![OWLv2 for Masterton/Hurley's Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)](https://s3.amazonaws.com/compass-isbn-assets/textbook_empty_images/large_textbook_empty.svg)
The following data are for the system
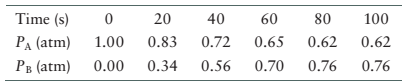
(a) How long does it take the system to reach equilibrium?
(b) How does the rate of the forward reaction compare with the rate of the reverse reaction after 30 s? After 90 s?
(a)
Interpretation:
The time required for the system to reach at equilibrium needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The system is said to be in equilibrium if the there is no change in the partial pressure or concentration of reactant and product takes place.
Answer to Problem 1QAP
80 s.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as follows:
The data for the system is given as follows:
| Time (s) | |
|
| 0 | 1 | 0.000 |
| 20 | 0.83 | 0.34 |
| 40 | 0.72 | 0.56 |
| 60 | 0.65 | 0.70 |
| 80 | 0.62 | 0.76 |
| 100 | 0.62 | 0.76 |
In a system, equilibrium is a stage when the partial pressure or concentration of both reactant and product become constant or no further change in the partial pressure or concentration of reactant and as well as product takes place.
From the data, the partial pressure of reactant, A decreases from 0 s to 80 s and then become constant. In the same way, the partial pressure of product, B increases from 0 s to 90 s and then become constant. Therefore, at 80 s the concentration of both reactant and product become constant therefore, system will reach equilibrium at 80 s.
(b)
Interpretation:
The relation between the rate of forward reaction and that of the reverse reaction needs to determine after 30 s and after 90 s.
Concept introduction:
The rate of the forward reaction depends on the partial pressure of reactant and that of the reverse reaction depends on the partial pressure of the product. At equilibrium, the rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of reverse reaction.
Answer to Problem 1QAP
After 30 s, the rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction and after 90 s, the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as follows:
The rate expression for the given system is represented as follows:
This is the rate of the forward reaction.
The same expression for the reverse reaction will be:
At equilibrium, the rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction thus,
Also, at equilibrium the partial pressures of reactant and product are 0.62 atm and 0.76 atm respectively, putting the values,
Thus,
Or,
Thus, the expression for the reverse reaction will be:
Now, after 30 s the partial pressure of gas A is 0.72 atm thus, rate of forward reaction will be:
The partial pressure of gas B after 30 s is 0.56 atm thus, the rate of reverse reaction will be:
Dividing equation (1) and (2),
Thus, the rate of forward reaction is 2.12 times the rate of reverse reaction or rate of forward reaction is greater than that of the reverse reaction after 30 s.
Now, after 90 s the partial pressure of gas A is 0.62 atm thus, rate of forward reaction will be:
The partial pressure of gas B after 90 s is 0.76 atm thus, the rate of reverse reaction will be:
Dividing equation (1) and (2),
Thus, the rate of forward reaction is approximately equals to the reverse reaction after 90 s.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
OWLv2 for Masterton/Hurley's Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)
- 3. Predict the major product and give a mechanism for the following reactions: (CH3)3COH/H₂SO4 a) b) NC CH₂O c) LOCH, (CH3)3COH/H2SO4 H,SO -OHarrow_forwardIndicate if the aldehyde shown reacts with the provided nucleophiles in acid or base conditions. a NaBH4 be Li eli -NH2 P(Ph3) f KCN g OH excess h CH3OH i NaCHCCH3arrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forward
- Polar solutes are most likely to dissolve into _____, and _____ are most likely to dissolve into nonpolar solvents. A. nonpolar solutes; polar solvents B. nonpolar solvents; polar solvents C. polar solvents; nonpolar solutes D. polar solutes; nonpolar solventsarrow_forwardDeducing the Peactants Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Xarrow_forwardDraw all 8 stereoisomers, circling each pair of enantiomer(s)/ mirror image compound(s)arrow_forward
- Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help Chemical Formula - Aktiv Che X + → C 11 a app.aktiv.com Google Chrome isn't your default browser Set as default Question 12 of 16 Q Fri Feb 2 Verify it's you New Chrome availabl- Write the balanced molecular chemical equation for the reaction in aqueous solution for mercury(I) nitrate and chromium(VI) sulfate. If no reaction occurs, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. 3 Hg(NO3)2(aq) + Cг2(SO4)3(aq) → 3 Hg₂SO (s) + 2 Cr(NO3), (aq) ean Ui mate co ence an climate bility inc ulnerabili women, main critic CLIMATE-INI ernational + 10 O 2 W FEB 1 + 4- 3- 2- 2 2 ( 3 4 NS 28 2 ty 56 + 2+ 3+ 4+ 7 8 9 0 5 (s) (1) Ch O 8 9 (g) (aq) Hg NR CI Cr x H₂O A 80 Q A DII A F2 F3 FA F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 #3 EA $ do 50 % 6 CO & 7 E R T Y U 8 ( 9 0 F10 34 F11 川 F12 Subr + delete 0 { P }arrow_forwardDeducing the reactants of a Diels-Alder reaction n the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. >arrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + Some important notes: A ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- if the answer is no reaction than state that and please hand draw!arrow_forward"I have written solutions in text form, but I need experts to rewrite them in handwriting from A to Z, exactly as I have written, without any changes."arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





