
(a)
Interpretation:
The appropriate alkene or alkyne from which the given compound can be produced is to be determined along with the necessary reagents and special reaction conditions.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation of
The initial addition of borane is a syn, anti-Markovnikov addition via a four-membered cyclic transition state. Boron adds to the less substituted (less hindered) carbon because it is less electronegative than hydrogen. This results in an anti-Markovnikov addition of a water molecule to the double bond.
Answer to Problem 12.53P
The appropriate alkene used to synthesize the given compound is
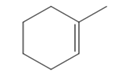
The necessary reagents and special reaction conditions for the synthesis are
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is
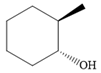
Alcohol with a specific stereochemistry is to be synthesized from an alkene. A reaction involving a carbocation needs to be avoided to prevent unwanted carbocation rearrangements. Also, the OH group must be added to a less substituted carbon, i.e., an anti-Markovnikov addition is needed. Therefore, the reaction needs to be carried out using hydroboration-oxidation.
The appropriate alkene for the synthesis of the given compound would be
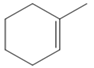
The given compound is synthesized by using the above alkene via hydroboration-oxidation reaction. So the necessary reagents for the reaction are
In the first step, an electrophilic addition of borane across the double bond of the alkene takes place either from above or below the plane of the alkene. So a mixture of enantiomers is obtained after oxidation of the adduct by basic
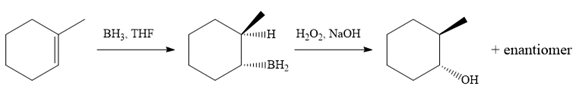
The alkene necessary for the synthesis of the given compound and the reagents and special conditions for the reaction are determined on the basis of the structure of the given compound.
(b)
Interpretation:
The appropriate alkene or alkyne from which the given compound can be produced is to be determined along with the necessary reagents and special reaction conditions.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation of alkenes and alkynes is carried out by the hydroboration-oxidation reaction. Alkenes are oxidized to alcohol while alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compounds. Terminal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding aldehyde, and internal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding ketone by a sterically hindered borane like disiamylborane
The initial addition of borane is a syn, anti-Markovnikov addition via a four-membered cyclic transition state. Boron adds to the less substituted (less hindered) carbon because it is less electronegative than hydrogen. This results in an anti-Markovnikov addition of a water molecule to the double bond.
Answer to Problem 12.53P
The appropriate alkyne used to synthesize the given compound is
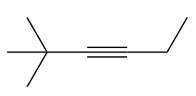
The necessary reagents and special reaction conditions to synthesize the given compound are
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
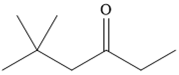
It is a ketone, so the starting compound must be an alkyne. A hydroboration-oxidation reaction can convert an alkyne into a ketone. Since only one molecule of borane is to be added, a bulky reagent like disiamylborane is more appropriate than borane. Also, the dialkylborane part must add to the less hindered carbon of the triple bond. Therefore, the triple bond must be between the carbon bonded to oxygen and the carbon close to the bulky tertiary carbon. Therefore, the alkyne that can be used is

A sterically hindered dialkylborane, like disiamylborane
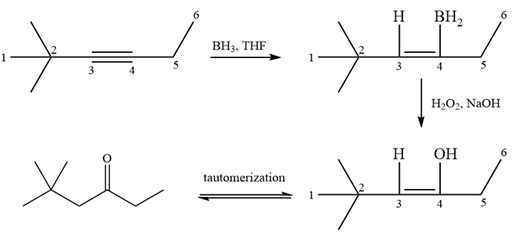
Thus the specific reagents and reaction conditions are
The alkene necessary for the synthesis of the given compound and the reagents and special conditions for the reaction are determined on the basis of the structure of the given compound.
(c)
Interpretation:
The appropriate alkene or alkyne from which the given compound can be produced is to be determined along with the necessary reagents and special reaction conditions.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation of alkenes and alkynes is carried out by the hydroboration-oxidation reaction. Alkenes are oxidized to alcohol while alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compounds. Terminal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding aldehyde, and internal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding ketone by a sterically hindered borane like disiamylborane
The initial addition of borane is a syn, anti-Markovnikov addition via a four-membered cyclic transition state. Boron adds to the less substituted (less hindered) carbon because it is less electronegative than hydrogen. This results in an anti-Markovnikov addition of a water molecule to the double bond.
Answer to Problem 12.53P
The appropriate alkyne used to synthesize the given compound is
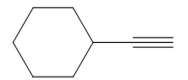
The necessary reagents and special reaction conditions to synthesize the given compound are
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
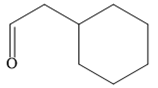
It is an aldehyde, so it can be prepared from a terminal alkyne by hydroboration-oxidation. In the hydroboration reaction, boron is added to the terminal carbon. So the appropriate alkyne for the synthesis of the given compound is
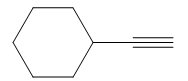
The alkyne is treated with the bulky disiamylborane to prevent the addition of a second molecule and formation of a mixture of products. Subsequent treatment of the adduct by
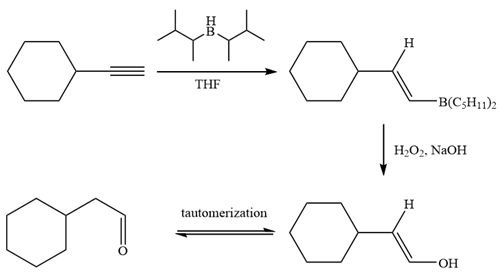
Thus, the necessary reagents and special reaction conditions for the synthesis are
The alkene necessary for the synthesis of the given compound and the reagents and special conditions for the reaction are determined on the basis of the structure of the given compound.
(d)
Interpretation:
The appropriate alkene or alkyne from which the given compound can be produced is to be determined along with the necessary reagents and special reaction conditions.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation of alkenes and alkynes is carried out by the hydroboration-oxidation reaction. Alkenes are oxidized to alcohol while alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compounds. Terminal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding aldehyde, and internal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding ketone by a sterically hindered borane like disiamylborane
The initial addition of borane is a syn, anti-Markovnikov addition via a four-membered cyclic transition state. Boron adds to the less substituted (less hindered) carbon because it is less electronegative than hydrogen. This results in an anti-Markovnikov addition of a water molecule to the double bond.
Answer to Problem 12.53P
The appropriate alkene used to synthesize the given compound is
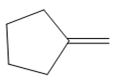
The necessary reagents and special reaction conditions for the synthesis are
Explanation of Solution
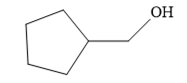
Since the product is an alcohol, an alkene with a methylene substituent on a cyclopentane ring would be appropriate as the starting compound.

Treating this alkene with borane in THF will add
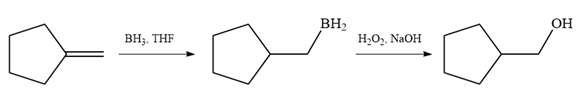
Thus, the necessary reagents for the reaction are
The alkene necessary for the synthesis of the given compound and the reagents and special conditions for the reaction are determined on the basis of the structure of the given compound.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms: Study Guide/solutions Manual (second)
- Explain why this data led Rayleigh to look for and to discover Ar.arrow_forward5) Confidence interval. Berglund and Wichardt investigated the quantitative determination of Cr in high-alloy steels using a potentiometric titration of Cr(VI). Before the titration, samples of the steel were dissolved in acid and the chromium oxidized to Cr(VI) using peroxydisulfate. Shown here are the results (as %w/w Cr) for the analysis of a reference steel. 16.968, 16.922, 16.840, 16.883, 16.887, 16.977, 16.857, 16.728 Calculate the mean, the standard deviation, and the 95% confidence interval about the mean. What does this confidence interval mean?arrow_forwardIn the Nitrous Acid Test for Amines, what is the observable result for primary amines? Group of answer choices nitrogen gas bubbles form a soluble nitrite salt yellow oily layer of nitrosoaminearrow_forward
- 3. a. Use the MS to propose at least two possible molecular formulas. For an unknown compound: 101. 27.0 29.0 41.0 50.0 52.0 55.0 57.0 100 57.5 58.0 58.5 62.0 63.0 64.0 65.0 74.0 40 75.0 76.0 20 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 m/z 99.5 68564810898409581251883040 115.0 116.0 77404799 17417M 117.0 12.9 118.0 33.5 119.0 36 133 0 1.2 157.0 2.1 159.0 16 169.0 219 170.0 17 171.0 21.6 172.0 17 181.0 1.3 183.0 197.0 100.0 198.0 200. 784 Relative Intensity 2 2 8 ō (ppm) 6 2arrow_forwardSolve the structure and assign each of the following spectra (IR and C-NMR)arrow_forward1. For an unknown compound with a molecular formula of C8H100: a. What is the DU? (show your work) b. Solve the structure and assign each of the following spectra. 8 6 2 ō (ppm) 4 2 0 200 150 100 50 ō (ppm) LOD D 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 500 HAVENUMBERI -11arrow_forward
- 16. The proton NMR spectral information shown in this problem is for a compound with formula CioH,N. Expansions are shown for the region from 8.7 to 7.0 ppm. The normal carbon-13 spec- tral results, including DEPT-135 and DEPT-90 results, are tabulated: 7 J Normal Carbon DEPT-135 DEPT-90 19 ppm Positive No peak 122 Positive Positive cus и 124 Positive Positive 126 Positive Positive 128 No peak No peak 4° 129 Positive Positive 130 Positive Positive (144 No peak No peak 148 No peak No peak 150 Positive Positive してしarrow_forward3. Propose a synthesis for the following transformation. Do not draw an arrow-pushing mechanism below, but make sure to draw the product of each proposed step (3 points). + En CN CNarrow_forwardShow work..don't give Ai generated solution...arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





