
Concept explainers
Novo, Inc., wants to develop an activity flexible budget for the activity of moving materials. Novo uses eight forklifts to move materials from receiving to stores. The forklifts are also used to move materials from stores to the production area. The forklifts are obtained through an operating lease that costs $18,000 per year per forklift. Novo employs 25 forklift operators who receive an average salary of $50,000 per year, including benefits. Each move requires the use of a crate. The crates are used to store the parts and are emptied only when used in production. Crates are disposed of after one cycle (two moves), where a cycle is defined as a move from receiving to stores to production. Each crate costs $1.80. Fuel for a forklift costs $3.60 per gallon. A gallon of gas is used every 20 moves. Forklifts can make three moves per hour and are available for 280 days per year, 24 hours per day (the remaining time is downtime for various reasons). Each operator works 40 hours per week and 50 weeks per year.
Required:
- 1. Prepare a flexible budget for the activity of moving materials, using the number of cycles as the activity driver.
- 2. Calculate the activity capacity for moving materials. Suppose Novo works at 80 percent of activity capacity and incurs the following costs:
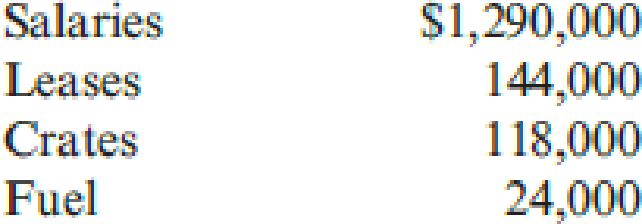
Prepare the budget for the 80 percent level and then prepare a performance report for the moving materials activity.
- 3. Calculate and interpret the volume variance for moving materials.
- 4. Suppose that a redesign of the plant layout reduces the demand for moving materials to one-third of the original capacity. What would be the budget formula for this new activity level? What is the budgeted cost for this new activity level? Has activity performance improved? How does this activity performance evaluation differ from that described in Requirement 2? Explain.
1.
Construct a flexible budget for N Company for the activity of moving materials using number of cycles as the activity driver.
Explanation of Solution
Flexible budget: A flexible budget is a statement of estimate regarding revenues and expenses for a future period that can be modified depending on the level of output.
| Resource |
Fixed ($) | Variable |
| Salaries | 1,250,000 (1) | - |
| Lease | 144,000 (2) | - |
| Crates | - | $1.80 |
| Fuel | - | (3) $0.36 |
| Total | 1,394,000 | $2.16 |
Table (1)
Working notes:
(1) Calculate the total salary expenses.
Salaries = Number of forklift operators × Average salary per year= 25 × $50,000= 1,250,000
(2) Calculate the total lease payable.
Salaries = Number of forklift × Lease rent payable per year per forklift= 8 × $18,000= 144,000
(3) Calculate the fuel consumption per machine per cycle.
Fuel consumption =Fuel expense per gallonNumber of cycles= $3.6010= $0.36
2.
Compute the activity capacity of N Company for moving materials assuming that N Company works at 80 percentage activity capacity. Construct a budget for 80 percent capacity level and also prepare a performance report for the moving materials activity if N Company incurred the following cost.
Salaries - $1,290,000
Lease - $144,000
Crates - $118,000
Fuel - $24,000
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a flexible budget for N Company at 80 percentage activity capacity.
| Resource |
Fixed ($) |
Variable ($) |
Activity output 60,000 cycles (6) ($) |
| Salaries | 1,250,000 (1) | - | 1,250,000 |
| Lease | 144,000 (2) | - | 144,000 |
| Crates | - | $1.80 | 108,000 (4) |
| Fuel | - | $0.36 (3) | 21,600 (5) |
| Total | 1,394,000 | $2.16 | 1,523,600 |
Table (2)
Working notes:
(4) Calculate the total activity output with respect to crates.
Salaries = Crate cost per unit × Capacity cycles= $1.80 × 60,000= 108,000
(5) Calculate the total activity output with respect to fuel.
Salaries = Fuel expense per gallon × Output capacity= 0.36 × $60,000= 21,600
(6) Compute the 80 percent activity capacity of N Company.
Activity capacity = Production cycle× Activity capacity= 75,000× 80%= 75,000(7)× 0.80= 60,000 cycles
(7) Compute the operator capacity of N Company.
Activity capacity = Moves per hour× Number of operators× 2000= 3 × 25× 2000= 150,000 moves or 75,000 cycles
Compute the forklift capacity of N Company.
Forklift capacity = [Moves per hour× Hours used per day× Available days in an year× Total forklift] = 3 × 24× 280 × 8= 161,280 moves or 80,640 cycles
Capacity is determined by the minimum f forklift capacity and operator capacity. Therefore, 75,000 cycles is the output capacity.
Prepare a performance report for moving materials of N Company.
N Company
Performance report
| Resource |
Actual costs ($) |
Budgeted cost ($) |
Budget variance ($) |
| (a) | (b) | (a) − (b) | |
| Salaries | 1,290,000 | 1,250,000 | 40,000 |
| Lease | 144,000 | 144,000 | 0 |
| Crates | 118,000 | 108,000 | 10,000 |
| Fuel | 24,000 | 21,600 | 2,400 |
| Total | 1,576,000 | 1,523,600 | 52,400 |
Table (3)
3.
Compute the volume variance of N Company and interpret the results.
Explanation of Solution
Since standard quantity equals zero, the volume variance is the capacity acquisition cost.
The volume variance is $1,394,000.
4.
Compute the budget formula and new activity level if a redesign of the plant layout reduces the demand for moving materials to one-third of the original capacity. Provide information and evaluate the calculated result with proper explanation.
Explanation of Solution
| Resource |
Fixed ($) |
Variable ($) |
Activity output 25,000 cycles ($) |
| Salaries | 450,000 | - | 450,000 (8) |
| Lease | 54,000 | - | 54,000 (9) |
| Crates | - | 1.80 | 45,000 (12) |
| Fuel | - | 0.36 | 9,000 (13) |
| Total | 504,000 | $2.16 | 558,000 |
Table (4)
Working notes:
(8) Compute the required operators for N Company for the need capacity.
Operators = Demand cyclecycles= 25,0003000 (10)= 8.33= 9 operatorsSalaries = $50,000 × 9Salaries = $450,000
(9) Compute the actual forklifts that will be required by N Company.
Forklifts required = Demand cycleOperator cycle= 25,00010,080(11)= 2.48= 3 forkliftsLease = $18,000 × 3Lease = $54,000
(10)Compute the cycle capacity for N Company for the need capacity.
Cycles = Total hours× Moves per hour2= (2,000 × 3)2= 3000 cycles
(11) Compute the forklift capacity of N Company.
Operators = Number of moves× Hours per day × Avaiable hours2= (3 × 24 × 280)2= 10,080 cycles
(12) Compute the activity output for crate of N Company.
Activity output = Crate× Demand cycle= 1.8 × 25,000= $45,000
(13) Compute the activity output for fuel consumption of N Company.
Activity output = Fuel per gallon× Demand cycle= 0.36 × 25,000= $9,000
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- I want to this question answer of this general Accounting questionarrow_forwardHii expert please given true answer general Accountingarrow_forwardOn December 31, Year 8, Suzi McDowell wants to have $60,000. She plans to make 6 deposits in a fund to provide this amount. Interest compounds annually at 12%. Required: Compute the equal annual amounts that Suzi must deposit assuming that he makes the first deposit on: December 31, Year 3 December 31, Year 2arrow_forward
- E14.10 (LO 1) (Information Related to Various Bond Issues) Pawnee Inc. has issued three types of debt on January 1, 2022, the start of the company's fiscal year. a. $10 million, 10-year, 13% unsecured bonds, interest payable quarterly. Bonds were priced to yield 12%. b. $25 million par of 10-year, zero-coupon bonds at a price to yield 12% per year. c. $15 million, 10-year, 10% mortgage bonds, interest payable annually to yield 12%. Instructions Prepare a schedule that identifies the following items for each bond: (1) maturity value, (2) number of interest periods over life of bond, (3) stated rate per each interest period, (4) effective-interest rate per each interest period, (5) payment amount per period, and (6) present value of bonds at date of issue. Hint: you don't need to prepare the amortization schedule to answer this question. Just a simple table is enough.arrow_forwardNeed correct answer of this question general Accountingarrow_forwardNeed help this questionarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


