
Concept explainers
The dominant C allele of a gene that controls color in corn produces kernels with color; plants homozygous for a recessive c allele of this gene have colorless or white kernels. What kinds of gametes, and in what proportions, would be produced by the plants in the following crosses? What seed color, and in what proportions, would be expected in the offspring of the crosses?
a.
b.
c.
To review:
On the basis of the data for dominant and recessive traits, the types of gametes formed, the color of the seed and its proportion, for the following crosses:
a. CC x Cc
b. Cc x cc
c. Cc x Cc
Introduction:
According to the law of dominance, the dominant trait is shown in homozygous as well as heterozygous form but the recessive trait is shown only when the homozygous allelic pair is present. The color of the kernels in corn is controlled by gene ‘C’, which is dominant in producing different colors, and gene
Explanation of Solution
a. The cross for CC × Cc can be made as follows:
The parents have the genotype CC (colored) × Cc (colored)
The cross can be made as:
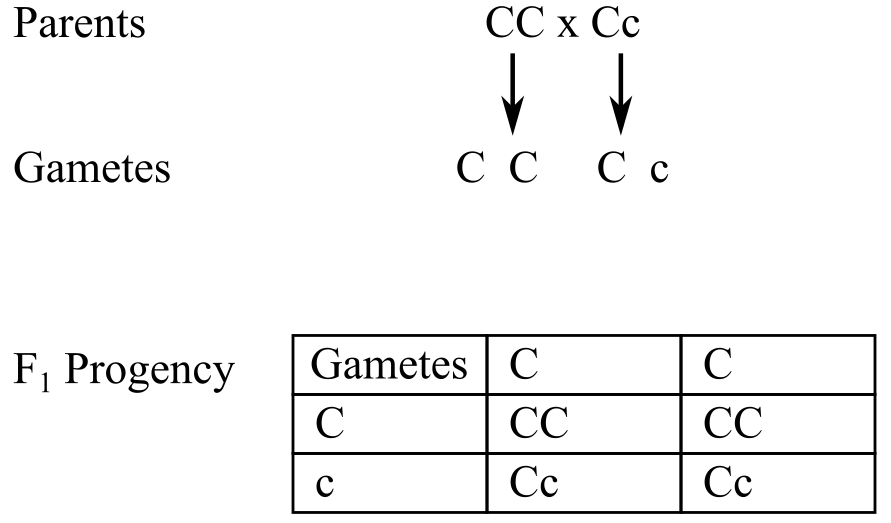
All the progenies will have colored kernels.
The CC plant produces all C gametes. Cc produces 50% of C and 50% of c gametes. Looking at the offspring produced, 50% (1/2) of homozygous (CC) colored and 50% (1/2) of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants are produced.
b. The cross for Cc × cc can be made as follows:
The parents have the genotype
The cross can be made as:
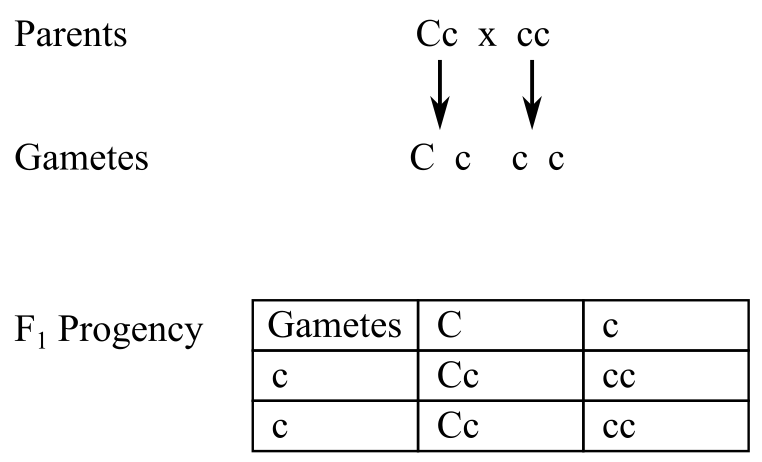
The progenies have the ratio of colored kernels to white kernels as
The Cc plant produces 50% of C and 50% of c gametes and the cc parent produces all c gametes. Looking at the offspring produced, 50% (1/2) of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants and 50% (1/2) of homozygous recessive plants are produced.
c. The cross for Cc × Cc can be made as follows:
The parents have the genotype Cc (colored) and Cc (colored).
The cross can be made as:
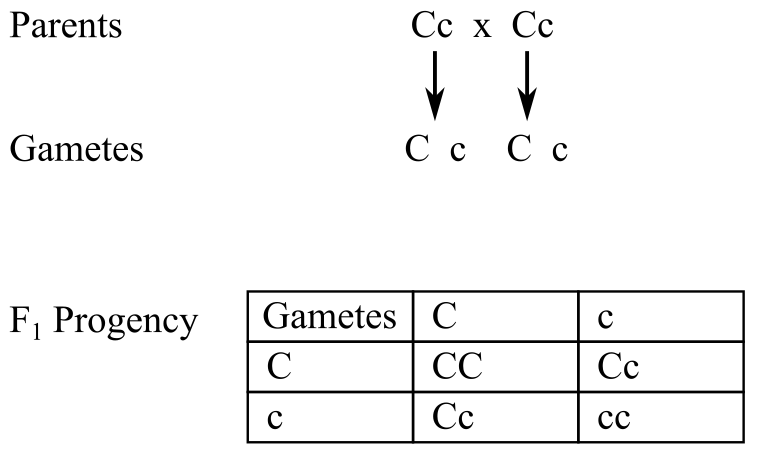
The progenies have the ratio of colored kernels to white kernels as
Both the Cc plants produce 50% of C and 50% of c gametes. Looking at the offspring produced, 50% (1/2) of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants, 25% (1/4) of homozygous recessive plants, and 25% (1/4) of homozygous colored plants are produced.
Therefore, it can be concluded that:
a. Cc produces 50% of C and 50% of c gametes. Half of homozygous (CC) colored and halh of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants are produced.
b. Cc produces 50% of C and 50% of c gametes and cc produces all c gametes. Half of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants and half of homozygous recessive plants are produced.
c. Both the Cc plants produce 50% of C and 50% of c gametes. Half of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants, 1/4 of homozygous recessive plants, and 1/4 of homozygous colored plants are produced.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
- Describe the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardPlease help me calculate drug dosage from the following information: Patient weight: 35 pounds, so 15.9 kilograms (got this by dividing 35 pounds by 2.2 kilograms) Drug dose: 0.05mg/kg Drug concentration: 2mg/mLarrow_forwardA 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 2-day history of fever, chills, severe headache, and confusion. She recently returned from a trip to sub-Saharan Africa, where she did not take malaria prophylaxis. On examination, she is febrile (39.8°C/103.6°F) and hypotensive. Laboratory studies reveal hemoglobin of 8.0 g/dL, platelet count of 50,000/μL, and evidence of hemoglobinuria. A peripheral blood smear shows ring forms and banana-shaped gametocytes. Which of the following Plasmodium species is most likely responsible for her severe symptoms? A. Plasmodium vivax B. Plasmodium ovale C. Plasmodium malariae D. Plasmodium falciparumarrow_forward
- please fill in missing parts , thank youarrow_forwardplease draw in the answers, thank youarrow_forwarda. On this first grid, assume that the DNA and RNA templates are read left to right. DNA DNA mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide _strand strand C с A T G A U G C A TRP b. Now do this AGAIN assuming that the DNA and RNA templates are read right to left. DNA DNA strand strand C mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide 0 A T G A U G с A TRParrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





