
The following are six observations collected from treatment 1, ten observations collected from treatment 2, and eight observations collected from treatment 3. Test the hypothesis that the treatment
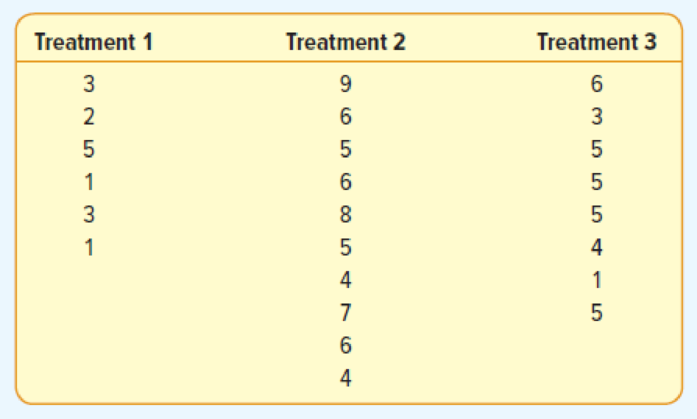
- a. State the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis.
- b. What is the decision rule?
- c. Compute SST, SSE, and SS total.
- d. Complete an ANOVA table.
- e. State your decision regarding the null hypothesis.
- f. If H0 is rejected, can we conclude that treatment 2 and treatment 3 differ? Use the 95% level of confidence.
a.
Obtain the null and the alternative hypotheses.
Explanation of Solution
The null and alternative hypotheses are given below:
Null Hypothesis
That is, mean of all treatments are equal.
Alternative Hypothesis
b.
Give the decision rule.
Explanation of Solution
The treatment and error degrees of freedom are given below:
Treatment degrees of freedom:
Error degrees of freedom:
The critical F value is as follows:
Here, the level of significance
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the critical F value using Excel-MegaStat:
- In EXCEL, Select Add-Ins > MegaStat > Probability.
- Choose probability> F-distribution> calculate F given probability.
- Enter P as 0.05.
- Enter df1 as 2.
- Enter df2 as 21.
- Click Ok.
Output using the Excel-MegaStat software is given below:
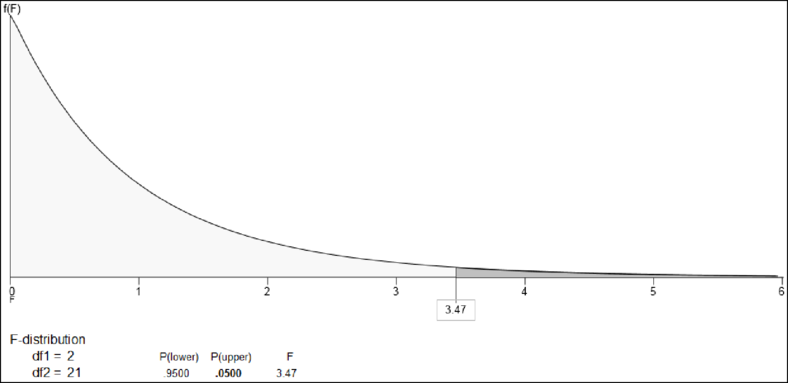
From the output, the critical F value is 3.47.
Decision rule:
If
Therefore, the decision rule is to reject
c.
Find the values of SST, SSE and SS total.
Answer to Problem 12E
The value of SST is 46.96.
The value of SSE is 53.00.
The value of SS total is 99.96.
Explanation of Solution
Here, the level of significance
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the sum of square total, sum of square treatment and sum of square error using Excel-MegaStat:
- Choose MegStat > Analysis of Variance > One-Factor ANOVA.
- Select the column of Treatment 1, Treatment 2 and Treatment 3 in Input range.
- Click OK.
Output using the Excel-MegaStat software is given below:
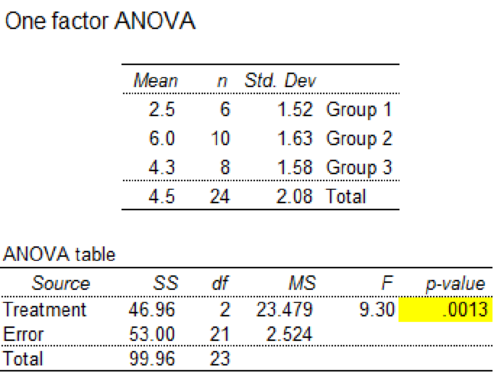
From the output, the values of SST is 46.96, SSE is 53.00 and SS total is 99.96.
d.
Find an ANOVA table.
Explanation of Solution
From the output in Part (c), the ANOVA table is obtained.
The ANOVA table is given below:
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | F |
| Treatments | 46.96 | 2 | 23.48 | 9.3 |
| Error | 53 | 21 | 2.52 | |
| Total | 99.96 | 23 |
e.
Find the decision regarding the null hypothesis.
Explanation of Solution
Conclusion:
The F value is 9.30 and the F critical value is 3.47.
Here, F value is greater than F critical value. That is, 9.30 > 3.47.
Using rejection rule, reject the null hypothesis.
Therefore, there is sufficient evidence that at least one treatment mean is different from others.
f.
Check whether there is significant difference between treatment 2 and treatment 3, if null hypothesis is rejected by using the 95% level of confidence.
Explanation of Solution
A 95% confidence interval is as follows:
Where,
From the output in Part (c), mean of treatment 2 is 6, mean of treatment 3 is 4.3, and MSE is 2.524.
Step-by-step procedure to obtain t-critical value using Excel-MegaStat:
- In EXCEL, Select Add-Ins > MegaStat > Probability > t-Distribution.
- Select calculate t given P.
- Enter probability as 0.05.
- Enter df as 21.
- Under Shading, choose two-tail.
- Click Ok.
Output using the Excel-MegaStat software is given below:
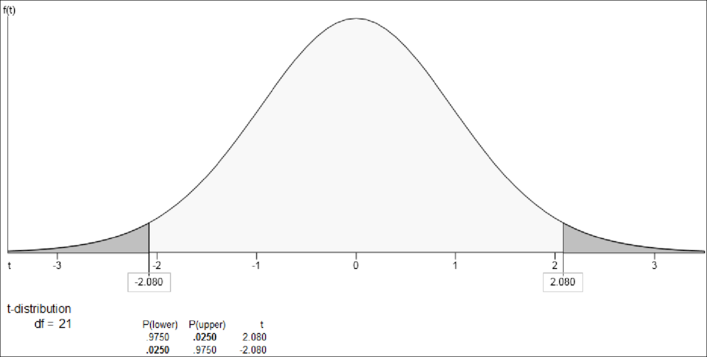
From the output, the t is
Therefore, a 95% confidence interval for that difference is 0.14 and 3.26. Here, 0 does not lie in the confidence interval. It means that there is a significant difference between the means of treatment 2 and treatment 3.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics
- (c) Utilize Fubini's Theorem to demonstrate that E(X)= = (1- F(x))dx.arrow_forward(c) Describe the positive and negative parts of a random variable. How is the integral defined for a general random variable using these components?arrow_forward26. (a) Provide an example where X, X but E(X,) does not converge to E(X).arrow_forward
- (b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) E(X)E(Y);arrow_forward(d) Under what conditions do we say that a random variable X is integrable, specifically when (i) X is a non-negative random variable and (ii) when X is a general random variable?arrow_forward29. State the Borel-Cantelli Lemmas without proof. What is the primary distinction between Lemma 1 and Lemma 2?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning


