
Concept explainers
Read bar graphs, line graphs, and circle graphs.
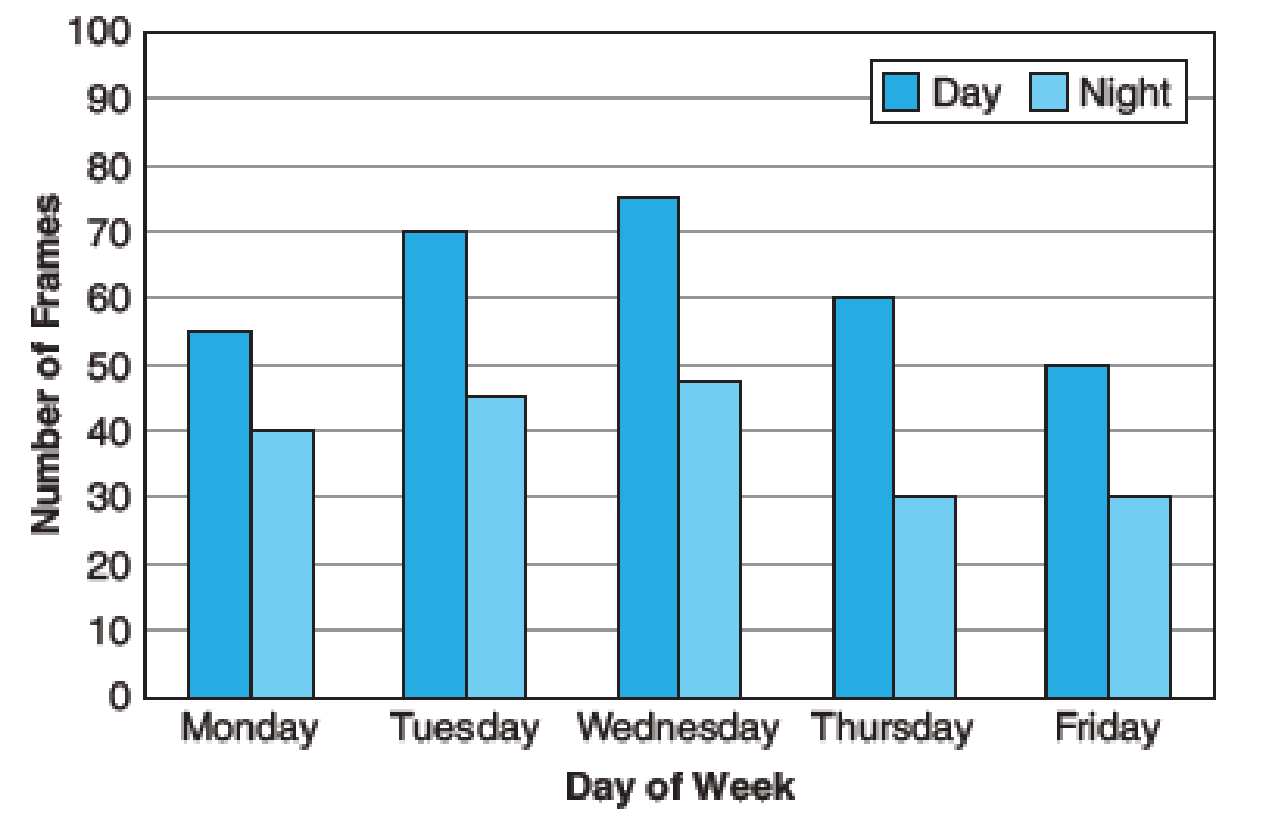
Trades Management From the bar graph below,
- (a) Determine the number of frames assembled by the Tuesday day shift. __________
- (b) Calculate the percent decrease in output from the Monday day shift to the Monday night shift. __________
Weekly Frame Assembly
Monthly Paint Jobs at Autobrite
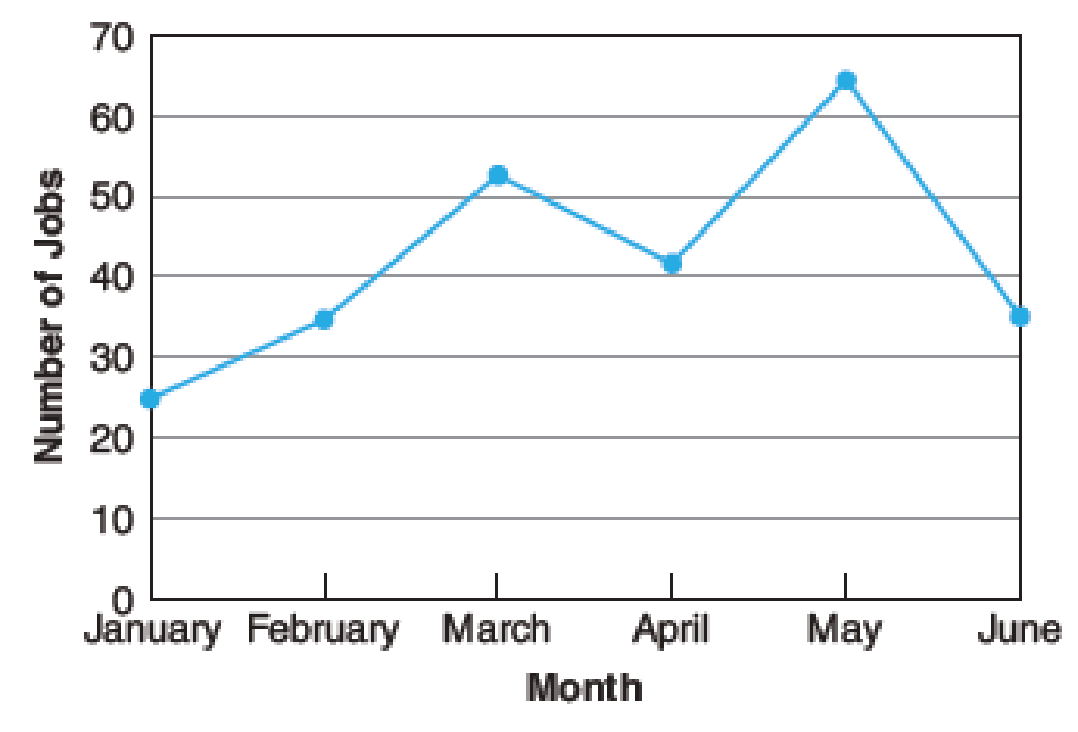
Problems (c) and (d) refer to the line graph above.
- (c) Determine the maximum number of paint jobs and the month during which they occurred. _________
- (d) Calculate the percent increase in the number of paint jobs from January to February. _________
- (e) The average job for ABC Plumbing generates $227.50. Use the circle graph on the next page to calculate what portion of this amount is spent on advertising. _________
Percent of Business Expenditures
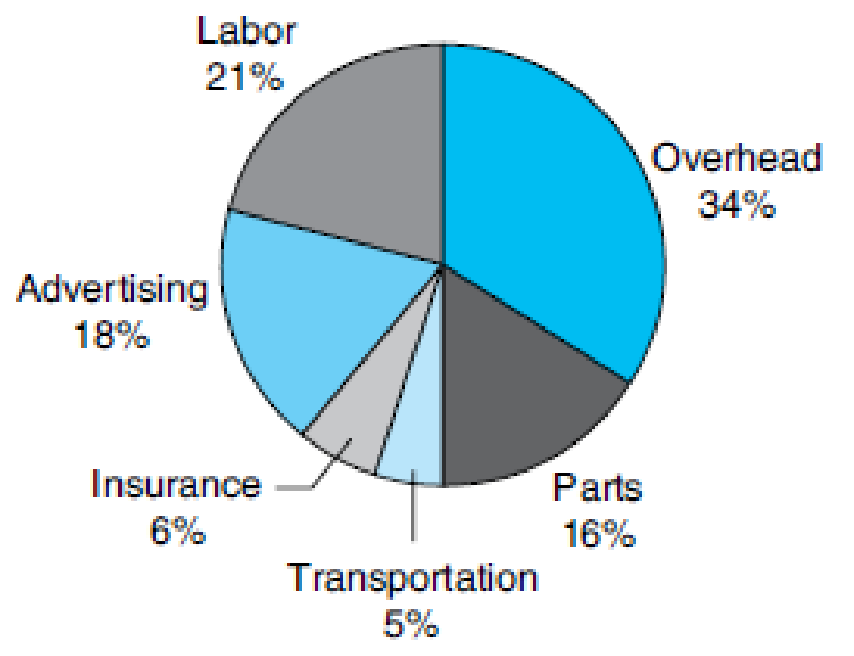
(a)
The number of frames assembled by the Tuesday day shift
Answer to Problem 1P
The number of frames assembled by the Tuesday day shift is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The bar graph for the weekly frame assembly that is the number of frames in the day shift and night shift is mentioned.
Calculation:
From the bar graph, the height of the bar corresponding to the day of Tuesday for the day shift is 70. That is, there are 70 frames in the day shift.
Thus, the number of frames assembled by the Tuesday day shift is
(b)
The percent decrease in output from the Monday day shift to the Monday night shift
Answer to Problem 1P
The percent decrease in output from the Monday day shift to the Monday night shift is
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Percent change in proportion:
Calculation:
From the bar graph, the height of the bar corresponding to the day of Monday for the day shift is 55. That is, there are 55 frames in the day shift. The day of Monday for the night shift is 40. That is, there are 40 frames in the day shift.
The difference in frames is,
Substitute 55 as base and 15 as amount of decrease in the percent formula.
Thus, the percent decrease in output from the Monday day shift to the Monday night shift is
(c)
The maximum number of paint jobs and the month during which they occurred
Answer to Problem 1P
The maximum number of paint jobs is
The month during which maximum number of paint jobs occurred is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The line graph of Monthly Paint Jobs at Autobrite is mentioned.
Calculation:
From the line graph it can be observed that the highest point of the paint jobs is 65 which correspond to the month of May. That is, the month of May has the highest jobs of 65.
Thus, the maximum number of paint jobs is
(d)
The percent increase in the number of paint jobs from January to February
Answer to Problem 1P
The percent increase in the number of paint jobs from January to February is
Explanation of Solution
From the line graph, the number of jobs corresponding to the month of January is 25 and the number of jobs corresponding to the month of February is 35.
The difference in jobs is,
Substitute 25 as base and 10 as amount of increase in the percent formula.
Thus, the percent increase in the number of paint jobs from January to February is
(e)
The portion of amount $227.50 that is spent on advertising based on the circle graph
Answer to Problem 1P
The portion of amount $227.50 that is spent on advertising based on the circle graph is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The circle graph of Percent of Business Expenditures is mentioned. Also, average job for ABC Plumbing generates $227.50.
Calculation:
From the circle graph, the percentage of the business expenditure spent on advertising is 18%.
The amount is,
Thus, the portion of amount $227.50 that is spent on advertising based on the circle graph is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Mathematics for the Trades: A Guided Approach (10th Edition) - Standalone book
- The following data show the year to date percent change (YTD % Change) for 30 stock-market indexes from around the word (The Wall Street Journal, August 26, 2013). Click on the datafile logo to reference the data. DATA file Country Australia Index S&P/ASX200 YTD % Change 10.2 Belgium Bel-20 12.6 Brazil São Paulo Bovespa -14.4 Canada S&P/TSX Comp 2.6 Chile Santiago IPSA -16.3 China Shanghai Composite -9.3 Eurozone EURO Stoxx 10.0 France CAC 40 11.8 Germany DAX 10.6 Hong Kong Hang Seng -3.5 India S&P BSE Sensex -4.7 Israel Tel Aviv 1.3 Italy FTSE MIB 6.6 Japan Nikkei 31.4 Mexico IPC All-Share -6.4 Netherlands AEX 9.3 Singapore Straits Times -2.5 South Korea Kospi -6.4 Spain IBEX 35 6.4 Sweden Switzerland SX All Share 13.8 Swiss Market 17.4 Taiwan Weighted 2.3 U.K. FTSE 100 10.1 U.S. S&P 500 16.6 U.S. DJIA 14.5 U.S. Dow Jones Utility 6.6 U.S. Nasdaq 100 17.4 U.S. Nasdaq Composite 21.1 World DJ Global ex U.S. 4.2 World DJ Global Index 9.9 a. What index has the largest positive YTD %…arrow_forwardWhat is the domain, range, increasing intervals (theres 3), decreasing intervals, roots, y-intercepts, end behavior (approaches four times), leading coffiencent status (is it negative, positivie?) the degress status (zero, undifined etc ), the absolute max, is there a absolute minimum, relative minimum, relative maximum, the root is that has a multiplicity of 2, the multiplicity of 3.arrow_forwardWhat is the vertex, axis of symmerty, all of the solutions, all of the end behaviors, the increasing interval, the decreasing interval, describe all of the transformations that have occurred EXAMPLE Vertical shrink/compression (wider). or Vertical translation down, the domain and range of this graph EXAMPLE Domain: x ≤ -1 Range: y ≥ -4.arrow_forward
- use a graphing utility to sketch the graph of the function and then use the graph to help identify or approximate the domain and range of the function. f(x)= x*sqrt(9-(x^2))arrow_forwarduse a graphing utility to sketch the graph of the function and then use the graph to help identify or approximate the domain and range of the function. f(x)=xsqrt(9-(x^2))arrow_forward4. Select all of the solutions for x²+x - 12 = 0? A. -12 B. -4 C. -3 D. 3 E 4 F 12 4 of 10arrow_forward
- 2. Select all of the polynomials with the degree of 7. A. h(x) = (4x + 2)³(x − 7)(3x + 1)4 B h(x) = (x + 7)³(2x + 1)^(6x − 5)² ☐ Ch(x)=(3x² + 9)(x + 4)(8x + 2)ª h(x) = (x + 6)²(9x + 2) (x − 3) h(x)=(-x-7)² (x + 8)²(7x + 4)³ Scroll down to see more 2 of 10arrow_forward1. If all of the zeros for a polynomial are included in the graph, which polynomial could the graph represent? 100 -6 -2 0 2 100 200arrow_forward3. Select the polynomial that matches the description given: Zero at 4 with multiplicity 3 Zero at −1 with multiplicity 2 Zero at -10 with multiplicity 1 Zero at 5 with multiplicity 5 ○ A. P(x) = (x − 4)³(x + 1)²(x + 10)(x — 5)³ B - P(x) = (x + 4)³(x − 1)²(x − 10)(x + 5)³ ○ ° P(x) = (1 − 3)'(x + 2)(x + 1)"'" (x — 5)³ 51 P(r) = (x-4)³(x − 1)(x + 10)(x − 5 3 of 10arrow_forward
- Match the equation, graph, and description of transformation. Horizontal translation 1 unit right; vertical translation 1 unit up; vertical shrink of 1/2; reflection across the x axis Horizontal translation 1 unit left; vertical translation 1 unit down; vertical stretch of 2 Horizontal translation 2 units right; reflection across the x-axis Vertical translation 1 unit up; vertical stretch of 2; reflection across the x-axis Reflection across the x - axis; vertical translation 2 units down Horizontal translation 2 units left Horizontal translation 2 units right Vertical translation 1 unit down; vertical shrink of 1/2; reflection across the x-axis Vertical translation 2 units down Horizontal translation 1 unit left; vertical translation 2 units up; vertical stretch of 2; reflection across the x - axis f(x) = - =-½ ½ (x − 1)²+1 f(x) = x²-2 f(x) = -2(x+1)²+2 f(x)=2(x+1)²-1 f(x)=-(x-2)² f(x)=(x-2)² f(x) = f(x) = -2x²+1 f(x) = -x²-2 f(x) = (x+2)²arrow_forwardWhat is the vertex, increasing interval, decreasing interval, domain, range, root/solution/zero, and the end behavior?arrow_forwardCalculate a (bxc) where a = i, b = j, and c = k.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill  Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





