early as day 10. The activity duration is 4 days. The actualstart day was day 12. The original schedule had a calculated total float of 7 days for this activity.The recalculated total float for the activity, when updated, would bearrow_forwardIn preparation for a public hearing, an engineer needs to estimate the travel time savings for a proposed highway bypass of a small city in a rural area. The existing highway goes through the downtown area for 4.1 miles between the points where the bypass will connect. (a) If the engineer anticipates a standard deviation of 7 mi/h and would like a 95% confidence of estimating the mean speed within ±4 mi/h, how many runs should a travel time study include? (Enter the minimum number of runs that achieves a 95% confidence level.) runs (b) If the engineer measures an average speed of 34.9 mi/h through the town and the bypass is expected to operate at speeds of 65 mi/h over a distance of 6.2 miles, what is the expected travel time saving (in minutes) per vehicle? minutes Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





